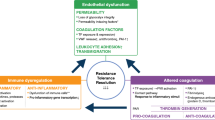
Abstract
In critically ill patients, the activation of blood coagulation occurs in parallel with the release of inflammatory mediators, which characterizes systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis and sepsis-related conditions such as severe sepsis and septic shock. As a consequence, the overall hemostatic balance is shifted toward the activation of the coagulation, due to either the activation of the clotting system or the downregulation of the anticoagulant pathways. Systemic inflammation during sepsis leads to the generation of proinflammatory cytokines that, among other things, orchestrate coagulation and fibrinolytic activation. Abundant intravascular fibrin formation leads to microvascular thrombosis, which causes widespread ischemic organ damage up to organ necrosis and clinically impresses as widespread skin necrosis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. On the basis of the pathophysiologic concepts and the striking anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory properties of coagulation inhibitors in models for severe sepsis, administration of these inhibitors has been considered an attractive therapeutic approach for human sepsis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dempfle CE (2004) Coagulopathy of sepsis. Thromb Haemost 91(2):213–224
Bone RC, Sibbald WJ, Sprung CL (1992) The ACCP-SCCM consensus conference on sepsis and organ failure. Chest 101(6):1481–1483
Esmon CT (2005) The interactions between inflammation and coagulation. Br J Haematol 131(4):417–430
McEver RP (2001) Adhesive interactions of leukocytes, platelets, and the vessel wall during hemostasis and inflammation. Thromb Haemost 86(3):746–756
Hack CE, Aarden LA, Thijs LG (1997) Role of cytokines in sepsis. Adv Immunol 66:101–195
Gando S, Kameue T, Matsuda N, Hayakawa M, Hoshino H, Kato H (2005) Serial changes in neutrophil-endothelial activation markers during the course of sepsis associated with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Res 116(2):91–100
Zeerleder S, Hack CE, Wuillemin WA (2005) Disseminated intravascular coagulation in sepsis. Chest 128(4):2864–2875
Levi M, Schultz M (2010) Coagulopathy and platelet disorders in critically ill patients. Minerva Anestesiol 76(10):851–859
Aird WC (2003) The hematologic system as a marker of organ dysfunction in sepsis. Mayo Clin Proc 78(7):869–881
Aird WC (2003) The role of the endothelium in severe sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Blood 101(10):3765–3777
Rocha E, Páramo JA, Montes R, Panizo C (1998) Acute generalized, widespread bleeding, diagnosis and management. Haematologica 83(11):1024–1037
Esmon CT, Fukudome K, Mather T, Bode W, Regan LM, Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, Kurosawa S (1999) Inflammation, sepsis, and coagulation. Haematologica 84(3):254–259
Gando S, Kameue T, Nanzaki S (1996) Disseminated intravascular coagulation is a frequent complication of systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Thromb Haemost 75:224–228
Dellinger RP, Carlet JM, Masur H (2004) Surviving sepsi campaign guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med 32:858–873
Hack CE (2001) Fibrinolysis in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Semin Thromb Haemost 27:633–638
Gando S, Nanzaki S, Kemmotsu O (1999) Disseminated intravascular coagulation and sustained systemic inflammatory response syndrome predict organ dysfunctions after trauma: application of clinical decision analysis. Ann Surg 229:121–127
Taylor FB Jr, Toh CH, Hoots WK (2001) Towards definition, clinical and laboratory criteria, and a scoring system for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost 86:1327–1330
Ten Cate H, Timmerman JJ, Levi M (1999) The pathophysiology of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost 82:713–717
Welty-Wolf KE, Carraway MS, Miller DL, Ortel TL, Ezban M, Ghio AJ, Idell S, Piantadosi CA (2001) Coagulation blockade prevents sepsis-induced respiratory and renal failure in baboons. Crit Care Med 164(10 Pt 1):1988–1996
Bick RL (1996) Disseminated intravascular coagulation: objective clinical and laboratory diagnosis, treatment, and assessment of therapeutic response. Semin Thromb Haemostas 22:69–88
Eisele B, Lamy M, Thijs LG (1998) Antithrombin III in patients with severe sepsis: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind multicenter trial plus meta-analysis on all randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trials with antithrombin III in severe sepsis. Intensive Care Med 24:663–672
Siegal T, Seligsohn V, Aghal E, Modan M (1978) Clinical and laboratory aspects of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC): a study of 118 cases. Thromb Haemostas 39:122–134
Hartl WH (1998) Effect of antithrombin III supplementation on inflammatory response in patients with severe sepsis. Shock 10:90–96
Baudo F, Caimi TM, de Cataldo F (1998) Antithrombin III (ATIII) replacement therapy in patients with sepsis and/or postsurgical complications: a controlled double-blind, randomized, multicenter study. Intensive Care Med 24:336–342
Bernard GR, Ely EW, Wright TJ, Fraiz J, Stasek JE Jr, Russell JA, Mayers I, Rosenfeld BA, Morris PE, Yan SB, Helterbrand JD (2001) Safety and dose relationship of recombinant human activated protein C for coagulopathy in severe sepsis. Crit Care Med 29(11):2051–2059
Ely EW, Angus DC, Williams MD, Bates B, Qualy R, Bernard GR (2003) Drotrecogin alfa (activated) treatment of older patients with severe sepsis. Crit Care Med 37(2):187–195
Laterre PF, Levy H, Clermont G, Ball DE, Garg R, Nelson DR, Dhainaut JF, Angus DC (2004) Hospital mortality and resource use in subgroups of the recombinant human activated protein C worldwide evaluation in severe sepsis (PROWESS) trial. Crit Care Med 32(11):2207–2218
Wheeler A, Steingrub J, Schmidt GA, Sanchez P, Jacobi J, Linde-Zwirble W, Bates B, Qualy RL, Woodward B, Zeckel M (2008) A retrospective observational study of drotrecogin alfa (activated) in adults with severe sepsis: comparison with a controlled clinical trial. Crit Care Med 36(1):14–23
Bernard GR, Vincent JL, Laterre PF (2001) Efficacy and safety of recombinant human activated protein C for severe sepsis. N Engl J Med 344:699–709
Angus DA (2012) Drotrecogin alpha activated…a sad final fizzle to a roller-coaster party. Crit care 2012 16:107–109
Abraham E, Laterre PF, Garg R et al (2005) Drotrecogin alpha (activated) for adults with severe sepsis and low risk of death. New Engl J Med 353:1332–1341
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer-Verlag Italia
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Vessella, W., Prisco, L., Berlot, G. (2012). Inflammation and Coagulation. In: Berlot, G. (eds) Hemocoagulative Problems in the Critically Ill Patient. Springer, Milano. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-88-470-2448-9_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-88-470-2448-9_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Milano
Print ISBN: 978-88-470-2447-2
Online ISBN: 978-88-470-2448-9
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)