Abstract
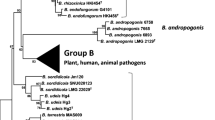
This chapter presents a historical overview of the development and changes in scientific approaches to classifying members of the Agrobacterium genus. We also describe the changes in the inference of evolutionary relationships among Agrobacterium biovars and Agrobacterium strains from using the 16S rRNA marker to recA genes and to the use of multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA). Further, the impacts of the genomic era enabling low cost and rapid whole genome sequencing on Agrobacterium phylogeny are reviewed with a focus on the use of new and sophisticated bioinformatics approaches to refine phylogenetic inferences. An updated genome-based phylogeny of ninety-seven Agrobacterium tumefaciens complex isolates representing ten known genomic species is presented, providing additional support to the monophyly of the Agrobacterium clade. Additional taxon sampling within Agrobacterium genomovar G3 indicates potential exceptions to interpretation of the concept of bacterial genomics species as ecological species because the genomovar G3 genomic cluster, which initially includes clinical strains, now also includes plant-associated and cave isolates.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auch AF, von Jan M, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2010) Digital DNA-DNA hybridization for microbial species delineation by means of genome-to-genome sequence comparison. Stand Genomic Sci 2:117–134
Bai Y et al (2015) Functional overlap of the Arabidopsis leaf and root microbiota. Nature 528:364–369
Bankevich A et al (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comp Biol 19:455–477
Bennasar A, Mulet M, Lalucat J, García-Valdés E (2010) PseudoMLSA: a database for multigenic sequence analysis of Pseudomonas species. BMC Microbiol 10:118
Bhullar K et al (2012) Antibiotic resistance is prevalent in an isolated cave microbiome. PLoS ONE 7:e34953
Cai H, Thompson R, Budinich MF, Broadbent JR, Steele JL (2009) Genome sequence and comparative genome analysis of Lactobacillus casei: insights into their niche-associated evolution. Genome Bio Evol 1:239–257
Colston SM, Fullmer MS, Beka L, Lamy B, Gogarten JP, Graf J (2014) Bioinformatic genome comparisons for taxonomic and phylogenetic assignments using Aeromonas as a test Case. mBio 5
Costechareyre D et al (2010) Rapid and efficient identification of Agrobacterium species by recA allele analysis. Microb Ecol 60:862–872
de Lajudie P et al (1998) Allorhizobium undicola gen. nov., sp. nov., nitrogen-fixing bacteria that efficiently nodulate Neptunia natans in Senegal. Int J Syst Bacteriol 4:1277–1290
Delamuta JRM, Ribeiro RA, Menna P, Bangel EV, Hungria M (2012) Multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) of Bradyrhizobium strains: revealing high diversity of tropical diazotrophic symbiotic bacteria. Braz J Microbiol 43:698–710
Ding W, Baumdicker F, Neher RA (2017) panX: pan-genome analysis and exploration. Nucleic Acids Res 25
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Farrand SK, O’Morchoe SP, McCutchan J (1989) Construction of an Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 recA mutant. J Bacteriol 171:5314–5321
Farrand SK, van Berkum PB, Oger P (2003) Agrobacterium is a definable genus of the family Rhizobiaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1681–1687
Genetello C, Van Larebeke N, Holsters M, De Picker A, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1977) Ti plasmids of Agrobacterium as conjugative plasmids. Nature 265:561–563
Goodner B et al (2001) Genome sequence of the plant pathogen and biotechnology agent Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58. Science 294:2323–2328
Hedges SB (2002) The origin and evolution of model organisms. Nat Rev Gen 3:838–849
Henkel CV, den Dulk-Ras A, Zhang X, Hooykaas PJJ (2014) Genome sequence of the octopine-type Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain Ach5. Genome Announcements 2:e00225–00214
Huang Y-Y, Cho S-T, Lo W-S, Wang Y-C, Lai E-M, Kuo C-H (2015) Complete genome sequence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ach5. Genome Announc 3:e00570–00515
Huo Y-B, Chan Y, Lacap-Bugler DC, Mo S, Woo PC, Leung WK, Watt RM (2017) Multilocus sequence analysis of phylogroup 1 and 2 oral treponeme strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:e02499–02416
Janda JM, Abbott SL (2007) 16S rRNA gene sequencing for bacterial identification in the diagnostic laboratory: pluses, perils, and pitfalls. J Clin Microbiol 45:2761–2764
Johnson ZI, Zinser ER, Coe A, McNulty NP, Woodward EMS, Chisholm SW (2006) Niche partitioning among Prochlorococcus ecotypes along ocean-scale environmental gradients. Science 311:1737–1740
Jones KJ, Moore K, Sambles C, Love J, Studholme DJ, Aves SJ (2016) Draft genome sequences of Achromobacter piechaudii GCS2, Agrobacterium sp. Strain SUL3, Microbacterium sp. Strain GCS4, Shinella sp. Strain GWS1, and Shinella sp. strain SUS2 isolated from consortium with the hydrocarbon-producing alga Botryococcus braunii. Genome Announc 4
Kanie S et al (2007) Roles of RecA protein in spontaneous mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. Genes Genet Syst 82:99–108
Kim K, Gan HM (2017) A glimpse into the genetic basis of symbiosis between Hydrogenophaga and their helper strains in the biodegradation of 4-aminobenzenesulfonate. J Genomics 5:77–82
Kisand V, Wikner J (2003) Limited resolution of 16S rDNA DGGE caused by melting properties and closely related DNA sequences. J Microbiol Meth 54:183–191
Konstantinidis KT, Ramette A, Tiedje JM (2006) The bacterial species definition in the genomic era. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 361:1929–1940
Kowalczykowski SC, Dixon DA, Eggleston AK, Lauder SD, Rehrauer WM (1994) Biochemistry of homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev 58:401–465
Kuzminov A, Stahl FW (1997) Stability of linear DNA in recA mutant Escherichia coli cells reflects ongoing chromosomal DNA degradation. J Bacteriol 179:880–888
Lassalle F et al (2011) Genomic species are ecological species as revealed by comparative genomics in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Genome Bio Evol 3:762–781
Lefébure T, Pavinski Bitar PD, Suzuki H, Stanhope MJ (2010) Evolutionary dynamics of complete Campylobacter pan-genomes and the bacterial species concept. Genome Bio Evol 2:646–655
Lloyd AT, Sharp PM (1993) Evolution of the recA gene and the molecular phylogeny of bacteria. J Mol Evol 37:399–407
MacLean D, Jones JD, Studholme DJ (2009) Application of next-generation sequencing technologies to microbial genetics. Nat Rev Gen 7:287–296
Martens M, Dawyndt P, Coopman R, Gillis M, De Vos P, Willems A (2008) Advantages of multilocus sequence analysis for taxonomic studies: a case study using 10 housekeeping genes in the genus Ensifer (including former Sinorhizobium). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:200–214
Menna P, Barcellos FG, Hungria M (2009) Phylogeny and taxonomy of a diverse collection of Bradyrhizobium strains based on multilocus sequence analysis of the 16S rRNA gene, ITS region and glnII, recA, atpD and dnaK genes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2934–2950
Metzker ML (2010) Sequencing technologies—the next generation. Nat Rev Gen 11:31–46
Mousavi SA et al (2014) Phylogeny of the Rhizobium-Allorhizobium-Agrobacterium clade supports the delineation of Neorhizobium gen. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 37:208–215
Mousavi SA, Willems A, Nesme X, de Lajudie P, Lindstrom K (2015) Revised phylogeny of Rhizobiaceae: proposal of the delineation of Pararhizobium gen. nov., and 13 new species combinations. Syst Appl Microbiol 38:84–90
Ochman H, Elwyn S, Moran NA (1999) Calibrating bacterial evolution. PNAS 96:12638–12643
Ooms G, Hooykaas PJ, Van Veen RJ, Van Beelen P, Regensburg-Tuïnk TJ, Schilperoort RA (1982) Octopine Ti-plasmid deletion mutants of Agrobacterium tumefaciens with emphasis on the right side of the T-region. Plasmid 7:15–29
Ormeno-Orrillo E et al (2015) Taxonomy of rhizobia and agrobacteria from the Rhizobiaceae family in light of genomics. Syst Appl Microbiol 38:287–291
Popoff MY, Kersters K, Kiredjian M, Miras I, Coynault C (1984) Taxonomic position of Agrobacterium strains of hospital origin. Ann Microbiol 3:427–442
Porwollik S, Wong RM-Y, McClelland M (2002) Evolutionary genomics of Salmonella: gene acquisitions revealed by microarray analysis. PNAS 99:8956–8961
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2010) FastTree 2—approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 5:e9490
Ramirez-Bahena MH et al (2014) Single acquisition of protelomerase gave rise to speciation of a large and diverse clade within the Agrobacterium/Rhizobium supercluster characterized by the presence of a linear chromid. Mol Phylogenet Evol 73:202–207
Richter M, Rossello-Mora R, Oliver Glockner F, Peplies J (2016) JSpeciesWS: a web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 32:929–931
Rosenberg MS, Kumar S (2003) Taxon sampling, bioinformatics, and phylogenomics. Syst Biol 52:119
Sakamoto M, Ohkuma M (2011) Identification and classification of the genus Bacteroides by multilocus sequence analysis. Microbiology 157:3388–3397
Seemann T (2014) Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30:2068–2069
Segata N, Bornigen D, Morgan XC, Huttenhower C (2013) PhyloPhlAn is a new method for improved phylogenetic and taxonomic placement of microbes. Nat Commun 4
Shimodaira H, Hasegawa M (1999) Multiple comparisons of log-likelihoods with applications to phylogenetic inference. Mol Biol Evol 16:1114–1114
Slater SC et al (2009) Genome sequences of three Agrobacterium biovars help elucidate the evolution of multichromosome genomes in bacteria. J Bacteriol 191:2501–2511
Slater S et al (2013) Reconciliation of sequence data and updated annotation of the genome of Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58, and distribution of a linear chromosome in the genus Agrobacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:1414–1417
Smit S, Widmann J, Knight R (2007) Evolutionary rates vary among rRNA structural elements. Nucleic Acids Res 35:3339–3354
Smith EF, Townsend CO (1907) A plant-tumor of bacterial origin. Science 25:671–673
Stackebrandt E, Goebel B (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 44:846–849
Stackebrandt E, Frederiksen W, Garrity GM, Grimont PAD, Kamper P, Maiden MCJ, Nesme X, Rossello-Mora R, Swings J et al (2002) Report of the ad hoc committee for the re-evaluation of the species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1043–1047
Tran PN, Savka MA, Gan HM (2017) In-silico taxonomic classification of 373 genomes reveals species misidentification and new genospecies within the genus Pseudomonas. Front Microbiol 8:1296
Velázquez E et al (2010) Analysis of core genes supports the reclassification of strains Agrobacterium radiobacter K84 and Agrobacterium tumefaciens AKE10 into the species Rhizobium rhizogenes. Syst Appl Microbiol 33:247–251
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR et al (1987) International committee on systematic bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Woo P, Lau S, Teng J, Tse H, Yuen KY (2008) Then and now: use of 16S rDNA gene sequencing for bacterial identification and discovery of novel bacteria in clinical microbiology laboratories. Clin Microbiol Infect 14:908–934
Wood DW et al (2001) The genome of the natural genetic engineer Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58. Science 294:2317–2323
Young J, Kuykendall L, Martinez-Romero E, Kerr A, Sawada H (2001) A revision of Rhizobium Frank 1889, with an emended description of the genus, and the inclusion of all species of Agrobacterium Conn 1942 and Allorhizobium undicola de Lajudie et al. 1998 as new combinations: Rhizobium radiobacter, R. rhizogenes, R. rubi, R. undicola and R. vitis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:89–103
Young JM (2008) Agrobacterium—Taxonomy of plant-pathogenic Rhizobium species. In: Tzfira T, Citovsky V (eds) Agrobacterium: from biology to biotechnology. Springer, New York, pp 183–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-72290-0_5
Zhang L, Li X, Zhang F, Wang G (2014) Genomic analysis of Agrobacterium radiobacter DSM 30147(T) and emended description of A. radiobacter (Beijerinck and van Delden 1902) Conn 1942 (Approved Lists 1980) emend. Sawada et al. 1993. Stand Genomic Sci 9:574–584
Acknowledgements
M.A.S. and H.M.G acknowledge funding for research provided by the Gosnell School of Life Science at Rochester Institute of Technology. H.M.G was partially supported by a research start-up grant from the Deakin University Centre of Integrative Ecology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Gan, H.M., Savka, M.A. (2018). One More Decade of Agrobacterium Taxonomy. In: Gelvin, S. (eds) Agrobacterium Biology. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, vol 418. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/82_2018_81
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/82_2018_81
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-03256-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-03257-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)