Abstract
Background
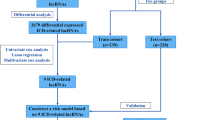
DNA-directed RNA polymerase (DDRP) related genes and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play an important role in the development of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Therefore, we aimed to construct a DDRP-associated lncRNA model to predict the prognosis of LUAD and to evaluate its sensitivity to immunotherapy and chemotherapy.
Methods
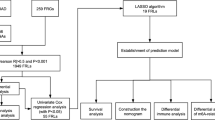
To construct a predictive signature, we used univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses, as well as the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression analysis. The prognostic model was verified by applying the ROC curve analysis, Kaplan–Meier analysis, GO/KEGG analysis, and a predictive nomogram. Eventually, immunotherapy and drug susceptibility were examined and stemness indices were analyzed.
Results
24 DDRP-associated lncRNAs were found as independent prognosis factors, which may be further developed as potential therapeutic vaccines for LUAD. The area under the ROC curve and the conformance index showed that the constructed model can predict the prognosis of LUAD patients. The predicted incidences of overall survival showed perfect conformance. And there were significant changes in immunological markers between the two risk subgroups in the model. Finally, an analysis of 50% maximum inhibitory concentration between the two risk subgroups showed that the high-risk subgroup was more sensitive to certain chemotherapy drugs.
Conclusion
We constructed a model that accurately predicts the outcomes of LUAD based on 24 DDRP-related lncRNAs and provided promising treatment options for the future.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Availability of supporting data
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bonekamp NA et al (2020) Small-molecule inhibitors of human mitochondrial DNA transcription. Nature 588:712–716. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-03048-z
Chan TA, Wolchok JD, Snyder A (2015) Genetic basis for clinical response to CTLA-4 blockade in melanoma. N Engl J Med 373:1984. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1508163
Chen T, Qin S, Gu Y, Pan H, Bian D (2019a) Long non-coding RNA NORAD promotes the occurrence and development of non-small cell lung cancer by adsorbing MiR-656–3p. Mol Genet Genom Med 7:757. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.757
Chen B et al (2019b) The POLR2E rs3787016 polymorphism is strongly associated with the risk of female breast and cervical cancer. Pathol Res Pract 215:1061–1065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2019.02.015
Deng YZ et al (2018) Cilia loss sensitizes cells to transformation by activating the mevalonate pathway. J Exp Med 215:177–195. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20170399
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, Chen L (1999) B7–H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med 5:1365–1369. https://doi.org/10.1038/70932
Fu J et al (2020) Large-scale public data reuse to model immunotherapy response and resistance. Genome Med 12:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-020-0721-z
Graczyk D, White RJ, Ryan KM (2015) Involvement of RNA polymerase III in immune responses. Mol Cell Biol 35:1848–1859. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00990-14
Hong X, Wang X, Wang T, Zhang X (2018) Correlation of T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT) and programmed death 1 (PD-1) with clinicopathological characteristics of renal cell carcinoma may indicate potential targets for treatment. Med Sci Monit 24:6861–6872. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.910388
Huang X, Zhang G, Tang T, Liang T (2021) Identification of tumor antigens and immune subtypes of pancreatic adenocarcinoma for mRNA vaccine development. Mol Cancer 20:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01310-0
Ito K et al (2019) Prognostic value of baseline metabolic tumor volume measured on (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 46:930–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-018-4211-0
Jiang P et al (2018) Signatures of T cell dysfunction and exclusion predict cancer immunotherapy response. Nat Med 24:1550–1558. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0136-1
Kang M et al (2015) Long noncoding RNAs POLR2E rs3787016 C/T and HULC rs7763881 A/C polymorphisms are associated with decreased risk of esophageal cancer. Tumour Biol 36:6401–6408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3328-z
Leapman MS et al (2020) Association of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression status with receipt of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Netw Open 3:e207205. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.7205
Li Y et al (2020) Non-coding RNA in bladder cancer. Cancer Lett 485:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.04.023
Liu Z et al (2013) The long noncoding RNA HOTAIR contributes to cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma cells via downregulation of p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression. PLoS ONE 8:e77293. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077293
Liu Y et al (2015) TP53 loss creates therapeutic vulnerability in colorectal cancer. Nature 520:697–701. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14418
Liu X, Huang G, Zhang J, Zhang L, Liang Z (2020) Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 15:e0240321. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240321
Liu SJ, Dang HX, Lim DA, Feng FY, Maher CA (2021) Long noncoding RNAs in cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 21:446–460. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-021-00353-1
Luo Q, Vogeli TA (2020) A methylation-based reclassification of bladder cancer based on immune cell genes. Cancers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12103054
Malta TM et al (2018) Machine learning identifies stemness features associated with oncogenic dedifferentiation. Cell 173:338-354 e315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.034
Nakamura T et al (2011) Predictive value of remnant lipoprotein for cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease after the achievement of LDL-cholesterol goals. Atherosclerosis 218:163–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.04.040
Powles T et al (2014) MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in metastatic bladder cancer. Nature 515:558–562. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13904
Rao J, Li W, Chen C (2021) Pyroptosis-mediated molecular subtypes and tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in colon cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:766503. https://doi.org/10.3389/cell.2021.766503
Sanchez Calle A, Kawamura Y, Yamamoto Y, Takeshita F, Ochiya T (2018) Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in cancer. Cancer Sci 109:2093–2100. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13642
Shah AA, Rosen A, Hummers L, Wigley F, Casciola-Rosen L (2010) Close temporal relationship between onset of cancer and scleroderma in patients with RNA polymerase I/III antibodies. Arthritis Rheum 62:2787–2795. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27549
Sung H et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Vannini A, Cramer P (2012) Conservation between the RNA polymerase I, II, and III transcription initiation machinery. Mol Cell 45:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.01.023
Wu ZH, Tang Y, Yu H, Li HD (2021) The role of ferroptosis in breast cancer patients: a comprehensive analysis. Cell Death Discov 7:93. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-021-00473-5
Xu J et al (2019) Precise targeting of POLR2A as a therapeutic strategy for human triple-negative breast cancer. Nat Nanotechnol 14:388–397. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0381-6
Yao J, Lu X, Wang Y, Li J, Ni B (2020) Long noncoding RNAs AC026904.1 is essential for TGF-beta-induced migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through functioning as an enhancer of Slug in lung cancer cells. Environ Toxicol 35:942–951. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22930
Ye L et al (2017) The genetic landscape of benign thyroid nodules was revealed by whole exome and transcriptome sequencing. Nat Commun 8:15533. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15533
Ye W, Wu Z, Gao P, Kang J, Xu Y, Wei C, Zhang M, Zhu X (2022) Identified gefitinib metabolism-related lncRNAs can be applied to predict prognosis, tumor microenvironment, and drug sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol 12:939021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.939021
Zhang X et al (2017) Attenuation of RNA polymerase II pausing mitigates BRCA1-associated R-loop accumulation and tumorigenesis. Nat Commun 8:15908. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15908
Zhang X et al (2022) Characterization of DNA damage response deficiency in pancreatic cancer patients from China. Cancer Commun (lond) 42:70–74. https://doi.org/10.1002/cac2.12238
Zhao X, Subramanian S (2017) Intrinsic resistance of solid tumors to immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancer Res 77:817–822. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2379
Zingg D et al (2018) EZH2-mediated primary cilium deconstruction drive metastatic melanoma formation. Cancer Cell 34:69-84 e14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.06.001
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL and XZ conceived the work. JY studied and drafted the manuscript. XZ assisted with data analysis. LL and CL discussed and edited the manuscript. XZ checked the statistical and bioinformatic accuracy as an expert in statistics and bioinformatics. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The work was approved by the Guangdong Medical University ethics committee (YS2021159). Informed consent forms are not required for patient data extracted from public databases.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Lan, L., Liu, C. et al. Improved prediction of prognosis and therapy response for lung adenocarcinoma after identification of DNA-directed RNA polymerase-associated lncRNAs. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 12737–12754 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05118-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05118-x