Summary
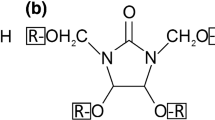
Using sulfur dioxide (SO2) as catalyst, wood specimens were treated with nonformaldehyde cross-linking reagents such as glyoxal, glutaraldehyde and dimethylol dihydroxy ethyleneurea (DMDHEU). The results of dimensional stability, acoustic properties, and mechanical strength tests were compared with those obtained from formaldehyde treatment. With glyoxal and glutaraldehyde treatments, antiswelling efficiency (ASE) reached around 70%, which is comparable to the values attained by formaldehyde treatment, although the accompanying weight gain was much larger than for the latter, whereas DMDHEU did not give sufficiently high ASE. None of the treatments, significantly increased specific dynamic Young's modulus (E/ρ) with the exception of the DMDHEU treatment, loss tangent (tan δ) decreased substantially, about 50 and 60% in longitudinal and radial directions respectively, which were somewhat exceeding the formaldehyde treatment. The results suggested that the improvement of the dimensional stability and acoustic properties is partly attributed to the formation of cross-links.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Akitsu, H.; Norimoto, M.; Morooka, T. 1991: Vibrational Properties of chemically modified wood. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 37(7): 590–597
Frick, J. G.; Harper, R. J. 1982: Crosslinking cotton cellulose with aldehydes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 27: 983–988
Meyer, U.; Müller, K.; Zollnger, H. 1976: Comparison of textile mechanical properties of cotton in crosslinking with dimethylolethyleneurea and formaldehyde. Textile Res. J. 46: 813–817
Minato, K.; Yano, H. 1990a: Improvement of dimensional stability and acoustic properties of wood for musical instruments by sulfur dioxide catalyzed formalization. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 36(5): 362–367
Minato, K.; Yasuda, R.; Yano, H. 1990b: Improvement of dimensional stability and acoustic properties of wood for musical instruments with cyclic oxymethylenes II. Formalization with tetraoxane. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 36(11): 990–996
Rossin, E. H. 1956: Surface sizing resins. A progress report. TAPPI 39(1): 156A
Stamm, A. J. 1964: Wood and cellulose science, pp. 326, pp. 331. New York: The Ronald Press
Tanaka, C.; Nakao, T.; Takahashi, A. 1987: Acoustic property of wood I. Impact sound analysis of wood. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 33(10): 811–817
Weaver, J. W.; Nielson, J. F.; Goldstein, I. S. 1960: Dimensional stabilization of wood with aldehydes & Related Compounds. Forest Products J. 10: 306–310
Yano, H.; Yamada, T.; Minato, K. 1986: Changes in acoustical properties of sitka spruce due to reaction with formaldehyde. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 32(12): 984–989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasuda, R., Minato, K. Chemical modification of wood by non-formaldehyde cross-linking reagents. Wood Sci.Technol. 28, 101–110 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192689
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192689