Abstract
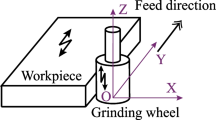
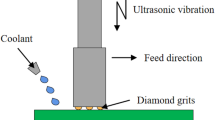
Research into the single grain cutting mechanism is important for understanding complex grinding mechanisms. Based on the characteristics of ultrasonic vibration, the motion equation of the grain is established, and the generated trajectory is theoretically analyzed. By adopting the method of combining high-speed grinding technology with ultrasonic vibration, abrasive wear forms of single cubic boron nitride (CBN) grains under common and ultrasonic conditions are studied. Further studies are conducted on the influence of the grain itself and the main grinding parameters on abrasive wear. Research shows that the main forms of abrasive wear during ultrasonic-assisted grinding are shearing wear and removing wear. However, common grinding leads to micro-crushing wear and a small amount of abrasion wear; the different forms of wear correspond to different grinding force signals. The greater the initial grain protrusion height, the greater is the abrasion of the protrusion; for the same grain protrusion height, the abrasive wear due to ultrasonic-assisted grinding is larger than that due to common grinding. As the grinding depth increases, the abrasive wear of both processing modes increases; however, in the case of ultrasonic machining, the abrasive wear increases slowly and is larger than that under common grinding. This study provides a certain decision basis for real-time monitoring of the ultrasonic-assisted high-speed grinding process. Additionally, it provides guidance and reference for the manufacture and selection of the grinding wheel and for the selection of reasonable processing parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
He YH, Zhou Q, Lang XJ (2016) Grinding force of axial ultrasonic vibration assisted grinding. Journal of Vibration and Shock 35:170–176
Liu DF, Cong WL, Pei ZJ (2012) A cutting force model for rotary ultrasonic machining of brittle materials. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 52:77–84
Bahman A, Taghi T (2011) Development of a novel ultrasonic unit for grinding of ceramic matrix composites. Int Adv Manuf Technol 57:945–955
Christian B, Ralf S, Andreas W, Christian W, Sophia H (2010) New systematic and time-saving procedure to design cup grinding wheels for the application of ultrasonic-assisted grinding. Int Adv Manuf Technol 47:153–159
Ishikawa K, Suwabe H, Nishide T, Uneda M (1998) A study on combined vibration drilling by ultrasonic and low-frequency vibrations for hard and brittle materials. Precis Eng 22:196–205
Peng Y, Wu YB, Liang ZQ, Guo YB, Lin X (2011) An experimental study of ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding of polysilicon using two-dimensional vertical workpiece vibration. Int Adv Manuf Technol 54:941–947
Wang X, Zhou M, Gan JGK, Ngoi B (2002) Theoretical and experimental studies of ultraprecision machining of brittle materials with ultrasonic vibration. Int Adv Manuf Technol 20:99–102
Gong XB (2013) The effect of ultrasonic vibration on the grinding performance of grinding wheel. Master’s thesis of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics
Ding K, Fu YC et al (2014) Wear of diamond grinding wheel in ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding of silicon carbide. Int Adv Manuf Technol 71:1929–1938
SHI Z, MALKIN S (2003) An investigation of grinding with electroplated CBN wheels. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology 52:267–270
Li F, Su HH et al (2011) Wear of electroplated CBN wheels in high speed grinding of superalloy. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering 12:29–37
Huang W et al (2016) Wear experiment of single brazed diamond abrasive. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering 4:15–18
Li BM, Zhao B (2003) Modern grinding technology. China Machine Press, Beijing
Yan L, Jiang F, Rong YM (2012) Grinding mechanism based on single grain cutting simulation. Journal of Mechanical Engineering 48:172–182
Cha TJ (2013) Grinding wheel wear and grinding force in cup-wheel spherical grinding process. Master’s thesis of Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, D., Zhou, Z., Liu, Z. et al. Abrasive wear of a single CBN grain in ultrasonic-assisted high-speed grinding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 98, 67–75 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0409-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0409-8