Abstract
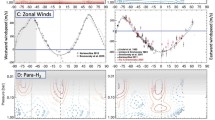
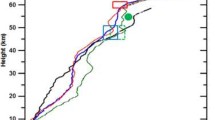
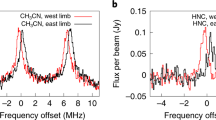
Titan, after Venus, is the second example in the solar system of an atmosphere with a global cyclostrophic circulation, but in this case a circulation that has a strong seasonal modulation in the middle atmosphere. Direct measurement of Titan's winds, particularly observations tracking the Huygens probe at 10°S, indicate that the zonal winds are mostly in the sense of the satellite's rotation. They generally increase with altitude and become cyclostrophic near 35 km above the surface. An exception to this is a sharp minimum centered near 75 km, where the wind velocity decreases to nearly zero. Zonal winds derived from temperatures retrieved from Cassini orbiter measurements, using the thermal wind equation, indicate a strong winter circumpolar vortex, with maximum winds of 190 m s −1 at mid northern latitudes near 300 km. Above this level, the vortex decays. Curiously, the stratospheric zonal winds and temperatures in both hemispheres are symmetric about a pole that is offset from the surface pole by ~4°. The cause of this is not well understood, but it may reflect the response of a cyclostrophic circulation to the offset between the equator, where the distance to the rotation axis is greatest, and the seasonally varying subsolar latitude. The mean meridional circulation can be inferred from the temperature field and the meridional distribution of organic molecules and condensates and hazes. Both the warm temperatures near 400 km and the enhanced concentration of several organic molecules suggest subsidence in the north-polar region during winter and early spring. Stratospheric condensates are localized at high northern latitudes, with a sharp cut-off near 50°N. Titan's winter polar vortex appears to share many of the same characteristics of isolating high and low-latitude air masses as do the winter polar vortices on Earth that envelop the ozone holes. Global mapping of temperatures, winds, and composition in the troposphere, by contrast, is incomplete. The few suitable discrete clouds that have been found for tracking indicate smaller velocities than aloft, consistent with the Huygens measurements. Along the descent trajectory, the Huygens measurements indicate eastward zonal winds down to 7 km, where they shift westward, and then eastward again below 1 km down to the surface. The low-latitude dune fields seen in Cassini RADAR images have been interpreted as longitudinal dunes occurring in a mean eastward zonal wind. This is not like Earth, where the low-latitude winds are westward above the surface. Because the net zonal-mean time-averaged torque exerted by the surface on the atmosphere should vanish, there must be westward flow over part of the surface; the question is where and when. The meridional contrast in tropospheric temperatures, deduced from radio occultations at low, mid, and high latitudes, is small, ~5 K at the tropopause and ~3 K at the surface. This implies efficient heat transport, probably by axisymmetric meridional circulations. The effect of the methane “hydrological” cycle on the atmospheric circulation is not well constrained by existing measurements. Understanding the nature of the surface-atmosphere coupling will be critical to elucidating the atmospheric transports of momentum, heat, and volatiles.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
For a harmonic disturbance, the relevant time scale is the period divided by 2 π (see, e.g., Section V of the review by Hunten et al. 1984) .
References
Achterberg RK, Conrath BJ, Gierasch PJ, Flasar FM, Nixon CA (2008a) Titan's middle-atmospheric temperatures and dynamics observed by the Cassini composite infrared spectrometer. Icarus 194:263–277. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2007.09.029
Achterberg RK, Conrath BJ, Gierasch PJ, Flasar FM, Nixon CA (2008b) Observation of a tilt of titan's middle-atmospheric superrotation. Icarus 197:549–555 doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2008. 05.014
Andrews DG, Holton JR, Leovy CB (1987) Middle atmosphere dynamics. Academic, Orlando
Atkinson DH (1989) Measurement of planetary wind fields by Doppler monitoring of an atmospheric entry vehicle. Ph.D. Thesis. Washington State University, Pullman, WA
Atkinson DH, Pollack JB, Seiff A (1990) Measurement of a zonal wind profile on Titan by Doppler tracking of the Cassini entry probe. Radio Sci 25:865–882
Atkinson DH, Kazeminejad B, Lebreton J-P, Witasse O, Pérez-Ayūcar M, Matson DL (2007) The Huygens probe descent trajectory working group: organizational framework, goals, and implementation. Planet Space Sci 55:1877–1885
Awal M, Lunine JI (1994) Moist convective clouds in Titan's atmosphere. Geophys Res Lett 21:2491–2494
Baines KH, Drossart P, Momary TW, Formisano V, Griffith C, Bellucci G, Bibring J-P, Brown R.H, Buratti BJ, Capaccioni F, Cerroni P, Clark RN, Coradini A, Cruikshank DP, Jaumann R, Langevin Y, Matson DL, McCord TB, Mennella V, Nelson RM, Nicholson PD, Sicardy B, Sotin C (2005) The atmospheres of Saturn and Titan in the near-infrared: first results of Cassini/VIMS. Earth Moon Planets 96:119–147
Barth EL, Rafkin SCR (2007) TRAMS: a new dynamic cloud model for Titan's methane. Geophys Res Lett 34:L03203
Bézard B, Coustenis A, McKay CP (1995) Titan's stratospheric temperature asymmetry: a radiative origin? Icarus 113:267–276
Bird MK, Heyl M, Allison M, Asmar SW, Atkinson DH, Edenhofer P, Plettemeier D, Wohlmuth R, Iess L, Tyler GL (1997) The Huygens doppler wind experiment. In: Huygens science payload and mission, ESA SP-1177:139–162
Bird MK, Allison M, Asmar SW, Atkinson DH, Avruch IM, Dutta-Roy R, Dzierma Y, Edenhofer P, Folkner WM, Gurvits LI, Johnston DV, Plettemeier D, Pogrebenko SV, Preston RA, Tyler GL (2005) The vertical profile of winds on Titan. Nature 438:800–802
Bouchez AH (2003) Seasonal trends in Titan's atmosphere: haze, wind, and clouds. Ph. D. Thesis. California Institute of Technology. http:// resolver.caltech.edu/CaltechETD:etd-10272003-092206
Bouchez AH, Brown ME (2005) Statistics of Titan's south polar tropo-spheric clouds. Astrophys J 618:L53–L56
Brown ME, Bouchez AH, Griffith CA (2002) Direct detection of variable tropospheric clouds near Titan's South Pole. Nature 420:795–797
Brown RH, Baines KH, Bellucci G, Buratti BJ, Capacionni F, Cerroni P, Clark RN, Coradini A, Cruikshank DP, Drossart P, Formisano V, Jaumann R, Langevin Y, Matson DL, McCord TB, Mennella V, Nelson RM, Nicholson PD, Sicardy B, Sotin C, Baugh N, Griffith C, Hansen G, Hibbitts K, Showalter MR (2006) Observations in the Saturn system during approach and orbital insertion, with Cassini's visual and infrared mapping spectrometer (VIMS). Astron Astrophys 446:707–716
Chapman S, Lindzen RS (1970) Atmospheric tides. Reidel, Dordrecht
Colombatti G, Withers P, Ferri F, Aboudan A, Ball AJ, Bettanini C, Gaborit V, Harri AM, Hathi B, Leese MR, Makinen T, Stoppato PL, Towner MC, Zarnecki JC, Angrilli F, Fulchignoni M (2008) Reconstruction of the trajectory of the Huygens probe using the Huygens atmospheric structure instrument (HASI). Planet Space Sci 56:586–600
Counselman CC III, Gourevitch SA, King RW, Loriot GB, Ginsberg ES (1980) Zonal and meridional circulation of the lower atmosphere of Venus determined by radio interferometry. J Geophys Res 85:8026–8030
Coustenis A, Bézard B (1995) Titan's atmosphere from Voyager infrared observations. IV. Latitudinal variations of temperature and composition. Icarus 115:126–140
Coustenis A, Achterberg RK, Conrath BJ, Jennings DE, Marten A, Gautier D, Nixon CA, Flasar FM, Teanby NA, Bézard B, Samuelson RE, Carlson RC, Lellouch E, Bjoraker GL, Romani PN, Taylor FW, Irwin PGJ, Fouchet T, Hubert A, Orton GS, Kunde VG, Vinatier S, Mondellini J, Abbas MM, Courtin R (2007) The composition of Titan's stratosphere from Cassini/CIRS mid-infrared spectra. Icarus 189:35–62
Coustenis A, Schmitt B, Khanna RK, Trotta F (1999) Plausible condensates in Titan's stratosphere from Voyager infrared spectra. Planet Space Sci 47:1305–1329
Crespin A, Lebonnois S, Vinatier S, Bézard B, Coustenis A, Teanby NA, Achterberg RK, Rannou P, Hourdin F (2008) Diagnostics of Titan's stratospheric dynamics using Cassini/CIRS data and the 2-dimensional IPSL circulation model. Icarus 192(2):556–571. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2008.05.010
Del Genio AD, Zhou W, Eichler TP (1993) Equatorial superrotation in a slowly rotating GCM: implications for Titan and Venus. Icarus 101:1–17
Dunkerton T (1978) On the mean meridional mass motions of the stratosphere and mesosphere. J Atmos Sci 35:2325–2333
Dutta-Roy R, Bird MK (2004) The Huygens doppler wind experiment: a Titan zonal wind retrieval algorithm. In: Planetary probe atmospheric entry and descent trajectory analysis and science, ESA SP-544:109–116
Dzierma Y, Bird MK, Dutta-Roy R, Perez-Ayucar M, Plettemeier D, Edenhofer P (2007) Huygens probe descent dynamics inferred from channel B signal level measurements. Planet Space Sci 55:1886–1895
Flasar FM (1998a) The composition of Titan's atmosphere: a meteorological perspective. Planet Space Sci 46:1109–1124
Flasar FM (1998b) The dynamic meteorology of Titan. Planet Space Sci 46:1125–1147
Flasar FM, Achterberg RK (2009) The structure and dynamics of Titan's middle atmosphere. Phil Trans Roy Soc London 367:649–664
Flasar FM, Conrath BJ (1990) Titan's stratospheric temperature: a case for dynamical inertia? Icarus 85:346–354
Flasar FM, Samuelson RE, Conrath BJ (1981) Titan's atmosphere: temperature and dynamics. Nature 292:693–698
Flasar FM, Allison M, Lunine JI (1997) Titan zonal wind model. In: Huygens science payload and mission, ESA SP-1177:287–298
Flasar FM, Kunde VG, Abbas MM, Achterberg RK, Ade P, Barucci A, Bézard B, Bjoraker GL, Brasunas JC, Calcutt S, Carlson R, Césarsky CJ, Conrath BJ, Coradini A, Courtin R, Coustenis A, Edberg S, Edgington S, Ferrari C, Gautier D, Gierasch PJ, Grossman K, Irwin P, Jennings DE, Lellouch E, Mamoutkine AA, Marten A, Meyer JP, Nixon CA, Orton GS, Owen TC, Pearl JC, Prangé R, Raulin F, Read PL, Romani PN, Samuelson RE, Segura ME, Showalter MR, Simon-Miller AA, Smith MD, Spencer JR, Spilker LJ, Taylor FW (2004) Exploring the Saturn system in the thermal infrared: the composite infrared spectrometer. Space Sci Rev 115:169–297
Flasar FM, Achterberg RK, Conrath BJ, Gierasch PJ, Kunde VG, Nixon CA, Bjoraker GL, Jennings DE, Romani PN, Simon-Miller AA, Bézard B, Coustenis A, Irwin PGJ, Teanby NA, Brasunas JC, Pearl JC, Segura ME, Carlson RC, Mamoutkine AA, Schinder PJ, Barucci A, Courtin R, Fouchet T, Gautier D, Lellouch E, Marten A, Prangé R, Vinatier S, Strobel DF, Calcutt SB, Read PL, Taylor FW, Bowles N, Samuelson RE, Orton GS, Spilker LJ, Owen TC, Spencer JR, Showalter MR, Ferrari C, Abbas MM, Raulin F, Edgington S, Ade P, Wishnow EH (2005) Titan's atmospheric temperatures, winds, and composition. Science 308:975–978
Folkner WM, Preston RA, Border JS, Navarro J, Wilson WE, Oestreich M (1997) Earth-based radio tracking of the Galileo Probe for Jupiter wind estimation. Science 275:644–646
Folkner WM, Border JS, Lowe ST, Preston RA, Bird MK (2004) Ground-based tracking of the Huygens Probe during the Titan descent. In: Planetary probe atmospheric entry and descent trajectory analysis and science, ESA SP-544:191–196
Folkner WM, Asmar SW, Border JS, Franklin GW, Finley SG, Gorelik J, Johnston DV, Kerzhanovich VV, Lowe ST, Preston RA, Bird MK, Dutta-Roy R, Allison M, Atkinson DH, Edenhofer P. Plettemeier D, Tyler GL (2006) Winds on Titan from ground-based tracking of the Huygens probe. J Geophys Res 111:E07S02
Friedson AJ, West RA, Wilson EH, Oyafuso F, Orton GS (2009) A global climate model of Titan's atmosphere and surface. Planet Sp Sci (in press), doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2009.05.006
Fulchignoni M, Ferri F, Angrilli F, Ball AJ, Bar-Nun A, Barucci MA, Bettanini C, Bianchini G, Borucki W, Colombatti G, Coradini M, Coustenis A, Debei S, Falkner P, Fanti G, Flamini E, Gaborit V, Grard R, Hamelin M, Harri AM, Hathi B, Jernej I, Leese MR, Lehto A, Lion Stoppato PF, López-Moreno JJ, Mäkinen T, McDonnell JAM, McKay CP, Molina-Cuberos G, Neubauer FM, Pirronello V, Rodrigo R, Saggin B, Schwingenschuh K, Seiff A, Simões F, Svedhem H, Tokano T, Towner MC, Trautner R, Withers P, Zarnecki JC (2005) Titan's physical characteristics measured by the Huygens atmospheric structure instrument (HASI). Nature 438:785–791
Gibbard SG, Macintosh B, Gavel D, Max CE, de Pater I, Roe HG, Ghez AM, Young EF, McKay CP (2004) Speckle imaging of Titan at 2 microns: surface albedo, haze optical depth, and tropospheric clouds 1996–1998. Icarus 169:429–439
Gierasch PJ (1975) Meridional circulation and the maintenance of the Venus atmospheric rotation. J Atmos Sci 32:1038–1044
Gierasch PJ, Goody RM, Young RE, Crisp D, Edwards C, Kahn R, Rider D, Del Genio A, Greeley R, Hou A, Leovy CB, McCleese D, Newman M. (1997) The general circulation of the Venus atmosphere: An assessment. In: Bougher SW, Hunten DM, Phillips RJ (eds) Venus II. University of Arizona Press, Tucson, AZ, pp 459–500
Griffith CA, Hall JL, Geballe TR (2000) Detection of daily clouds in Titan. Science 290:509–513
Griffith CA, Penteado P, Baines K, Drossart P, Barnes J, Bellucci G, Bibring J, Brown R, Buratti B, Capaccioni F, Cerroni P, Clark R, Combes M, Coradini A, Cruikshank D, Formisano V, Jaumann R, Langevin Y, Matson D, McCord T, Mennella V, Nelson R, Nicholson P, Sicardy B, Sotin C, Soderblom LA, Kursinski R (2005) The evolution of Titan's mid-latitude clouds. Science 310:474–477
Griffith CA, Penteado P, Rannou P, Brown R, Boudon V, Baines KH, Clark R, Drossart P, Buratti B, Nicholson P, McKay CP, Coustenis A, Negrao A, Jaumann R (2006) Evidence for a polar ethane cloud on Titan. Science 313:1620–1622
Held IM, Hou AY (1980) Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere. J Atmos Sci 37:515–533
Hide R (1969) The viscous boundary layer at the rigid bounding surface of an electrically-conducting rotating fluid in the presence of a magnetic field. J Atmos Sci 26:847–853
Hinson DP, Tyler GL (1983) Internal gravity waves in Titan's atmosphere observed by Voyager radio occultation. Icarus 54:337–352
Hirtzig M, Coustenis A, Gendron E, Drossart P, Negrão A, Combes M, Lai O, Rannou P, Lebonnois S, Luz D (2006) Monitoring atmospheric phenomena on Titan. Astron Astroph 456:761–774
Holton JR (1979) An introduction to dynamic meteorology, 2nd edn. Academic, New York
Hou AY, Farrell BF (1987) Superrotation induced by critical-level absorption of gravity waves on Venus: an assessment. J Atmos Sci 44:1049–1061
Hourdin F, Talagrand O, Sadourny R, Courtin R, Gautier D, McKay CP (1995) Numerical simulation of the general circulation of the atmosphere of Titan. Icarus 117:358–374
Hourdin F, Lebonnois S, Luz D, Rannou P (2004) Titan's stratospheric composition driven by condensation and dynamics. J Geophys Res 109:E12005. doi:10.1029/2004JE002282
Hubbard WB, Sicardy B, Miles R, Hollis AJ, Forrest RW, Nicolson IKM, Appleby G, Beisker W, Bittner C, Bode H-J, Bruns M, Denzau H, Nezel M, Riedel E, Struckmann H, Arlot JE, Roques F, Sevre F, Thuillot W, Hoffmann M, Geyer EH, Buil C, Colas F, Lecacheux J, Klots A, Thouvenot E, Vidal JL, Carreira E, Rossi F, Blanco C, Cristaldi S, Nevo Y, Reitsema HJ, Brosch N, Cernis K, Zdanavicius K, Wasserman LH, Hunter DM, Gautier D, Lellouch E, Yelle RV, Rizk B, Flasar FM, Porco CC, Toublanc D, Corugedo G (1993) The occultation of 28 Sgr by Titan. Astron Astrophys 269:541–563
Hueso R, Sánchez-Lavega A (2006) Methane storms on Saturn's moon Titan. Nature 442:428–431
Hunten DM, Tomasko MG, Flasar FM, Samuelson RE, Strobel DF, Stevenson DJ (1984) Titan. In: Gehrels T, Matthews M (eds) Saturn. University of Arizona Press, Tucson, pp 671–759
Karatekin Ö, Van Hoolst T (2006) The effect of a dense atmosphere on the tidally induced potential of Titan. Icarus 183:230–232
Karkoschka E, Lorenz RD (1997) Latitudinal variation of aerosol sizes inferred from Titan's shadow. Icarus 125:369–379
Karkoschka E, Tomasko MG, Doose LR, See C, McFarlane EA, Schröder SE, Rizk B (2007) DISR imaging and the geometry of the descent of the Huygens probe within Titan's atmosphere. Planet Space Sci 55:1896–1935
Kazeminejad B, Atkinson DH, Pérez-Ayūcar M, Lebreton J-P, Sollazzo C (2007) Huygens' entry and descent through Titan's atmosphere: methodology and results of the trajectory reconstruction. Planet Space Sci 55:1845–1876
Khanna RK (2005) Condensed species in Titans atmosphere: identification of crystalline propionitrile (C2H5CN, CH3CH2C≡N) based on laboratory infrared data. Icarus 177:116–121
Kostiuk T, Fast KE, Livengood TA, Hewagama T, Goldstein JJ, Espenak F, Buhl D (2001) Direct measurement of winds on Titan. Geophys Res Lett 28:2361–2364
Kostiuk T, Livengood TA, Hewagama T, Sonnabend G, Fast KE, Murakawa K, Tokunaga AT, Annen J, Buhl D, Schmülling F (2005) Titan's stratospheric zonal wind, temperature and ethane abundance a year prior to Huygens insertion. Geophys Res Lett 32:L22205
Kostiuk T, Livengood TA, Sonnabend G, Fast KE, Hewagama T, Murakawa K, Tokunaga AT, Annen J, Buhl D, Schmülling F, Luz D, Witasse O (2006) Stratospheric global winds on Titan at the time of the Huygens descent. J Geophys Res 111:E07S03
Lellouch E, Coustenis A, Gautier D, Raulin F, Dubouloz N, Frére C (1989) Titan's atmosphere and hypothesized ocean: a reanalysis of the Voyager 1 radio-occultation and IRIS 7.7μm data. Icarus 79:328–349
Leovy CB (1973) Rotation of the upper atmosphere of Venus. J Atmos Sci 30:1218–1220
Leovy CB (1987) Zonal winds near Venus' cloud top level: an analytic model of the equatorial wind speed. J Atmos Sci 69:193–201
Leovy CB, Pollack JB (1973) A first look at atmospheric dynamics and temperature variations on Titan. Icarus 19:195–201
Lindal GF, Wood GE, Hotz HB, Sweetnam DN, Eshleman V, Tyler GL (1983) The atmosphere of Titan: an analysis of the Voyager 1 radio occultation measurements. Icarus 53:348–363
Lindzen RS, Hou AY (1988) Hadley circulations for zonally averaged heated centered off the equator. J Atmos Sci 42:2416–2427
Lorenz RD (1993) The life, death, and afterlife of a raindrop on Titan. Planet Space Sci 41:647–655
Lorenz RD (2006) Thermal interactions of the Huygens probe with the Titan environment: constraints on near-surface wind. Icarus 182:559–566
Lorenz RD, McKay CP (2003) A simple expression for vertical convective fluxes in planetary atmospheres. Icarus 165:407–413
Lorenz RD, Smith PH, Lemmon MT, Karkoschka E, Lockwood GW, Caldwell J (1997) Titan's north–south asymmetry from HST and voyager imaging: comparison with models and ground-based photometry. Icarus 127:173–189
Lorenz RD, Griffith CA, Lunine JI, McKay CP, Rennò NO (2005) Convective plumes and the scarcity of Titan's clouds. Geophys Res Lett 32:L01201
Lorenz RD, Wall S, Radebaugh J, Boubin G, Reffet E, Janssen M, Stofan E, Lopes R, Kirk R, Elachi C, Lunine J, Mitchell K, Paganelli F, Soderblom L, Wood C, Wye L, Zebker H, Anderson Y, Ostro S, Allison M, Boehmer R, Callahan P, Encrenaz P, Ori GG, Francescatti G, Gim Y, Hamilton G, Hensley G, Johnson W, Kelleher K, Muhleman D, Picardi G, Posa F, Roth L, Seu R, Shaffer S, Stiles B, Vetralla S, Flamini E, West R (2006) The sand seas of Titan: Cassini RADAR observations of longitudinal dunes. Science 312:724–727
Lorenz RD, Zarnecki JC, Towner MC, Leese MR, Ball AJ, Hathi B, Hagermann A, Ghafoor NAL (2007) Descent motions of the Huygens probe as measured by the surface science package (SSP): turbulent evidence for a cloud layer. Planet Space Sci 55:1936–1948
Lorenz RD, Stiles BW, Kirk RL, Allison MD, Persi del Marmo P, Iess L, Lunine JI, Ostro SJ, Hensley S (2008) Titan's rotation reveals an internal ocean and changing zonal winds. Science 319:1649–1651
Lorenz RD, Brown ME, Flasar FM (2009) Seasonal change on Titan. In: Brown RH, Lebreton J-P, Waite JH (eds) Titan from Cassini-Huygens. Springer
Lunine JI, Atreya SK (2008) The methane cycle on Titan. Nature Geosci 1:159–164
Luz D, Hourdin F, Rannou P, Lebonnois S (2003) Latitudinal transport by barotropic waves in Titan's stratosphere. II. Results from a coupled dynamics-microphysics-photochemistry GCM. Icarus 166:343–358
Luz D, Civeit T, Courtin R, Lebreton J-P, Gautier D, Rannou P, Kaufer A, Witasse O, Lara L, Ferri F (2005) Characterization of zonal winds in the stratosphere of Titan with UVES. Icarus 179:497–510
Luz D, Civeit T, Courtin R, Lebreton J-P, Gautier D, Witasse O, Kaufer A, Ferri F, Lara L, Livengood T, Kostiuk T (2006) Characterization of zonal winds in the stratosphere of Titan with UVES: 2. Observations coordinated with the Huygens probe entry. J Geophys Res 111:E08S90
Mäkinen JTT, Harri A-M, Tokano T, Savijärvi H, Siili T, Ferri F (2006) Vertical atmospheric flow on Titan as measured by the HASI instrument on board the Huygens probe. Geophys Res Lett 33:L21803
McKay CP, Pollack JB, Courtin R (1989) The thermal structure of Titan's atmosphere. Icarus 80:23–53
McKay CP, Pollack JB, Courtin R (1991) The greenhouse and antigreen-house effects on Titan. Science 253:1118–1121
Mitchell JL (2008) The drying of Titan's dunes: Titan's methane hydrology and its impact on atmospheric circulation. J Geophys Res 113:E08105
Mitchell JL, Pierrehumbert RT, Frierson DMW, Caballero R (2006) The dynamics behind Titan's methane clouds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18421–18426
Mitri G, Showman AP, Lunine JI, Lorenz RD (2007) Hydrocarbon lakes on Titan. Icarus 186:385–394
Moreno R, Marten A, Hidayat T (2005) Interferometric measurements of zonal winds on Titan. Astron Astrophys 437:319–328
Pechmann JB, Ingersoll AP (1984) Thermal tides in the atmosphere of Venus: comparison of model results with observations. J Atmos Sci 41:3290–3313
Penteado PF, Griffith CA, Tomasko MG, Engel S, See C, Doose L (2009) Latitudinal variations in Titan's methane and haze from Cassini VIMS observations. Icarus (in press)
Pogrebenko SV, Gurvits LI, Campbell RM, Avruch IM, Lebreton J-P, van't Klooster CGM (2004) VLBI tracking of the Huygens probe in the atmosphere of Titan. In: Planetary probe atmospheric entry and descent trajectory analysis and science, ESA SP-544:197–204
Porco CC, Baker E, Barbara J, Beurle K, Brahic A, Burns JA, Charnoz S, Cooper N, Dawson D, Del Genio AD, Denk T, Dones L, Dyudina U, Evans MW, Fussner S, Glese B, Grazier K, Helfenstein P, Ingersoll AP, Jacobson RA, Johnson TV, McEwen A, Murray CD, Neukum G, Owen WM, Perry J, Roatsch T, Spitale J, Squyres S, Thomas P, Tiscareno M, Turtle EP, Vasavada AR, Veverka J, Wagner R, West R (2005) Imaging of Titan from the Cassini spacecraft. Nature 434:159–168
Radebaugh J, Lorenz RD, Lunine JI, Wall SD, Boubin G, Reffet E, Kirk RL, Lopes RM, Stofan ER, Soderblom L, Allison M, Janssen M, Paillou P, Callahan P, Spencer C (2008) the Cassini radar team: dunes on Titan observed by Cassini radar. Icarus 194:690–703
Rannou P, Hourdin F, McKay CP, Luz D (2004) A coupled dynamics-microphysics model of Titan's atmosphere. Icarus 170:443–479
Rannou P, Montmessin F, Hourdin F, Lebonnois S (2006) The latitudinal distribution of clouds on Titan. Science 311:201–205
Richardson MI, Toigo AD, Newman CE (2007) PlanetWRF: a general purpose, local to global numerical model for planetary atmospheric and climate dynamics. J Geophys Res 112:E09001
Rodriguez S, Le Mouélic S, Rannou P, Tobie G, Baines KH, Barnes JW, Griffith CA, Hirtzig M, Pitman KM, Sotin C, Brown RH, Buratti BJ, Clark RN, Nicholson PD (2009) Global circulation as the main source of cloud activity on Titan. Nature 459:678–682
Roe HG, de Pater I, Macintosh A, McKay CP (2002) Titan's clouds from Gemini and Keck adaptive optics imaging. Astrophys J 581:1399–1406
Roe HG, Brown ME, Schaller EL, Bouchez AH, Trujillo CA (2005) Geographic control of Titan's mid-latitude clouds. Science 310:477–479
Roman MT, West RA, Banfield DJ, Gierasch PJ, Achterberg RK, Nixon CA, Thomas PC (2009) Determining a tilt in Titan's north–south albedo asymmetry from Cassini images. Icarus. (in press) doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2009.04.021
Samuelson RE, Mayo LA, Knuckles MA, Khanna RK (1997) C4N2 ice in Titan's north polar stratosphere. Planet Space Sci 45:941–948
Samuelson RE, Smith MD, Achterberg RK, Pearl JC (2007) Cassini CIRS update on stratospheric ices at Titan's winter pole. Icarus 189:63–71
Schaller EL, Brown ME, Roe HG, Bouchez AH (2006a) A large cloud outburst at Titan's south pole. Icarus 182:224–229
Schaller EL, Brown ME, Roe HG, Bouchez AH, Trujillo CA (2006b) Dissipation of Titan's south polar clouds. Icarus 184:517–523
Schneider T (2006) The general circulation of the atmosphere. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 34:65–688
Sicardy B et al (1999) The structure of Titan's stratosphere from the 28 Sgr occultation. Icarus 142:357–390
Sicardy B, Colas F, Widemann T et al (2006) The two Titan stellar occultations of 14 November 2003. J Geophys Res 111:E11S91. doi: 10.1029/2005JE002624
Smith BA, Soderblom L, Beebe R, Boyce J, Briggs G, Bunker A, Collins SA, Hansen CJ, Johnson TV, Mitchell JL, Terrile RJ, Carr M, Cook II AF, Cuzzi J, Pollack JB, Danielson GE, Ingersoll A, Davies ME, Hunt GE, Masursky H, Shoemaker E, Morrison D, Owen T, Sagan C, Veverka J, Strom R, Suomi VE (1981) Encounter with Saturn: Voyager 1 imaging science results. Science 212:163–191
Sromovsky LA, Suomi VE, Pollack JB, Krauss RJ, Limaye SS, Owen T, Revercomb HE, Sagan C (1981) Implications of Titan's north– south brightness asymmetry. Nature 292:698–702
Stiles BW, Kirk RL, Lorenz RD, Hensley S, Lee E, Ostro SJ, Allison MD, Callahan PS, Gim Y, Iess L, Persi del Marmo P, Hamilton G, Johnson WTK, West RD, the Cassini RADAR Team (2008) Determining Titan's spin state from Cassini RADAR images. Astron J 135:1669–1680
Stofan ER, Elachi C, Lunine JI, Lorenz RD, Stiles B, Mitchell KL, Ostro S, Soderblom L, Wood C, Zebker H, Wall S, Janssen M, Kirk R, Lopes R, Paganelli F, Radebaugh J, Wye L, Anderson Y, Allison M, Boehmer R, Callahan P, Encrenaz P, Flamini E, Francescetti G, Gim Y, Hamilton G, Hensley S, Johnson WTK, Kelleher K, Muhleman D, Paillou P, Picardi G, Posa F, Roth L, Seu R, Shaffer S, Vetrella S, West R (2007) The lakes of Titan. Nature 445:61–64
Strobel DF (2006) Gravitational tidal waves in Titan's upper atmosphere. Icarus 182:251–258
Strobel DF, Atreya SK, Bézard B, Ferri F, Flasar FM, Fulchignoni M, Lellouch E, Müller-Wodarg I (2009) Atmospheric composition and structure. In: Brown RH, Lebreton J-P, Waite JH (eds) Titan from Cassini-Huygens. Springer
Teanby NA, Irwin PGJ, de Kok R, Nixon CA, Coustenis A, Bézard B, Calcutt SB, Bowles NE, Flasar FM, Fletcher L, Howett C, Taylor FW (2006) Latitudinal variations of HCN, HC3N, and C2N2 in Titan's stratosphere derived from Cassini CIRS data. Icarus 181:243–255
Teanby NA, Irwin PGJ, de Kok R, Nixon CA, Coustenis A, Bézard B, Calcutt SB, Bowles NE, Flasar FM, Fletcher L, Howett C, Taylor FW (2007) Latitudinal variations of HCN, HC3 N and C2N2 in Titan's stratosphere derived from Cassini CIRS data. Icarus 181:364–384
Teanby NA, de Kok R, Irwin PGJ, Osprey S, Vinatier S, Gierasch PJ, Read PL, Flasar FM, Conrath BJ, Achterberg RK, Bézard B, Nixon CA, Calcutt S (2008) Titan's winter polar vortex structure revealed by chemical tracers. J Geophys Res 113:E12003
Teanby NA, Irwin PGJ, de Kok R, Nixon CA (2009) Dynamical implications of seasonal and spatial variations in Titan's stratospheric composition. Phil Trans Roy Soc London 367:697–711
Tokano T (2005) Meteorological assessment of the surface temperatures on Titan: constraints on the surface type. Icarus 173:222–242
Tokano T (2007) Near-surface winds at the Huygens site on Titan: interpretation by means of a general circulation model. Planet Space Sci 55:1990–2009
Tokano T (2008) Dune-forming winds on Titan and the influence of topography. Icarus 194:243–262
Tokano T (2009) The dynamics of Titan's troposphere. Phil Trans Roy Soc London 367:633–648
Tokano T, Neubauer FM (2002) Tidal winds on Titan caused by Saturn. Icarus 158:499–515
Tokano T, Neubauer FM (2005) Wind-induced seasonal angular momentum exchange at Titan's surface and its influence on Titan's length-of-day. Geophys Res Lett 32:L24203
Tokano T, Neubauer FM, Laube M, McKay CP (1999) Seasonal variation of Titan's atmospheric structure simulated by a general circulation model. Planet Space Sci 47:493–520
Tokano T, Neubauer FM, Laube M, McKay CP (2001) Three-dimensional modeling of the tropospheric methane cycle on Titan. Icarus 153:130–147
Tokano T, Ferri F, Colombatti G, Mäkinen T, Fulchignoni M (2006) Titan's planetary boundary layer structure at the Huygens landing site. J Geophys Res 111:E08007
Tomasko MG, Smith PH (1982) Photometry and Polarimetry of Titan: Pioneer 11 observations and their implications for aerosol properties. Icarus 51:65–95
Tomasko MG, Archinal B, Becker T, Bézard B, Bushroe M, Combes M, Cook D, Coustenis A, de Bergh C, Dafoe C, Doose LE, Douté S, Eibl A, Engel S, Gliem F, Grieger B, Holso K, Howington-Kraus E, Karkoschka E, Keller HU, Kirk R, Kramm R, Küppers M, Lanagan P, Lellouch E, Lemmon M, Lunine J, McFarlane E, Moores J, Prout GM, Rizk B, Rosiek M, Rueffer P, Schröder SE, Schmitt B, See C, Smith P, Soderblom L, Thomas N, West R (2005) Rain, winds and haze during the Huygens probe's descent to Titan's surface. Nature 438:765–778
Tomasko MG, Bézard B, Doose L, Engel S, Karkoschka E, Vinatier S (2008) Heat balance in Titan's atmosphere. Planet Space Sci 56:648–659
Toon OB, McKay CP, Courtin R, Ackerman TP (1988) Methane rain on Titan. Icarus 75:255–284
Turtle EP, Perry JE, McEwen AS, DelGenio AD, Barbara J, West RA, Fussner S, Dawson DD, Porco CC (2009) Cassini Imaging of Titan's high-latitude lakes, clouds, and south-polar surface changes. Geophys Res Lett 36: L02204, doi: 10.1029/2008GL036186
Vander Auwera J, Moazzen-Ahmadi N, Flaud J-M (2007) Towards an accurate database for the 12 mm region of the ethane spectrum. Astrophys J 662:750–757. doi:10.1086/515567
Walterscheid RL, Schubert G (2006) A tidal explanation for the Titan haze layers. Icarus 183:471–478
Williams GP (1988) The dynamical range of global circulations–II. Climate Dynamics 3:45–84
Witasse O, Lebreton JP, Bird MK, Dutta-Roy R, Folkner, WM, Preston RA, Asmar SW, Gurvits LI, Pogrebenko SV, Avruch IM, Campbell RM, Bignall HE, Garrett MA, van Langevelde HJ, Parsley SM, Reynolds C, Szomoru A, Reynolds JE, Phillips CJ, Sault RJ, Tzioumis AK, Ghigo F, Langston G, Brisken W, Romney JD, Mujunen A, Ritakari J, Tingay SJ, Dodson RG, van't Klooster CGM, Blancquaert T, Coustenis A, Gendron E, Sicardy B, Hirtzig M, Luz D, Negrao A, Kostiuk T, Livengood TA, Hartung M, de Pater I, Adamkovics M, Lorenz RD, Roe H, Schaller E, Brown M, Bouchez AH, Trujillo CA, Buratti BJ, Caillault L, Magin T, Bourdon A, Laux C (2006) Overview of the coordinated ground-based observations of Titan during the Huygens mission. J Geophys Res 111:E07S01. doi: 10.1029/2005JE002640
Yelle RV, Strobel D, Lellouch E, Gautier D (1997) Engineering models for Titan's atmosphere. In Huygens: Science, Payload and Mission, ed. J.-P. Lebreton, Eur. Space Agency Spec. Publ. ESA SP1177, 243–256
Zhu X (2006) Maintenance of equatorial superrotation in the atmospheres of Venus and Titan. Planet Space Sci 54:761–773
Zhu X, Strobel DF (2005) On the maintenance of thermal wind balance and equatorial superrotation in Titan's stratosphere. Icarus 176:331–350
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Flasar, F., Baines, K., Bird, M., Tokano, T., West, R. (2009). Atmospheric Dynamics and Meteorology. In: Brown, R.H., Lebreton, JP., Waite, J.H. (eds) Titan from Cassini-Huygens. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-9215-2_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-9215-2_13
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-9214-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-9215-2
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)