Abstract
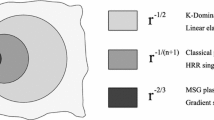
Recent experiments have shown that the microscale material behavior is very different from that of bulk materials, and displays strong size effects when the characteristic length associated with the deformation is on the order of microns. Conventional continuum theories, however, can not predict this size dependence because they do not have an intrinsic length in their constitutive models. A new continuum theory, namely the strain gradient theory, has been proposed to investigate the deformation of solids at the microscale. For materials undergoing plastic deformation, the basis of strain gradient theory is the dislocation theory in materials science, and strain gradient plasticity has agreed remarkably well with experiments. For elastic materials with microstructures, it has also been established that the material behavior can be represented by an elastic strain gradient theory. A general approach to investigate fracture of materials with strain gradient effects is established. Both the near-tip asymptotic fields and the elastic full-field solutions are obtained in closed form. Due to stain gradient effects, stresses ahead of a crack tip are significantly higher than those in the classical K field. The plastic zone size surronunding a crack tip is estimated by elastic near-tip fields, as well as by the Dugdale model. It is established that the plastic zone is, in general, much more round and larger than that estimated from the classical K field.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
N. A. Fleck, G. M. Muller, M. F. Ashby, and J. W. Hutchinson,Acta metall. mater. 42, 475 (1994).
J. S. Stolken, “The Role of Oxygen in Nickel-Sapphire Interface Fracture”,Ph.D. Dissertation, University of California, Santa Barbara (1997).
W. D. Nix,Metall. Trans. 20A, 2217 (1998).
N. A. Stelmashenko, A. G. Walls, L. M. Brown and Y. V. Milman,Acta metall. mater. 41, 2855 (1993).
Q. Ma and D. R. Clarke,J. Mater. Res. 10, 853 (1996).
W. J. Poole, M. F. Ashby and N. A Fleck,Scripta metall. mater. 34, 559 (1996).
K. W. McElhaney, J. J. Vlassak and W. D. Nix, “Determination of indenter tip geometry and indentation contact area for depth-sensing indentation eperiments,J. Mat. Res. (in press).
J. F. Nye,Acta metall. 1, 153 (1953).
A. H. Cottrell, “The mechanical properties of materials” ,J. Willey, 277 (1964).
M. F. Ashby,Phil. Mag. 21, 399 (1970).
N. A. Fleck and J. W. Hutchinson,J. Mech. Phys. Solids 41, 1825 (1993).
N. A. Fleck and J. W. Hutchinson, inAdvances in applied Mechanics (eds., Hutchinson, J. W. and Wu, T. Y.), v. 33, p. 295, Academic Press (1996).
M. E. Curtin,Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 19, 339 (1965).
A. Acharya and J. L. Bassani, inFracture and Plastic Instabilities-Proceedings of an AMD symposium at the ASME Summer Meeting at UCLA (1995).
A. Acharya and T. G. Shawki,J. Mech. Phys. Solids 43, 1751 (1995).
W. D. Nix and H. Gao, “Indentation size efects in crystalline materials: A law for strain gradient plasticity”,J. Mech. Phys. Solids (in press).
J. W. Hutchinson, inAdvances in Fracture Research (eds, B. L. Karihaloo, Y.-W. Mai, M. I. Ripley and R. O. Ritchite), p. 1, Pregamon Press, New York (1997).
Y. Huang, L. Zhang, T. F. Guo and K. C. Hwang, inIUTAM Symposium on Nonlinear Analysis of Fracture (ed., Willis, J. R.), p. 231, Kluwer Academic Publisher (1995).
Z. C. Xia and J. W. Hutchinson,J. Mech. Phys. Solids 44, 1621 (1996).
Y. Huang, L. Zhang, T. F. Guo and K. C. Hwang,J. Mech. Phys. Solids 45, 439 (1997).
Y. Wei and J. W. Hutchinson,J. Mech. Phys. Solids 45, 1253 (1997).
Y. Huang, L. Zhang, T. F. Guo and K. C. Hwang, inAdvances in Fracture Research (eds., B. L. Karihaloo, Y.-W. Mai, M. I. Ripley and R. O. Ritchie), P. 2275, Pregamon Press, New York (1997).
J. Y. Chen, Y. Hang and M. Ortiz, “Fracture analysis of cellular materials: A strain gradient model”,I. Mech. Phys. Solids (in press).
N. A. fleck and J. Shu,J. Mech. Phys. Solids 43, 1887 (1995).
R. A. Toupin,Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 11, 385 (1962).
W. T. Koiter,Proc. Ned. Akad. Wet. (B) 67, 17 (1964).
R. D. Mindlin,Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 16, 51 (1964).
R. D. Mindlin,Int. J. Solids Struct. 1, 417 (1965).
C. Atkinson and F. G. Leppington,Int. J. Solids Struct. 13, 1103 (1977).
Y. Huang, J. Y. Chen, T. F. Guo, L. Zhang and K. C. Hwang, “Analytical and numerical studies on mode I and mode II fracture in elastic-plastic materials with strain gradient effects”,Int. J. Fracture (in press).
D. S. Dugdale,J. Mech. Phys. Solids 8, 100 (1960).
G. I. Barenblatt, inAdvances in Applied Mechanics, p. 7, Academic Press, (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, K.C., Cuo, T.F., Huang, Y. et al. Fracture in strain gradient elasticity. Metals and Materials 4, 593–600 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03026364
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03026364