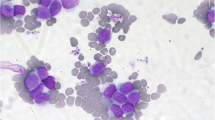
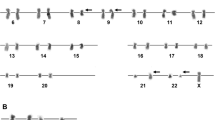
Abstract
BCR-ABL-positive acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a rare subtype of AML that is now included as a provisional entity in the 2016 revised WHO classification of myeloid malignancies. Since a clear distinction between de novo BCR-ABL+ AML and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) blast crisis is challenging in many cases, the existence of de novo BCR-ABL+ AML has been a matter of debate for a long time. However, there is increasing evidence suggesting that BCR-ABL+ AML is in fact a distinct subgroup of AML. In this study, we analyzed all published cases since 1975 as well as cases from our institution in order to present common clinical and molecular features of this rare disease. Our analysis shows that BCR-ABL predominantly occurs in AML-NOS, CBF leukemia, and AML with myelodysplasia-related changes. The most common BCR-ABL transcripts (p190 and p210) are nearly equally distributed. Based on the analysis of published data, we provide a clinical algorithm for the initial differential diagnosis of BCR-ABL+ AML. The prognosis of BCR-ABL+ AML seems to depend on the cytogenetic and/or molecular background rather than on BCR-ABL itself. A therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as imatinib, dasatinib, or nilotinib is reasonable, but—due to a lack of systematic clinical data—their use cannot be routinely recommended in first-line therapy. Beyond first-line treatment of AML, the use of TKI remains an individual decision, both in combination with intensive chemotherapy and/or as a bridge to allogeneic stem cell transplantation. In each single case, potential benefits have to be weighed against potential risks.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Konoplev S, Yin CC, Kornblau SM, Kantarjian HM, Konopleva M, Andreeff M, Lu G, Zuo Z, Luthra R, Medeiros LJ, Bueso-Ramos CE (2013) Molecular characterization of de novo Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. doi:10.3109/10428194.2012.701739
Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, Walker H, Chatters S, Goldstone AH, Wheatley K, Harrison CJ, Burnett AK, National Cancer Research Institute Adult Leukaemia Working Group (2010) Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid leukemia: determination of prognostic significance of rare recurring chromosomal abnormalities among 5876 younger adult patients treated in the United Kingdom Medical Research Council trials. Blood. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-11-254441
Keung YK, Beaty M, Powell BL, Molnar I, Buss D, Pettenati M (2004) Philadelphia chromosome positive myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia-retrospective study and review of literature. Leuk Res 28(6):579–586
Soupir CP, Vergilio JA, Dal Cin P, Muzikansky A, Kantarjian H, Jones D, Hasserjian RP (2007) Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute myeloid leukemia: a rare aggressive leukemia with clinicopathologic features distinct from chronic myeloid leukemia in myeloid blast crisis. Am J Clin Pathol 127(4):642–650
Berger R (1993) Differences between blastic chronic myeloid leukemia and Ph-positive acute leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 11(Suppl 1):235–237
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, Bloomfield CD, Cazzola M, Vardiman JW (2016) The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood.
Grove CS, Vassiliou GS (2014) Acute myeloid leukaemia: a paradigm for the clonal evolution of cancer? Dis Model Mech. doi:10.1242/dmm.015974
Lawrence MS, Stojanov P, Polak P, Kryukov GV, Cibulskis K, Sivachenko A, Carter SL, Stewart C, Mermel CH, Roberts SA, Kiezun A, Hammerman PS, McKenna A, Drier Y, Zou L, Ramos AH, Pugh TJ, Stransky N, Helman E, Kim J, Sougnez C, Ambrogio L, Nickerson E, Shefler E, Cortés ML, Auclair D, Saksena G, Voet D, Noble M, DiCara D, Lin P, Lichtenstein L, Heiman DI, Fennell T, Imielinski M, Hernandez B, Hodis E, Baca S, Dulak AM, Lohr J, Landau DA, Wu CJ, Melendez-Zajgla J, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Koren A, McCarroll SA, Mora J, Lee RS, Crompton B, Onofrio R, Parkin M, Winckler W, Ardlie K, Gabriel SB, Roberts CW, Biegel JA, Stegmaier K, Bass AJ, Garraway LA, Meyerson M, Golub TR, Gordenin DA, Sunyaev S, Lander ES, Getz G (2013) Mutational heterogeneity in cancer and the search for new cancer-associated genes. Nature. doi:10.1038/nature12213
Döhner H, Weisdorf DJ, Bloomfield CD (2015) Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1406184
Gilliland DG (2002) Molecular genetics of human leukemias: new insights into therapy. Semin Hematol 39(4 Suppl 3):6–11
Bacher U, Haferlach T, Alpermann T, Zenger M, Hochhaus A, Beelen DW, Uppenkamp M, Rummel M, Kern W, Schnittger S, Haferlach C (2011) Subclones with the t(9;22)/BCR-ABL1 rearrangement occur in AML and seem to cooperate with distinct genetic alterations. Br J Haematol. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08472.x
Jaiswal S, Fontanillas P, Flannick J, Manning A, Grauman PV, Mar BG, Lindsley RC, Mermel CH, Burtt N, Chavez A, Higgins JM, Moltchanov V, Kuo FC, Kluk MJ, Henderson B, Kinnunen L, Koistinen HA, Ladenvall C, Getz G, Correa A, Banahan BF, Gabriel S, Kathiresan S, Stringham HM, McCarthy MI, Boehnke M, Tuomilehto J, Haiman C, Groop L, Atzmon G, Wilson JG, Neuberg D, Altshuler D, Ebert BL (2014) Age-related clonal hematopoiesis associated with adverse outcomes. N Engl J Med. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1408617
Genovese G, Kähler AK, Handsaker RE, Lindberg J, Rose SA, Bakhoum SF, Chambert K, Mick E, Neale BM, Fromer M, Purcell SM, Svantesson O, Landén M, Höglund M, Lehmann S, Gabriel SB, Moran JL, Lander ES, Sullivan PF, Sklar P, Grönberg H, Hultman CM, McCarroll SA (2014) Clonal hematopoiesis and blood-cancer risk inferred from blood DNA sequence. N Engl J Med. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1409405
Biernaux C, Loos M, Sels A, Huez G, Stryckmans P (1995) Detection of major bcr-abl gene expression at a very low level in blood cells of some healthy individuals. Blood 86(8):3118–3122
Ismail SI, Naffa RG, Yousef AM, Ghanim MT (2014) Incidence of bcr-abl fusion transcripts in healthy individuals. Mol Med Rep. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.1951
Song J, Mercer D, Hu X, Liu H, Li MM (2011) Common leukemia- and lymphoma-associated genetic aberrations in healthy individuals. J Mol Diagn. doi:10.1016/j.jmoldx.2010.10.009
Bose S, Deininger M, Gora-Tybor J, Goldman JM, Melo JV (1998) The presence of typical and atypical BCR-ABL fusion genes in leukocytes of normal individuals: biologic significance and implications for the assessment of minimal residual disease. Blood 92(9):3362–3367
Wu Y, Slovak ML, Snyder DS, Arber DA (2006) Coexistence of inversion 16 and the Philadelphia chromosome in acute and chronic myeloid leukemias: report of six cases and review of literature. Am J Clin Pathol 125(2):260–266
Ninomiya S, Kanemura N, Tsurumi H, Kasahara S, Hara T, Yamada T, Moriwaki H (2011) Coexistence of inversion 16 and the Philadelphia chromosome comprising P190 BCR-ABL in chronic myeloid leukemia blast crisis. Int J Hematol. doi:10.1007/s12185-011-0854-3
Secker-Walker LM, Morgan GJ, Min T, Swansbury GJ, Craig J, Yamada T, Desalvo L, Medina JW, Chowdhury V, Donahue RP (1992) Inversion of chromosome 16 with the Philadelphia chromosome in acute myelomonocytic leukemia with eosinophilia. Report of two cases. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 58(1):29–34
Miura I, Takatsu H, Yamaguchi A, Hashimoto K, Nimura T, Nishinari T, Niitsu H, Miura AB (1994) Standard Ph chromosome, t(9;22)(q34;q11), as an additional change in a patient with acute myelomonocytic leukemia (M4Eo) associated with inv(16)(p13q22). Am J Hematol 45(1):94–96
Siddiqui AD, Sheikh ZS, Liu D, Seiter K (2002) Coexistence of inversion 16 and the Philadelphia chromosome in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 43(5):1137–1140
Tirado CA, Valdez F, Klesse L, Karandikar NJ, Uddin N, Arbini A, Fustino N, Collins R, Patel S, Smart RL, Garcia R, Doolittle J, Chen W (2010) Acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16) with CBFB-MYH11, 3'CBFB deletion, variant t(9;22) with BCR-ABL1, and del(7)(q22q32) in a pediatric patient: case report and literature review. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. doi:10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2010.03.001
Roth CG, Contis L, Gupta S, Agha M, Safyan E (2011) De novo acute myeloid leukemia with Philadelphia chromosome (BCR-ABL) and inversion 16 (CBFB-MYH11): report of two cases and review of the literature. Leuk Lymphoma. doi:10.3109/10428194.2010.538941
Dai HP, Xue YQ, Wu LL, Pan JL, Gong YL, Wu YF, Zhang J, Wu DP, Chen SN (2012) p210 BCR-ABL1 as a secondary change in a patient with acute myelomonocytic leukemia (M4Eo) with inv(16). Int J Hematol. doi:10.1007/s12185-012-1190-y
Svaldi M, Lanthaler A, Venturi R, Coser P, Mitterer M (2001) Simultaneous occurrence of bcr-abl and inv16 in a case of M1 acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 15(4):695
Mecucci C, Noens L, Aventin A, Testoni N, Van den Berghe H (1988) Philadelphia-positive acute myelomonocytic leukemia with inversion of chromosome 16 and eosinobasophils. Am J Hematol 27(1):69–71
Cividin M, Brizard F, Sorel N, Renaud M, Guilhot F, Brizard A (2004) p190(BCR-ABL) rearrangement as a secondary change in a case of acute myelo-monocytic leukemia with inv(16)(p13q22). Leuk Res 28(1):97–99
Preudhomme C, Lai JL, Plantier I, Demory JL, Zandecki M, Fenaux P (1992) Cytogenetic and molecular remission in a case of acute myeloid leukaemia(AML) with inversion of chromosome 16 (inv(16)) and Philadelphia chromosome (Ph). Br J Haematol 82(3):623–626
Cho BS, Kim HJ, Lee S, Eom KS, Min WS, Lee JW, Kim CC (2007) Successful interim therapy with imatinib prior to allogeneic stem cell transplantation in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute myeloid leukemia. Eur J Haematol 79(2):170–173
Dallorso S, Sessarego M, Garré ML, Haupt R, Pasino M, Sansone R (1990) Secondary acute promyelocytic leukemia with t(8;21) and t(9;22) at onset and loss of the Philadelphia chromosome at relapse. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 47(1):41–46
Verhaak RG, Goudswaard CS, van Putten W, Bijl MA, Sanders MA, Hugens W, Uitterlinden AG, Erpelinck CA, Delwel R, Löwenberg B, Valk PJ (2005) Mutations in nucleophosmin (NPM1) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): association with other gene abnormalities and previously established gene expression signatures and their favorable prognostic significance. Blood 106(12):3747–3754
Suzuki T, Kiyoi H, Ozeki K, Tomita A, Yamaji S, Suzuki R, Kodera Y, Miyawaki S, Asou N, Kuriyama K, Yagasaki F, Shimazaki C, Akiyama H, Nishimura M, Motoji T, Shinagawa K, Takeshita A, Ueda R, Kinoshita T, Emi N, Naoe T (2005) Clinical characteristics and prognostic implications of NPM1 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 106(8):2854–2861
Reboursiere E, Chantepie S, Gac AC, Reman O (2015) Rare but authentic Philadelphia-positive acute myeloblastic leukemia: two case reports and a literature review of characteristics, treatment and outcome. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. doi:10.1016/j.hemonc.2014.09.002
Mozziconacci MJ, Sainty D, Gabert J, Arnoulet C, Simonetti J, Toiron Y, Costello R, Hagemeijer A, Lafage-Pochitaloff M (1998) The Philadelphia chromosome as a secondary abnormality in two cases of acute myeloid leukemia. Br J Haematol 102(3):873–875
Ding L, Ley TJ, Larson DE, Miller CA, Koboldt DC, Welch JS, Ritchey JK, Young MA, Lamprecht T, McLellan MD, McMichael JF, Wallis JW, Lu C, Shen D, Harris CC, Dooling DJ, Fulton RS, Fulton LL, Chen K, Schmidt H, Kalicki-Veizer J, Magrini VJ, Cook L, McGrath SD, Vickery TL, Wendl MC, Heath S, Watson MA, Link DC, Tomasson MH, Shannon WD, Payton JE, Kulkarni S, Westervelt P, Walter MJ, Graubert TA, Mardis ER, Wilson RK, DiPersio JF (2012) Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Nature. doi:10.1038/nature10738
Nacheva EP, Grace CD, Brazma D, Gancheva K, Howard-Reeves J, Rai L, Gale RE, Linch DC, Hills RK, Russell N, Burnett AK, Kottaridis PD (2013) Does BCR-ABL1 positive acute myeloid leukaemia exist? Br J Haematol. doi:10.1111/bjh.12301
Nacheva EP, Brazma D, Virgili A, Howard-Reeves J, Chanalaris A, Gancheva K, Apostolova M, Valgañon M, Mazzullo H, Grace C (2010) Deletions of immunoglobulin heavy chain and T cell receptor gene regions are uniquely associated with lymphoid blast transformation of chronic myeloid leukemia. BMC Genomics. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-11-41
Merzianu M, Medeiros LJ, Cortes J, Yin C, Lin P, Jones D, Glassman A, Kantarjian H, Huh Y (2005) inv(16)(p13q22) in chronic myelogenous leukemia in blast phase: a clinicopathologic, cytogenetic, and molecular study of five cases. Am J Clin Pathol 124(5):807–814
Tsuboi K, Komatsu H, Miwa H, Iida S, Banno S, Wakita A, Nitta M, Ueda R (2002) Lymphoid blastic crisis of chronic myelogenous leukaemia with inv(16)(p13;q22). Leuk Res 26(8):771–774
Evers JP, Bagg A, Himoe E, Zwiebel JA, Jacobson RJ (1992) Temporal association of marrow eosinophilia with inversion of chromosome 16 in recurrent blast crises of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 62(2):134–139
Asou N, Sanada I, Tanaka K, Hidaka M, Suzushima H, Matsuzaki H, Kawano F, Takatsuki K (1992) Inversion of chromosome 16 and bone marrow eosinophilia in a myelomonocytic transformation of chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 61(2):197–200
Heim S, Christensen BE, Fioretos T, Sørensen AG, Pedersen NT (1992) Acute myelomonocytic leukemia with inv(16)(p13q22) complicating Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 59(1):35–38
Patel BB, Mohamed AN, Schiffer CA (2006) "Acute myelogenous leukemia like" translocations in CML blast crisis: two new cases of inv(16)/t(16;16) and a review of the literature. Leuk Res 30(2):225–232
Myint H, Ross FM, Hall JL, Hamblin TJ (1997) Early transformation to acute myeloblastic leukaemia with the acquisition of inv(16) in Ph positive chronic granulocytic leukaemia. Leuk Res 21(5):473–474
Mohamed AN, Pemberton P, Zonder J, Schiffer CA (2003) The effect of imatinib mesylate on patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia with secondary chromosomal aberrations. Clin Cancer Res 9(4):1333–1337
Silva PM, Lourenço GJ, Bognone RA, Delamain MT, Pinto-Junior W, Lima CS (2006) Inherited pericentric inversion of chromosome 16 in chronic phase of chronic myeloid leukaemia. Leuk Res 30(1):115–117
Colović M, Janković G, Bila J, Djordjević V, Wiernik PH (1998) Inversion of chromosome 16 in accelerated phase of chronic myeloid leukaemia: report of a case and review of the literature. Med Oncol 15(3):199–201
Palmisano M, Grafone T, Ottaviani E, Testoni N, Baccarani M, Martinelli G (2007) NPM1 mutations are more stable than FLT3 mutations during the course of disease in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 92(9):1268–1269
Kondo T, Tasaka T, Sano F, Matsuda K, Kubo Y, Matsuhashi Y, Nakanishi H, Sadahira Y, Wada H, Sugihara T, Tohyama K (2009) Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute myeloid leukemia (Ph + AML) treated with imatinib mesylate (IM): a report with IM plasma concentration and bcr-abl transcripts. Leuk Res. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2009.03.017
Paietta E, Racevskis J, Bennett JM, Neuberg D, Cassileth PA, Rowe JM, Wiernik PH (1998) Biologic heterogeneity in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute leukemia with myeloid morphology: the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group experience. Leukemia 12(12):1881–1885
Sindt A, Deau B, Brahim W, Staal A, Visanica S, Villarese P, Rault JP, Macintyre E, Delabesse E (2006) Acute monocytic leukemia with coexpression of minor BCR-ABL1 and PICALM-MLLT10 fusion genes along with overexpression of HOXA9. Genes Chromosom Cancer 45(6):575–582
Smadja N, Krulik M, De Gramont A, Brissaud P, Debray J (1985) Acquisition of a Philadelphia chromosome concomitant with transformation of a refractory anemia into an acute leukemia. Cancer 55(7):1477–1481
Kohn G, Manny N, Eldor A, Cohen MM (1975) De novo appearance of the ph-1 chromosome in a previously monosomic bone marrow (45,XX,-6): conversion of a myeloproliferative disorder to acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 45(5):653–657
Katsuno M, Yamashita S, Sadamura S, Umemura T, Hirata J, Nishimura J, Nawata H (1994) Late-appearing Philadelphia chromosome in a patient with acute nonlymphocytic leukaemia derived from myelodysplastic syndrome: detection of P210- and P190-type BCR-ABL fusion gene transcripts at the leukaemic stage. Br J Haematol 87(1):51–56
Hirsch-Ginsberg C, Childs C, Chang KS, Beran M, Cork A, Reuben J, Freireich EJ, Chang LC, Bollum FJ, Trujillo J, et al. (1988) Phenotypic and molecular heterogeneity in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute leukemia. Blood 71(1):186–195
Maddox AM, Keating MJ, Trujillo J, Cork A, Youness E, Ahearn MJ, McCredie KB, Freireich EJ (1983) Philadelphia chromosome-positive adult acute leukemia with monosomy of chromosome number seven: a subgroup with poor response to therapy. Leuk Res 7(4):509–522
Yamashita S, Umemura T, Sadamura S, Takahira H, Nishimura J, Nawata H, Katsuno M, Okamura J, Horibe K (1996) Acute leukemias expressing p210-and p 190-type BCR-ABL mRNAs: report of two cases and review of the literature. Acta Haematol 96(2):99–104
Ohyashiki K, Kocova M, Ryan DH, Rowe JM, Sandberg AA (1986) Secondary acute myeloblastic leukemia with a Ph translocation in a treated Wegener's granulomatosis. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 19(3–4):331–333
Ohyashiki K, Ohyashiki JH, Raza A, Preisler HD, Sandberg AA (1987) Phenylbutazone-induced myelodysplastic syndrome with Philadelphia translocation. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 26(2):213–216
Lesesve JF, Troussard X, Bastard C, Hurst JP, Nouet D, Callat MP, Lenormand B, Piguet H, Flandrin G, Macintyre E (1996) p190BCR-ABL rearrangement in myelodysplastic syndromes: two reports and review of the literature. Br J Haematol 95(2):372–375
Larripa I, Gutiérrez M, Giere I, Acevedo S, Bengió R, Slavutsky I (1992) Complex karyotype with PH1 chromosome in myelodysplasia: cytogenetic and molecular studies. Leuk Lymphoma 6:401–406
Papageorgiou SG, Pappa V, Economopoulou C, Tsirigotis P, Konsioti F, Ionnidou ED, Chondropoulos S, Vasilatou D, Papageorgiou E, Economopoulos T, Dervenoulas J (2010) Dasatinib induces long-term remission in imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute megakaryoblastic leukemia but fails to prevent development of central nervous system progression. Leuk Res. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2010.03.032
Fukunaga A, Sakoda H, Iwamoto Y, Inano S, Sueki Y, Yanagida S, Arima N (2013) Abrupt evolution of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute myeloid leukemia in myelodysplastic syndrome. Eur J Haematol. doi:10.1111/ejh.12056
Isoda A, Nakahashi H, Hoshino T, Mitsui T, Yoshida Y (2007) Insufficient outcomes with imatinib mesylate: case report of Ph-positive acute myeloid leukemia evolving from myelodysplastic syndrome. Am J Hematol 82(6):501–502
Kelemen K, Galani K, Conley CR, Greipp PT (2014) Secondary Philadelphia chromosome and erythrophagocytosis in a relapsed acute myeloid leukemia after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Cancer Genet. doi:10.1016/j.cancergen.2014.05.013
Nakase K, Yamamoto Y, Morita K, Yamaguchi T, Nishii K, Shiku H (2006) Haunting appearance of BCR-ABL fusion gene products in a patient with therapy related leukaemia. Leuk Res 30(1):106–108
Kurzrock R, Shtalrid M, Talpaz M, Kloetzer WS, Gutterman JU (1987) Expression of c-abl in Philadelphia-positive acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 70(5):1584–1588
Alimena G, Cedrone M, Nanni M, De Cuia MR, Lo Coco F, De Sanctis V, Cimino G, Mancini M (1995) Acute leukemia presenting a variant Ph chromosome with p190 expression, dup 3q and -7, developed after malignant lymphoma treated with alkylating agents and topoisomerase II inhibitors. Leukemia 9(9):1483–1486
Han JY, Theil KS (2006) The Philadelphia chromosome as a secondary abnormality in inv(3)(q21q26) acute myeloid leukemia at diagnosis: confirmation of p190 BCR-ABL mRNA by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 165(1):70–74
Najfeld V, Geller M, Troy K, Scalise A (1998) Acquisition of the Ph chromosome and BCR-ABL fusion product in AML-M2 and t(8;21) leukemia: cytogenetic and FISH evidence for a late event. Leukemia 12(4):517–519
Jacobsen RJ, Himoe E, Sacher RA, Shashaty GG (1986) Late appearance of Philadelphia chromosome. Br J Haematol 63(2):392–394
Aoki J, Kakihana K, Kobayashi T, Hirashima Y, Akiyama H, Ohashi K, Sakamaki H (2012) Tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for acute myeloid leukemia with late-appearing Philadelphia chromosome. Leuk Res. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2011.10.008
Yagyu S, Morimoto A, Kakazu N, Tamura S, Fujiki A, Nakase Y, Iehara T, Hosoi H, Kuroda H (2008) Late appearance of a Philadelphia chromosome in a patient with therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia and high expression of EVI1. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. doi:10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2007.09.023
Shah N, Leaker MT, Teshima I, Baruchel S, Abdelhaleem M, Ye CC (2008) Late-appearing Philadelphia chromosome in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. doi:10.1002/pbc.21317
Prebet T, Michallet AS, Charrin C, Hayette S, Magaud JP, Thiébaut A, Michallet M, Nicolini FE (2004) Secondary Philadelphia chromosome after non-myeloablative peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for a myelodysplastic syndrome in transformation. Bone Marrow Transplant 33(2):247–249
Neuendorff NR, Schwarz M, Hemmati P, Türkmen S, Bommer C, Burmeister T, Dörken B, le Coutre P, Arnold R, Westermann J (2015) BCR-ABL1(+) acute myeloid leukemia: clonal selection of a BCR-ABL1(−) subclone as a cause of refractory disease with nilotinib treatment. Acta Haematol. doi:10.1159/000368176
Weinberg OK, Seetharam M, Ren L, Alizadeh A, Arber DA (2014) Mixed phenotype acute leukemia: a study of 61 cases using World Health Organization and European Group for the Immunological Classification of Leukaemias criteria. Am J Clin Pathol. doi:10.1309/AJCPPVUPOTUVOIB5
Heesch S, Neumann M, Schwartz S, Bartram I, Schlee C, Burmeister T, Hänel M, Ganser A, Heuser M, Wendtner CM, Berdel WE, Gökbuget N, Hoelzer D, Hofmann WK, Thiel E, Baldus CD (2013) Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage in adults: molecular and clinical characterization. Ann Hematol. doi:10.1007/s00277-013-1694-4
Atfy M, Al Azizi NM, Elnaggar AM (2011) Incidence of Philadelphia-chromosome in acute myelogenous leukemia and biphenotypic acute leukemia patients: and its role in their outcome. Leuk Res. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2011.04.011
Walter RB, Othus M, Burnett AK, Löwenberg B, Kantarjian HM, Ossenkoppele GJ, Hills RK, van Montfort KG, Ravandi F, Evans A, Pierce SR, Appelbaum FR, Estey EH (2013) Significance of FAB subclassification of "acute myeloid leukemia, NOS" in the 2008 WHO classification: analysis of 5848 newly diagnosed patients. Blood. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-10-462440
Chen SJ, Flandrin G, Daniel MT, Valensi F, Baranger L, Grausz D, Bernheim A, Chen Z, Sigaux F, Berger R (1988) Philadelphia-positive acute leukemia: lineage promiscuity and inconsistently rearranged breakpoint cluster region. Leukemia 2(5):261–273
O’Donnell MR, Tallman MS et al (2016) NCCN Clinical Practise Guidelines in Oncology: AML. Version 1. Available at: NCCN.org
Röllig C, Bornhäuser M, Thiede C, Taube F, Kramer M, Mohr B, Aulitzky W, Bodenstein H, Tischler HJ, Stuhlmann R, Schuler U, Stölzel F, von Bonin M, Wandt H, Schäfer-Eckart K, Schaich M, Ehninger G (2011) Long-term prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia according to the new genetic risk classification of the European LeukemiaNet recommendations: evaluation of the proposed reporting system. J Clin Oncol. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.32.8500
Bhatt VR, Akhtari M, Bociek RG, Sanmann JN, Yuan J, Dave BJ, Sanger WG, Kessinger A, Armitage JO (2014) Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute myeloid leukemia. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 12(7):963–968
Ueda K, Horiike S, Zen K, Misawa S, Taniwaki M (2006) Complete cytogenetic and molecular response to treatment with imatinib mesylate for Philadelphia chromosome positive acute myeloid leukemia with multilineage dysplasia. Leuk Lymphoma 47(9):1967–1969
Hehlmann R (2012) How I treat CML blast crisis. Blood. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-03-380147
Baccarani M, Deininger MW, Rosti G, Hochhaus A, Soverini S, Apperley JF, Cervantes F, Clark RE, Cortes JE, Guilhot F, Hjorth-Hansen H, Hughes TP, Kantarjian HM, Kim DW, Larson RA, Lipton JH, Mahon FX, Martinelli G, Mayer J, Müller MC, Niederwieser D, Pane F, Radich JP, Rousselot P, Saglio G, Saußele S, Schiffer C, Silver R, Simonsson B, Steegmann JL, Goldman JM, Hehlmann R (2013) European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-05-501569
Wassmann B, Pfeifer H, Goekbuget N, Beelen DW, Beck J, Stelljes M, Bornhäuser M, Reichle A, Perz J, Haas R, Ganser A, Schmid M, Kanz L, Lenz G, Kaufmann M, Binckebanck A, Brück P, Reutzel R, Gschaidmeier H, Schwartz S, Hoelzer D, Ottmann OG (2006) Alternating versus concurrent schedules of imatinib and chemotherapy as front-line therapy for Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph + ALL). Blood 108(5):1469–1477
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was not supported by any grant.
Conflict of interest
J.W. receives research support and/or honoraria from Novartis, BMS, and Celgene; T.B. received research support from Novartis; N.R.N. receives a scholarship from Medac. Bernd Dörken declares that he has no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 611 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neuendorff, N.R., Burmeister, T., Dörken, B. et al. BCR-ABL-positive acute myeloid leukemia: a new entity? Analysis of clinical and molecular features. Ann Hematol 95, 1211–1221 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-016-2721-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-016-2721-z