Abstract
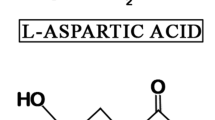
Aspartic acid racemisation (AAR) results in an age-dependent accumulation of d-aspartic acid in durable human proteins and can be used as a basis for age estimation. Routinely, age estimation based on AAR is performed by analysis of dentine. However, in forensic practise, teeth are not always available. Non-dental tissues for age estimation may be suitable for age estimation based on AAR if they contain durable proteins that can be purified and analysed. Elastin is such a durable protein. To clarify if purified elastin from arteries is a suitable sample for biochemical age estimation, AAR was determined in purified elastin from arteries from individuals of known age (n = 68 individuals, including n = 15 putrefied corpses), considering the influence of different stages of atherosclerosis and putrefaction on the AAR values. AAR was found to increase with age. The relationship between AAR and age was good enough to serve as basis for age estimation, but worse than known from dentinal proteins. Intravital and post-mortem degradation of elastin may have a moderate effect on the AAR values. Age estimation based on AAR in purified elastin from arteries may be a valuable additional tool in the identification of unidentified cadavers, especially in cases where other methods cannot be applied (e.g., no available teeth and body parts).





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Notes
In proteins, the so-called racemisation of aspartic acid involves both aspargine and aspartic acid that decompose via a succimide ring to the same four residues, namely l-aspartyl, d-aspartyl, l-isoaspartyl, and d-isoaspartyl residues, all of which are in chemical equilibrium via the succimide ring (for overview, see [24]). Asparingyl, aspartyl, isoaspartyl, and succinimidyl residues are all converted to free aspartic acid during acid hydrolysis, a preparative step in chromatographic amino acid analysis for biochemical age estimation.
References
Daamen WF, Hafmans T, Veerkamp JH, van Kuppevelt TH (2001) Comparison of five procedures for the purification of insoluble elastin. Biomaterials 22:1997–2005
Fu S-J, Fan C-C, Song H-W, Wei F-Q (1995) Age estimation using a modified HPLC determination of ratio of aspartic acid in dentin. Forensic Sci Int 73:35–40
Heems D, Luck G, Fradeau C, Vérette E (1998) Fully automated precolumn derivatization, online dialysis and high-performance liquid chromatography analysis of amino acids in food, beverages and foodstuff. J Chromatogr A 789:9–17
Holman RL, Brown BW, Gore I et al (1960) An index for the evaluation of arteriosclerotic lesions in the abdominal aorta. Circulation 27:1137–1143
Kaufman DS, Manley WF (1998) A new procedure for determining DL amino acid ratios in fossils using reverse phase liquid chromatography. Quat Geochronol 17:987–1000
Landa MI, Garamendi PM, Botella MC, Alemán I (2009) Application of the method of Kvaal et al. to digital orthopantomograms. Int J Legal Med 123:123–128
Miller EJ (1984) Chemistry of the collagens and their distribution. In: Piez KA, Reddi AH (eds) Extracellular matrix proteins. Elsevier, New York, Amsterdam, Oxford, pp 40–81
Mörnstad H, Pfeiffer H, Teivens A (1994) Estimation of dental age using HPLC technique to determine the degree of aspartic acid racemization. J Forensic Sci 39:1425–1431
Ogino T, Ogino H, Nagy B (1985) Application of aspartic acid racemization to forensic odontology: post mortem designation of age of death. Forensic Sci Int 29:259–267
Ohtani S (1995) Estimation of age from the teeth of unidentified corpses using the amino acid racemization method with reference to actual cases. Am J Forensic Med Pathol 16:238–242
Ohtani S (1995) Estimation of age from dentin by using the racemization reaction of aspartic acid. Am J Forensic Med Pathol 16:158–161
Ohtani S, Yamamoto K (1987) Age estimation using the racemisation of aspartic acid in human dentin. Nippon Hoigaku Zasshi 41:181–190
Paewinsky E, Pfeiffer H, Brinkmann B (2005) Quantification of secondary dentine formation from orthopantomograms—a contribution to forensic age estimation in adults. Int J Legal Med 119:27–30
Parks WC (1997) Posttranscriptional regulation of lung elastin production. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 17:1–2
Pfeiffer H, Mörnstad H, Teivens A (1995) Estimation of chronological age using the aspartic-acid racemization method. 1. On human rib cartilage. Int J Legal Med 108:19–23
Pfeiffer H, Mörnstad H, Teivens A (1995) Estimation of chronological age using the aspartic-acid racemization method. 2. On human cortical bone. Int J Legal Med 108:24–26
Powell JT, Vine N, Crossman M (1992) On the accumulation of d-aspartate in elastin and other proteins of the aging aorta. Atherosclerosis 97:201–208
Prockop DJ, Kivirikko KI, Tuderman L, Guzman NA (1979) Biosynthesis of collagen and its disorders. N Engl J Med 301(13–23):77–85
Ritz S, Schütz HW (1993) Aspartic acid racemization in intervertebral discs as an aid to post mortem estimation of age at death. J Forensic Sci 38:633–640
Ritz S, Schütz H-W, Schwarzer B (1990) The extent of aspartic acid racemization in dentin: a possible method for a more accurate determination of age at death? Z Rechtsmed 103:457–462
Ritz S, Schütz HW, Peper C (1993) Postmortem estimation of age at death based on aspartic acid racemization in dentin: its applicability for root dentin. Int J Legal Med 105:289–293
Ritz S, Stock R, Schütz HW, Kaatsch H-J (1995) Age estimation in biopsy specimens of dentin. Int J Legal Med 108:135–139
Ritz-Timme S (1999) Lebensaltersbestimmung aufgrund des Razemisierungsgrades von Asparaginsäure. Grundlagen, Methodik, Möglichkeiten, Grenzen, Anwendungsbereiche. In: Berg S, Brinkmann B (eds) Arbeitsmethoden der medizinischen und naturwissenschaftlichen Kriminalistik, Band 23. Lübeck, Schmidt-Römhild, pp 15–41
Ritz-Timme S, Collins MJ (2002) Racemization of aspartic acid in human proteins. Age Res Rev 1:43–59
Ritz-Timme S, Cattaneo C, Collins M, Waite ER, Schütz HW, Kaatsch H-J, Borrman HIM (2000) Age estimation: the state of the art in relation to the specific demands of forensic practise. Int J Legal Med 113:129–136
Ritz-Timme S, Rochholz G, Schütz HW, Collins MJ, Waite ER, Cattaneo C, Kaatsch HJ (2000) Quality assurance in age estimation based on aspartic acid racemization. Int J Legal Med 114:83–86
Ritz-Timme S, Laumeier I, Collins M (2003) Age estimation on aspartic acid racemization in elastin from the yellow ligaments. Int J Legal Med 117:96–101
Ritz-Timme S, Laumeier I, Collins M (2003) Aspartic acid racemization: evidence for marked longevitiy of elastin in human skin. Br J Dermatol 149:951–959
Rösing FW, Kvaal SI (1998) Dental age in adults. A review of estimation methods. In: Rösing FW, Kvaal SI, Alt KW, Rösing FW, Teschler-Nicola M (eds) Dental anthropology. Fundamentals, limits, and prospects Springer, Wien New York, pp 443–469
Rucker RB, Dubick MA (1984) Elastin metabolism and chemistry: potential roles in lung development and structure. Env Hlth Pers 55:179–191
Schmeling A, Reisinger W, Loreck D, Vendura K, Markus W, Geserick G (2000) Effects of ethnicity on skeletal maturation: consequences for forensic age estimations. Int J Legal Med 113:253–258
Schmeling A, Schulz R, Danner B, Rösing FW (2006) The impact of economic progress and modernization in medicine on the ossification of hand and wrist. Int J Legal Med 120:121–126
Schmeling A, Grundmann C, Fuhrmann A, Kaatsch H-J, Knell B, Ramsthaler F, Reisinger W, Riepert T, Ritz-Timme S, Rösing FW, Rötzscher K, Geserick G (2008) Criteria for age estimatin in living individuals. Int J Legal Med 122:457–460
Shapiro SD, Endicott SK, Province MA, Pierce JA, Campbell EJ (1991) Marked longevity of human lung parenchymal elastic fibers deduced from prevalence of d-aspartate and nuclear weapons-related radiocarbon. J Clin Invest 87:1828–1834
Zhang M, Pierce RA, Wachi H, Mecham RP, Parks WC (1999) An open reading frame element mediates posttranscriptional regulation of tropoelastin and responsiveness to transforming growth factor β1. Mol Cell Biol 19:7314–7326
Zar JH (1984) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, pp 276–277
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobberstein, R.C., Tung, SM. & Ritz-Timme, S. Aspartic acid racemisation in purified elastin from arteries as basis for age estimation. Int J Legal Med 124, 269–275 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-009-0392-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-009-0392-1