Abstract
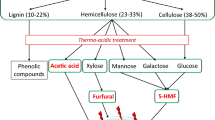
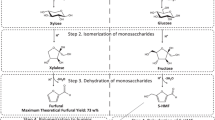
Lignocellulosic biomass has great potential as a cheap feedstock in biological processes to produce biofuels or chemicals; however, dilute acid pretreatment at high temperatures produces undesirable compounds. Toxicity tests were done with inhibitors in standard media, to predict the growth-limiting effects on thermophilic strains. The 22 inhibitors included furfural, levulinic acid, acetic acid, and cinnamaldehyde. Neutralizing reagents and additional treatment steps have been tested.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ingram, L. O, Gomez, P. F, Lai, X., Moniruzzaman, M., Wood, B. E., Yomano, L. P., and York, S. W. (1998), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 58, 204–214.
Jönsson, L. J., Palmquist, E., Nilvebrant, N. O., and Hahn Hägerdal, B. (1998), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 49, 691–697.
Amartey, S. and Jeffries, T. (1996), World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 12, 281–283.
McMillan, J. D. (1994), ACS Symp. Ser. 566, 411–437.
Nishikawa, N. K., Sutclife, R., and Saddler, J. N. (1988), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 27, 549–552.
Palmquist, E., Grage H., Meinander, N. Q., and Hahn-Hägerdal, B. (1999), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 63(1), 46–55.
Palmquist, E., Hahn-Hägerdal, B., Galbe, M., and Zacchi G. (1996), Enzyme Microb. Tech. 19, 470–476.
Van Zyl, C., Prior, B. A., and du Preez, J. C. (1991), Enzyme Microb. Tech. 13, 82–86.
Zaldivar, H. J., Martinez, A., and Ingram, L. O. (1999), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 65(1), 25–33.
Kuhad, R. C. (1993), Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 13(2), 151–172.
Danner, H., Madzingaidzo, L., Hartl, A., and Braun, R. (1998), in Proceedings of the 10th European Conference Biomass for Energy and Industry, Kopetz, H., Weber, T., Palz, W., et al., eds, C.A.R.M.E.N., Rimpar, Germany, pp. 446–449.
Beck, M. J. (1993), in Bioconversion of Forest and Agricultural Plant Residues, Saddler, J. N., ed., C.A.B. International, Wallingford, UK, pp. 211–230.
Parajo, C. J., Dominguez, H., and Dominguez, J. M. (1998), Bioresour. Technol. 66, 25–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Thomasser, C., Danner, H., Neureiter, M., Saidi, B., Braun, R. (2002). Thermophilic Fermentation of Hydrolysates. In: Finkelstein, M., McMillan, J.D., Davison, B.H. (eds) Biotechnology for Fuels and Chemicals. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-0119-9_62
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-0119-9_62
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-4612-6621-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4612-0119-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive