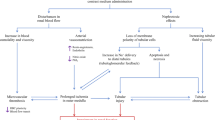
Acute renal failure is a sudden and rapid deterioration in renal function which results in the failure of the kidney to excrete nitrogenous waste products and to maintain fluid and electrolyte homeostasis. It may be a result of intravascular administration of radiographic and magnetic resonance (MR) contrast media (see also Chap. 22). Despite increased awareness, contrast medium-induced nephropathy remains the third most common cause of hospital-acquired kidney failure, and was responsible for 11% of cases in 2002 and 12% in 1979 (Hou et al. 1983; Nash et al. 2002). The mortality rate in those cases was 14%.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaqaband S, Tumuluri R, Malik AM et al (2002) Prospective randomized study of N-acetylcysteine, fenoldopam and saline for prevention of radiocontrast-induced nephropathy. Catheter Cardiovasc Intervent 57:279–283
Almén T, Frennby B, Sterner G (1999) Determination of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) with contrast media. In: Thomsen HS, Muller RN, Mattrey RF (eds) Trends in contrast media. Springer, Berlin, pp 81–94
Alonso A, Lau J, Jaber BL, Weintraub A, Sarnak MJ (2004) Prevention of contrast nephropathy with N-acetylcysteine in patients with chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Kidney Dis 43:1–9
Andrew E, Berg KJ (2004) Nephrotoxic effects of X-ray contrast media. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 42:325–332
Asif A, Epstein M (2004) Prevention of radiocontrast-induced nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 44:12–24
Aspelin P, Aubry P, Fransson S-G et al (2003) Nephrotoxic effects in high-risk patients undergoing angiography. N Engl. J Med 348:491–499
Atkins JL (1986) Effect of sodium bicarbonate preloading on ischemic renal failure. Nephron 44: 70–76
Bader BD, Berger ED, Heede MB et al (2004) What is the best hydration regimen to prevent contrast media-induced nephrotoxicity? Clin Nephrol 62:1–7
Bagshaw SM, Ghali WA (2004) Acetylcysteine for prevention of contrast induced nephropathy after intravascular angiography: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med 2:38
Bagshaw SM, Ghali WM (2005) Theophylline for prevention of radiocontrast nephropathy: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Arch Intern Med 176:1087–1093
Bagshaw SM, McAlister FA, Manns BJ, Gahli WA (2006) Acetylcysteine in the prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy. Arch Intern Med 166:161–166
Bakris GL, Lass N, Habaer AO et al (1990) Radiocontrast medium induced declines in renal function. A role for oxygen free radicals. Am J Physiol 175:57–60
Band RA, Gaieski DF, Mills AM et al (2007) Discordance between serum creatinine and creatinine clearance for identification of ED patients with abdominal pain at risk for contrast induced nephropathy. Am J Emerg Med 25:268–272
Barrett BJ, Parfrey PS (2006) Preventing nephropathy induced by contrast medium. N Engl J Med 354:379–386
Barrett BJ, Katzberg RW, Thomsen HS et al (2006) Contrast induced nephropathy in patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing computed tomography: a double blind comparison of iodixanol and iopamidol. Invest Radiol 41:815–821
Bartholomew BA, Harjai KJ, Dukkipati S et al (2004) Impact of nephropathy after percutaneous coronary intervention and a method for risk stratification. Am J Cardiol 93:1515–1519
Benigni A, Remuzzi G (1999) Endothelin antagonists. Lancet 353:133–138
Berns AS (1989) Nephrotoxicity of contrast media. Kidney Int 36:730–740
Bettmann MA (2005) Contrast medium-induced nephropathy: critical review of the existing clinical evidence Nephrol Dial Transplant 20(Suppl 1):i12–i17
Biondi-Zoccai GG, Lotrionte M, Abbate A et al (2006) Compliance with QUOROM and quality of reporting over overlapping meta-analysis on the role of acetylcysteine in the prevention of contrast associated nephropathy: case study Br Med J 332:202–209
Blaufox MD, Aurell M, Bubeck B et al (1996) Report of the Radionuclide in Nephrourology Committee on renal clearance. J Nucl Med 37:1883–1890
Bostrom AG, Kronenberg F, Ritz E (2002) Predictive performance of renal function equations for patients with chronic kidney disease and normal serum creatinine levels. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2140–2144
Briguori C, Colombo A, Airoldi F et al (2004a) N-acetylcysteine versus fenoldopam mesylate to prevent contrast agentassociated nephrotoxicity. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:762–765
Briguori C, Colombo A, Violante A et al (2004b) Standard vs. double dose of N-acetylcysteine to prevent contrast agent associated nephrotoxicity. Eur Heart J 25:206–211
Briguori C, Colombo A, Airoldi F et al (2006) Nephrotoxicity of low-osmolality versus iso-osmolality contrast agents: impact of N-acetylcysteine. Kidney Int 68:2250–2255
Briguori C, Airoldi F, D’Andrea D et al (2007) Renal insufficiency following contrast media administration trial (REMEDIAL): a randomized comparison of 3 preventive strategies. Circulation 115:1211–1217
Carraro M, Mancini W, Aretro M et al (1996) Dose effect of nitrendipine on urinary enzymes and microproteins following nonionic radiocontrast administration. Nephrol Dial Transplant 11:444–448
Carraro M, Malahan F, Antonione R et al (1998) Effects of a dimeric vs a monomeric nonionic contrast medium on renal function in patients with mild to moderate insufficiency: a double blind, randomized trail. Eur Radiol 8:144–147
Cavusoglu E, Chabra S, Marmur JD, Kini A, Sharma SK (2004) The prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Minerva Cardioangio 52:419–432
Chalmers N, Jackson RW (1999) Comparison of iodixanol and iohexol in renal impairment. Br J Radiol 72:701–703
Cheruvu B, Henning K, Mulligan J et al (2007) Iodixanol: risk of seubquent contrast nephropathy in cancer patients with underlying renal insufficiency undergoing diagnostic computed tomography examinations. J Comput Assist Tomogr 31:493–498
Choyke PL, Cady K, DePollar SL, Austin H (1998) Determination of serum creatinine prior to iodinated contrast media: is it needed in all patients? Tech Urol 4:65–69
Clavijo LC, Pinto TL, Kuchulakanti PK et al (2006) Effect of a rapid intraarterial infusion of dextrose 5% prior to coronary angiography on frequency of contrast-induced nephropathy in high-risk patients. Am J Cardiol 97:981–983
Cockroft DW, Gault MH (1976) Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16:31–41
Couchoud C, Pozet N, Labeeuw M, Pouteil-Noble C (1999) Screening early renal failure: cut-off values for serum creatinine as an indicator of renal impairment. Kidney Int 55:1878–1884
Curham GC (2003) Prevention of contrast nephropathy. JAMA 289:606–608
Dussol B, Morange S, Loundoun A et al (2006) A randomized trial of saline hydration to prevent contrast nephropathy in chronic renal failure patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:2120–2126
Eken C, Kilicaslan I (2007) Differences between various glomerular filtration rate calculation methods in predicting patients at risk for contrast-induced nephropathy. Am J Emerg Med 25:487 (Correspondence)
Erdogan A, Davidson CJ (2003) Recent clinical trials of iodixanol. Rev Cardiovasc Med 4(Suppl 5):S43–S50
Erley CM, Duda SH, Rehfuss D et al (1999) Prevention of radiocontrast-media-induced nephropathy in patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency by hydration in combination with the adenosine antagonist theophylline. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:1146–1149
Fishbane S, Durham JH, Marzo K, Rudnick M (2004) N-acetylcysteine in the prevention of radiocontrast-induced nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:251–260
Gare M, Haviv YS, Ben-Yehuda A et al (1999) The renal effect of low-dose dopamine in high-risk patients undergoing coronary angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 34:1682–1688
Gleeson T, Bulugahapitiya S (2004) Contrast induced nephropathy. Am J Roentgenol 183:1673–1689
Goldenberg I, Matezky S (2005) Nephropathy induced by contrast media: pathogenesis, risk factors and preventive strategies. CMAJ 172:1461–1467
Gruberg L, Mintz GS, Mehran R et al (2000) The prognostic implications of further renal function deterioration with 48 h of interventional coronary procedures in patients with pre-existent chronic renal insufficiency. J Am Coll Cardiol 36:1542–1548
Gupta RK, Kapoor, Tewari S, Sinha N, Sharma RK (1999) Captopril for prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in diabetic patients: a randomised study. Indian Heart J 51:521–536
Hans SS, Hans BA, Dhillon R, Dmuchowski C, Glover J (1998) Effect of dopamine on renal function after arteriography in patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency. Am Surg 64:432–436
Hardiek KJ, Katholi RE, Robbs RS, Katholi CE (2008) Renal effects of contrast media in diabetic patients undergoing diagnostic or interventional coronary angiography. J Diab Complications 22:171–177
Haylor JL, Morcos SK (2000) Endothelin antagonism and contrast nephropathy. Kidney Int 58:2239
Heinrich MC, Kuhlmann MK, Grgic A, Heckman M, Kramann B, Uder M (2005) Cytotoxic effects of ionic high-osmolar, nonioinic monomeric, and nonionic iso-osmolar dimeric iodinated contrast media on renal tubular cells in vitro. Radiology 235:843–849
Heyman SN, Rosenberger C, Rosen S (2005) Regional alterations in renal haemodynamics and oxygenation: a role contrast medium-induced nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20(Suppl 1):i6–i11
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analysis. Br Med J 327:557–560
Hoffmann U, Fischereder M, Kruger B, Drobnik W, Kramer BK (2004) The value of N-acetylcysteine in the prevention of radiocontrast agent-induced nephropathy seems questionable. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:407–410
Hou SH, Bushinsky DA, Wish JB et al (1983) Hospital acquired renal insufficiency: a prospective study. Am J Med 74:243–248
Huber W, Ilgman K, Page M et al (2002) Effect of theophylline on contrast material-induced nephropathy on patients with chronic renal insufficiency: controlled, randomized, double-blinded study. Radiology 223:772–779
Ix JH, McCulloch CE, Chertow GM (2004) Theophylline for the prevention of radiocontrast nephropathy: a meta-analysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:2747–2753
Jakobsen JA, Lundby B, Kristoffersen DT et al (1992) Evaluation of renal function with delayed CT after injection of nonionic monomeric and dimeric contrast media in healthy volunteers. Radiology 182:419–424
Jingwei N, Ruiyan Z, Jiansheng Z, Xian Z, Weifeng S (2006). Safety of isoosmolar dimer during percutaneous coronary intervention. J Interv Radiol 15:327–329
Jo S-H, Youn T-J, Koo B-K et al (2006) Renal toxicity evaluation and comparison between Visipaque (iodixanol) and Hexabrix (ioxaglate) in patients with renal insufficiency undergoing coronary angiography. The RECOVER study: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:924–930
Katzberg WR (1997) Urography into the 21st century: new contrast media, renal handling, imaging characteristics, and nephrotoxicity. Radiology 204:297–312
Katzberg R (2005) Contrast medium-induced nephrotoxicity: which pathways? Radiology 235:752–755
Katzberg R, Barrett B (2007) Risk of contrast-induced nephropathy with intravenous administration of iodinated contrast media. Radiology 243:622–628
Kini AS, Mitre CA, Kim M et al (2002) A protocol for prevention of radiographic contrast nephropathy during percutaneous coronary intervention: effect of selective dopamine receptor agonist fenoldopam. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 55:169–173
Kolehmainen H, Soiva M (2003) Comparison of Xenetix 300 and Visispaque 320 in patients with renal failure. Eur Radiol 13:B32–B33
Krasuski RA, Beard BM, Geoghagan JD et al (2003) Optimal timing of hydration to erase contrast-associated nephropathy: the OTHER CAN study. J Invasive Cardiol 15:699–702
Kshirsagar AV, Poole C, Mottl A et al (2004) N-acetylcysteine for the prevention of radiocontrast induced nephropathy: a metaanalysis of prospective controlled trials. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:761–769
Kuhn MJ, Chen N, Sahani DV et al (2008) The PREDICT study: a randomized double-Blind comparison of contrast-induced nephropathy after low- or isoosmolar contrast agent exposure. Am J Roentgenol 1991:151–157
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB et al (1999) A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Ann Intern Med 130:461–470
Liu R, Nair D, Ix J et al (2005) N-acetylcysteine and contrastinduced nephropathy: systematic review and metaanalysis. J Gen Intern Med 20:193–200
Love L, Johnson MS, Bresler ME et al (1994) The persistent computed tomography nephrogram: its significance in the diagnosis of contrast-associated nephrotoxicity. Br J Radiol 67:951–957
Maeder M, Klein M, Fehr T, Rickli H (2004) Contrast nephropathy: review focusing on prevention. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:1763–1771
Marenzi G, Lauri G, Assanelli E et al (2004) Contrast-induced nephropathy in patients undergoing primary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:1780–1785
Marenzi G, Assanelli E, Marana I et al (2006) N-acetylcysteine and contrast-induced nephropathy in primay angioplasty. N Engl J Med 354:273–278
McCarthy CS, Becker JA (1992) Multiple myeloma and contrast media. Radiology 183:519–521
McCullough PA, Wolyn R, Rocher LL et al (1997) Acute renal failure after coronary intervention: incidence, risk factors and relationship to mortality. Am J Med 103:368–375
McCullough PA, Bertrand ME, Brinker JA, Stacul F (2006) A meta-analysis of the renal safety of iso-osmolar iodixanol compared with low-osmolar contrast media. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:692–699
Mehran R, Aymong ED, Nikolsky E et al (2004) A simple risk score for prediction of contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary intervention. Development and initial validation. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:1393–1399
Mehran R for the ICON investigators (2006) Ionic versus nonionic contrast to obviate worsening nephropathy after angioplasty in chronic renal failure patients. Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapies Meeting (TCT), Washington DC, 22–26 April 2006
Merten GJ, Burgess W P, Gray LV et al (2004) Prevention of contrast induced nephropathy with sodium bicarbonate: a randomized trial. JAMA 291:2328–2338
Meschi M, Detrenis S, Musini S et al (2006) Facts and fallacies concerning the prevention of contrast medium induced nephropathy. Crit Care Med 34:2060–2068
Mitchell RL, Craig JC, Webster AC (2004) Cochrane renal group report. Am J Kidney Dis 43:752–756
Morcos SK (1998) Contrast media-induced nephrotoxicity — questions and answers. Br J Radiol 71:357–365
Morcos SK (2004) Prevention of contrast media nephrotoxicity — the story so far. Clin Radiol 59:381–389
Morcos SK (2005) Prevention of contrast media-induced nephrotoxicity after angiographic procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:13–23
Morcos SK, Thomsen HS, Webb JAW and members of contrast media safety committee of the European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) (1999) Contrast media induced nephrotoxicity: a consensus report. Eur Radiol 9:1602–1613
Mueller C, Burkle G, Buerkle HJ et al (2002) Prevention of contrast media-associated nephropathy. Randomized comparison of 2 hydration regimens in 1620 patients undergoing coronary angioplasty. Arch Intern Med 162:329–336
Nash K, Hafeez A, Hou S (2002) Hospital-acquired renal insufficiency. Am J Kidney Dis 39:930–936
Neumayer HH, Junge W, Kufner A, Wenning A (1989) Prevention of radiocontrast-media-induced nephrotoxicity by calcium channel blocker nitrendipine: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant 4:1030–1036
Nguyen SA, Suranyi P, Ravenel JG et al (2008) Iso-osmolality versus low-osmolality iodinated contrast medium at intravenous contrast-enhanced CT: effect on kidney function. Radiology 248:97–105
Nicholson T, Downes M (2003) Contrast nephrotoxicity and iso-osmolar contrast agents; implications of NEPHRIC. Clin Radiol 58:659–660
Nikolsky E, Mehran R (2003) Understanding the consequences of contrast-induced nephropathy. Rev Cardovasc Med 4(Suppl 5):S10–S18
Oldroyd SD, Haylor JL, Morcos SK (1995) Bosentan, an orally active endothelin antagonist: effect on the renal response to contrast media. Radiology 196:661–665
Oldroyd SD, Fang L, Haylor JL, Yates MS, El Nahas AM, Morcos SK (2000) Effects of adenosine receptor antagonists on the responses to contrast media in the isolated rat kidney. Clin Sci 98:303–311
Olsen JC, Salomon B (1996) Utility of the creatinine prior to intravenous contrast studies in the emergency department. J Emerg Med 14:543–546
Pannu N, Manns B, Lee H, Tonelli M (2004) Systematic review of the impact of N-acetylcysteine on contrast nephropathy. Kidney Int 65:1366–1374
Pannu N, Wiebe N, Tonelli M for the Alberta Kidney Disease Network (2006) Prophylaxis strategies for contrast-induced nephropathy. JAMA 295:2765–2779
Parfrey PS, Griffiths SM, Barrett BJ et al (1989) Contrast material-induced renal failure in patients with diabetes mellitus, renal insufficiency, or both: a prospective controlled study. N Engl J Med 320:143–149
Poletti PA, Saudan P, Platon A et al (2007) I.V. N-acetylcysteine and emergency CT: use of serum creatinine and Cystatin C as markers of radiocontrast nephrotoxicity. Am J Roentgenol 189:687–692
Pugh ND, Sissons GR, Ruttley et al (1993) Iodixanol in femoral arteriography (phase III): a comparative double double-blind parallel trial between iodixanol and iopromide. Clin Radiol 47:96–99
Recio-Mayoral A, Chaparro M, Pardo B et al (2007) The renoprotective effect of hydration with sodium bicarbonate plus N-acetylcystesine in patients undergoing emergency percutaneous coronary intervention: the RENO study. J Am Coll Cardiol 49:1283–1238
Rudnik MR, Goldfarb S, Wexler L et al (1995) Nephrotoxicity of ionic and nonionic contrast media in 1196 patients: a randomized trial. Kidney Int 47:254–261
Sadeghi HM, Stone GW, Grines CL et al (2003) Impact of renal insufficiency in patients undergoing primary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 108:2769–2775
Safirstein R, Andrade L, Viera JM (2000) Acetylcysteine and nephrotoxic effects of radiographic contrast agents — a new use for an old drug. N Engl J Med 342:210–211
Sharma SK, Kini A (2005) Effect of nonionic radiocontrast agents on the occurrence of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with mild-moderate chronic renal insufficiency: pooled analysis of the randomized trials. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 65:386–393
Solomon R (1998) Contrast medium-induced acute renal failure. Kidney Int 53:230–242
Solomon R (2005) The role of osmolality in the incidence of contrast-induced nephropathy: A systematic review of angiographic contrast media in high risk patients. Kidney Int 68:2256–2263
Solomon R, DuMouchel W (2006) Contrast media and nephropathy. Findings from systematic analysis and Food and Drug Administration reports of adverse effects. Invest Radiol 41:651–660
Solomon R, Werner C, Mann D, D’Elia J, Silva P (1994) Effects of saline, mannitol and furosemide on acute decreases in renal function induced by radiocontrast agents. N Engl J Med 331:1416–1420
Solomon R, Natarajan M, Doucet S et al (2007) The cardiacangiography in renally impaired patients (CARE) study: A randomized, double blind trial of contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) in high risk patients. Circulation 115:3189–3196
Spargias K, Alexopoulos E, Kyrzopoulos S et al (2004) Ascorbic acid prevents contrast mediated nephropathy in patients with renal dysfunction undergoing coronary angiography or intervention Circulation 110:2837–2842
Stevens MA, McCullough PA, Tobin KJ et al (1999) A prospective randomized trial of prevention measures in patients at high risk for contrast nephropathy. Results of the P.R.I.N.C.E study. J Am Coll Cardiol 33:403–411
Stevens LA, Coresh J, Greene T, Levey AS (2006) Assessing kidney function — measured and estimated glomerular filtration rate. N Engl J Med 354:2473–2483
Stone GW, McCullough PA, Tumlin JA et al (2003) CONTRAST investigators. Fenoldopam mesylate for the prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 290:2284–2291
Taylor AJ, Hotchkiss D, Morse RW, McCabe J (1998) PREPARED. Preparation for angiography in renal dysfunction: a randomized trial of inpatient vs outpatient hydration protocols for cardiac catheterization in mild-to-moderate renal dysfunction. Chest 114:1570–1574
Tepel M, Giet MVD, Schwarzfeld C et al (2000) Prevention of radiographic-contrast-agent-induced reductions in renal function by acetylcysteine. N Engl J Med 343:180–184
Thomsen HS (1999) Contrast nephropathy. In: Thomsen HS, Muller RN, Mattrey RF (eds) Trends in contrast media. Springer, Berlin, pp 103–116
Thomsen HS, Golman K, Hemmingsen L, Larsen S, Skaarup P, Svendsen O (1993) Contrast medium induced nephropathy: animal experiments. Front Eur Radiol 9:83–108
Thomsen HS, Morcos SK, Members of Contrast Media Safety Committee of European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) (2005) In which patients should serum-creatinine be measured before contrast medium administration? Eur Radiol 15:749–756
Thomsen HS, Morcos SK (2006) Contrast-medium-induced nephropathy: is there a new consensus? A review of published guidelines. Eur Radiol 16:1835–1840
Thomsen HS, Morcos SK (2008) Risk of contrast medium induced nephropathy in high risk patients undergoing MDCT — A pooled analysis of two randomized trials. Eur Radiol Epub DOI 10.1007/s00300-008-1206-4
Thomsen HS, Morcos SK, Barrett BJ (2008a) Contrast induced nephropathy: The wheel has turned 360 degrees. Acta Radiol 49:646–657
Thomsen HS; Morcos SK, Erley CM et al (2008b) The ACTIVE trial: Comparison of the effects on renal function of iomeprol-4000 and iodixanol-320 in patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing abdominal computed tomography. Invest Radiol 43:170–178
Tippins RB, Torres WE, Baumgartner BR, Baumgarten DA (2000) Are screening serum creatinine levels necessary prior to outpatient CT examinations? Radiology 216:481–484
Toprak O (2006) Angiotension converting emzymes inhibitors and contrast-induced nephropathy. Renal Fail 28:99–100
Toprak O, Cirit M, Mayata S, Yesil M, Aslan LS (2003) The effect of pre-procedural captopril on contrast media induced nephropathy who underwenet coronary angiography. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg 3:98–103
Trivedi HS, Moore H, Nasr S et al (2003) A randomized prospective trial to assess the role of saline hydration on the development of contrast nephrotoxicity. Nephron Clin Pract 93:c29–c34
Vaitkus PT, Brar C (2007) N-acetylcysteine in the prevention of contrast induced nephropathy: publication bias perpetuated by meta-analysis. Am Heart J 153:175–280
Wang A, Holcslaw T, Bashore TM et al (2000) Exacerbation of radiocontrast nephrotoxicity by endothelin receptor antagonism. Kidney Int 57:1675–1680
Weinstein JM, Heyman S, Brezis M (1992) Potential deleterious effect of furosemide in radiocontrast nephropathy Nephron 62:413–415
Weisberg L, Kurnik PB, Kurnik RC (1994) Risk of radiocontrast nephropathy in patients with and without diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int 45:259–265
Wessely R, Koppara T, Kastrati A, Bradoric C, Schultz S, Vorpahl M, Mehilli et al (2008) Iso-osmolar vs low-osmolar contrast medium in patients with impaired renal function undergoing PCI — CONTRAST. Society for cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions Meeting (SCAI), Chicago, 1 April 2008
Yamazaki H, Matsushita M, Inoue T et al (1997a) Renal cortical retention on delayed CT after angiography and contrast associated nephropathy. Br J Radiol 70:897–902
Yamazaki H, Oi H, Matsushita M et al (1997b) Lack of correlation between gallbladder opacification in delayed CT and contrast-associated nephropathy. Eur Radiol 7:1328–1331
Zagler A, Azadpour M, Mercado C, Hennekens CH (2005) N-acetylcysteine and contrast-induced nephropathy: a meta-analysis of 13 randomized trial. Am Heart J 151:140–145
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Thomsen, H.S. (2009). Contrast Medium-Induced Nephropathy. In: Thomsen, H.S., Webb, J.A.W. (eds) Contrast Media. Medical Radiology. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72784-2_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72784-2_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-72783-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-72784-2
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)