Abstract
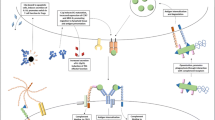
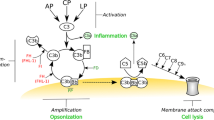
To discriminate self from non-self is an essential issue in the immune system. Autologous cells are protected against complement-mediated cell injury by the self-recognition mechanism using complement regulatory proteins composed of complement receptor type 1 (CR1, CD35), membrane cofactor protein (MCP, CD46), decay accelerating factor (DAF, CD55) and homologous restriction factor (protectin, CD59). Recently, the up-regulation of these molecules has been widely shown in inflammatory tissues and organs affected by autoimmune diseases, and in vitro assays have revealed that immune complexes or several cytokines, including interferon γ, tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin 1β and transforming growth factor β, can up-regulate these molecules. In contrast, it has been found that expression of these complement regulatory proteins is markedly decreased on autologous cells undergoing apoptosis. These findings suggest that complement regulatory proteins have dual roles at inflammatory sites: enhancement of cellular resistance to complement attack and acceleration of theclearance of cells injurious to the organism due to complement-mediated mechanisms. To assist the former function, a therapeutic approach using recombinant soluble complement regulatory proteins may provide a promising strategy for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson J. P. and Fairies T. (1987): Separation of self from non-self in the complement system. Immunol. Today, 8, 212–215.
Bardenstein D. S., Dietz Y., Lass J. H. and Medof M. E. (1994): Localization of the complement membrane attack complex inhibitor (CD59) in human conjunctiva and lacrimal gland. Curr. Eye Res., 13, 851–855.
Bjorge L., Jensen T. S., Ulvestad E., Vedeler C. A. and Matre R. (1995): The influence of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-lβ and interferon-γ on the expression and function of the complement regulatory protein CD59 on the human colonic adenocarcinoma cell line HT29. Scand. J. Immunol., 41, 350–356.
Brasoveanu L. I., Fonsatti E., Visintin A., Pavlovic M., Cattarossi I., Colizzi F., Gasparollo A., Coral S., Horejsi V., Altomonte M. and Maio M. (1997): Melanoma cells constitutively release an anchor-positive soluble form of protectin (sCD59) that retains functional activities in homologous complement-mediated cytotoxicity. J. Clin. Invest., 100, 1248–1255.
Cheung N. V., Walter E. I., Smith-Mensah W. H., Ratnoff W. D., Tykocinski M. L. and Medof M. E. (1988): Decay-accelerating factor protects human tumor cells from complement-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. J. Clin. Invest., 81, 1122–1128.
Christiansen D., Milland J., Thorley B. R., McKenzie I. F. C. and Loveland B. E. (1996): A functional analysis of recombinant soluble CD46 in vivo and a comparison with recombinant soluble forms of CD55 and CD35 in vitro. Eur. J. Immunol., 26, 578–585.
Cole J. L., Housley G. A. jr., Dykman T. R., MacDermott R. P. and Atkinson J. P. (1985): Identification of an additional class of C3-binding membrane proteins of human peripheral blood leukocytes and cell lines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 82, 859–863.
Cuida M., Legier D.W., Eidsheim M. and Jonsson R. (1997): Complement regulatory proteins in the salivary glands and saliva of Sjögren’s syndrome patients and healthy subjects. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol., 15, 615–623.
Davies A., Simmons D. L., Hale G., Harrison R. A., Tighe H., Lachmann P. J. and Waldmann H. (1989): CD59, an LY-6-like protein expressed in human lymphoid cells, regulates the action of the complement membrane attack complex on homologous cells. J. Exp. Med., 170, 637–654.
Davies M. E., Horner A., Loveland B. E. and McKenzie I. F. C. (1994): Upregulation of complement regulators MCP (CD46), DAF (CD55) and protectin (CD59) in arthritic joint disease. Scand. J. Rheumatol., 23, 316–321.
Devitt A., Moffatt O. D., Raykundalia C, Capra J. D., Simmons D. L. and Gregory C. D. (1998): Human CD14 mediates recognition and phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Nature, 392, 505–509.
Endoh M., Yamashina M., Ohi H., Funahashi K., Ikuno T., Yasugi T., Atkinson J. P. and Okada H. (1993): Immunohistochemical demonstration of membrane cofactor protein (MCP) of complement in normal and diseased kidney tissues. Clin. Exp. Immunol., 94, 182–188.
Falk R. J., Dalmasso A. P., Kim Y, Lam S. and Michael A. (1985): Radioimmunoassay of the attack complex of complement in serum from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med., 315, 1584–1589.
Garwryl M. A., Chudwin D. S., Longlois P. F. and Lint T. F. (1988): The terminal complement complex, C5b-9, a marker of disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum., 31, 188–195.
Gauthier V. J. and Emlen J. W. (1997): Immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. In Wallace D. J. and Hahn B. H.: Dubois’ lupus erythematosus. 5th ed. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore-Philadelphia-London-Paris-Bangkok-Buenos Aires-Hong Kong-Munich-Sydney-Tokyo-Wroclaw, 207–220.
Guc D., Gulati P., Lemercier C, Lappin D., Birnie G. D. and Whaley K. (1993): Expression of the components and regulatory proteins of the alternative complement pathway and the membrane attack complex in normal and diseased synovium. Rheumatol. Int., 13, 139–146.
Hara T, Kuriyama S., Kiyohara H., Nagase Y, Matsumoto M. and Seya T. (1992): Soluble forms of membrane cofactor protein (CD46, MCP) are present in plasma, tears, and seminal fluid in normal subjects. Clin. Exp. Immunol., 89, 490–494.
Hebert L. A. (1987): Clearance of immune complexes from the circulation of man and other primates. Am. J. Kidney Dis., 17, 352–361.
Janeway C. A. Jr. (1992): The immune system evolved to discriminate infectious nonself from noninfectious self. Immunol. Today, 13, 11–16.
Jarva H. and Meri S. (1999): Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria: the disease and a hypothesis for a new treatment. Scand. J. Immunol, 49, 119–125.
Jones J., Laffafian I., Cooper A. M., Williams B. D. and Morgan B. P. (1994): Expression of complement regulatory molecules and other surface markers on neutrophils from synovial fluid and blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Rheumatol., 33, 707–712.
Jones J. and Morgan B. P. (1995): Apoptosis is associated with reduced expression of complement regulatory molecules, adhesion molecules and other receptors on polymorphonuclear leucocytes: functional relevance and role in inflammation. Immunology, 86, 651–660.
Kawano M., Seya T., Koni I. and Mabuchi H. (1999): Elevated serum levels of soluble membrane cofactor protein (CD46, MCP) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Clin. Exp. Immunol., 116, 542–546.
Kawano M. Tsunoda S., Koni I., Mabuchi H., Muramoto H., Yachie A. and Seki H. (1997): Decreased expression of 20-kD homologous restriction factor (HRF20, CD59) on T lymphocytes in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-induced infectious mononucleosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol., 108, 260–265.
Kennedy S. P., Rollins S. A., Burton W. V., Sims P. J., Bothwell A. L. M., Squinto S. P. and Zavoico G. B. (1994): Protection of porcine aortic endothelial cells from complement-mediated cell lysis and activation by recombinant human CD59. Transplantation, 57, 1494–1501.
Lehto T., Honkanen E., Teppo A. M. and Meri S. (1995): Urinary excretion of protectin (CD59), complement SC5b-9 and cytokines in membranous glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int., 47, 1403–1411.
Mason J. C, Yarwood H., Sugars K., Morgan B. P., Davies K. A. and Haskard D. O. (1999): Induction of decay-accelerating factor by cytokines or the membrane-attack complex protects vascular endothelial cells against complement deposition. Blood, 94, 1673–1682.
Matsui H., Tsuji S., Nishimura H. and Nagasawa S. (1994): Activation of the alternative pathway of complement by apoptotic Jurkat cells. FEBS Lett., 351, 419–422.
Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Rutgers J. L., Knowles D. M. and Nussenzweig V. (1987): Identification of the complement decay-accelerating factor (DAF) on epithelium and glandular cells and in body fluids. J. Exp. Med., 165, 848–864.
Meri S., Mattila P. and Renkonen R. (1993): Regulation of CD59 expression on human endothelial cell line E. A. hy 926. Eur. J. Immunol., 23, 2511–2516.
Moran P., Beasley H., Gorrell A., Martin E., Gribling P., Fuchs H., Gillett N., Burton L. E. and Caras I. W. (1992): Human recombinant soluble decay accelerating factor inhibits complement activation in vitro and in vivo. J. Immunol., 149, 1736–1743.
Morgan B. P. (1989): Complement membrane attack on nucleated cells: resistance, recovery and non-lethal effect. Biochem. J., 264, 1–14.
Nangaku M., Meek R. L., Pippin J., Gordon K. L., Morgan B. P., Johnson R. J. and Couser W. G. (1996): Transfected CD59 protects mesangial cells from injury induced by antibody and complement. Kidney Int., 50, 257–266.
Nicholson-Weiler A., Burge J., Fearon D. T., Weller P. F. and Austen K. F. (1982): Isolation of a human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein with decay-accelerating activity for C3 convertase of the complement system. J. Immunol., 129, 184–189.
Nose M., Katoh M., Okada N., Kyogoku M. and Okada H. (1990): Tissue distribution of HRF 20, a novel factor preventing the membrane attack of homologous complement, and its predominant expression on endothelial cells in vivo. Immunology, 70, 145–149.
Pasch M. C, Bos J. D., Daha M. R. and Asghar S. S. (1999): Transforming growth factor-beta isoforms regulate the surface expression of membrane cofactor protein (CD46) and CD59 on human keratinocytes. Eur. J. Immunol., 29, 100–108.
Roitt I. M. (1997): Roitt’s essential immunology. 9th ed. Blackwell Science, London, 3–21.
Rooney I. A., Davies A., Griffiths D., Williams J. D., Davies M., Meri S., Lachmann P. J. and Morgan B. P. (1991): The complement-inhibiting protein, protectin (CD59 antigen), is present and functionally active on glomerular epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol., 83, 251–256.
Ronney I. A. and Morgan B. P. (1992): Characterization of the membrane attack complex inhibitory protein CD59 antigen on human amniotic cells and in amniotic fluid. Immunology, 76, 541–547.
Savill J., Fadok V., Henson P. and Haslett C. (1993): Phagocyte recognition of cells undergoing apoptosis. Immunol. Today, 14, 131–136.
Schmitt C. A., Schwaeble W, Wittig B. M., Meyer zum Buschenfelde K. H. and Dippold W. G. (1999): Expression and regulation by interferon-gamma on the membrane-bound complement regulators CD46 (MCP), CD55 (DAF) and CD59 in gastrointestinal tumours. Eur. J. Cancer, 35, 117–124.
Schur P. H. (1997): Complement and systemic lupus erythematosus. In Wallace D. J. and Hahn B. H.: Dubois’ lupus erythematosus. 5th ed. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore-Philadelphia-London-Paris-Bangkok-Buenos Aires-Hong Kong-Munich-Sydney-Tokyo-Wroclaw, 245–261.
Seya T., Hara T., Iwata K., Kuriyama S., Hasegawa T., Nagase Y, Miyagawa S., Matsumoto M., Hatanaka M. and Atkinson J. P. (1995): Purification and functional properties of soluble forms of membrane cofactor protein (MCP, CD46) of complement: Identification of forms increased in cancer patients’ sera. Int. Immunol., 7, 727–736.
Seya T., Hara T., Matsumoto M., Sugita Y. and Akedo H. (1990): Complement-mediated tumor cell damage induced by antibodies against membrane cofactor protein (MCP, CD46). J. Exp. Med., 172, 1673–1680.
Seya T., Turner J. R. and Atkinson J. P. (1986): Purification and characterization of a membrane protein (gp45-70) which is a cofactor for cleavage of C3b and C4b. J. Exp. Med., 163, 837–855.
Shibata T., Cosio F. G. and Birmingham D. J. (1991): Complement activation induces the expression of decay-acceleration factor on human mesangial cells. J. Immunol., 147, 3901–3908.
Sugita Y., Ito K., Shiozuka K., Suzuki H., Gushima H., Tornita M. and Masuho Y (1994): Recombinant soluble CD59 inhibits reactive hemolysis with complement. Immunology, 82, 34–41.
Tamai H., Matsuo S., Fukatsu A., Nishikawa K., Sakamoto N., Yoshioka K., Okada N. and Okada H. (1991): Localization of 20-kD homologous restriction factor (HRF20) in diseased human glomeruli. An immunofluorescence study. Clin. Exp. Immunol, 84, 256–262.
Tsuji S., Kaji K. and Nagasawa S. (1994): Activation of the alternative pathway of human complement by apoptotic human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Biochem., 116, 794–800.
Tsunoda S., Kawano M., Koni I., Kasahara Y, Yachie A., Miyawaki T. and Seki H. (2000): Diminished expression of CD59 on activated CD8+ T cells Undergoing apoptosis in SLE and Sjögren’s syndrome. Scand. J. Immunol., 51, 293–299.
Uehara T, Miyawaki T, Ohta K., Tamaru Y, Yokoi T, Nakamura S. and Taniguchi N. (1992): Apoptotic cell death of primed CD45RO+ T lymphocytes in Epstein-Barr virus-induced infectious mononucleosis. Blood, 80, 452–458.
Zhang H., Yu J., Bajwa E., Morrison S. L. and Tomlinson S. (1999): Targeting of functional antibody-CD59 fusion proteins to a cell surface. J. Clin. Invest., 103, 55–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kawano, M. (2001). Complement Regulatory Proteins and Autoimmunity. In: Górski, A., Krotkiewski, H., Zimecki, M. (eds) Autoimmunity. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0981-2_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0981-2_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-3877-5
Online ISBN: 978-94-010-0981-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive