Summary.
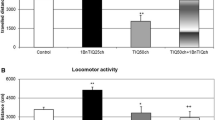
Diethyldithiocarbamate (DDC) is known to potentiate the neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). The aims of the present study were to provide biochemical, pathological and behavioral evidence for the degeneration of dopamine (DA) neurons in C57BL/6 strain mice treated simultaneously with DDC and MPTP, and to evaluate the effects of monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors on DDC-enhanced MPTP toxicity. DDC (400 mg/kg)+ MPTP (30 mg/kg) treatment decreased significantly the levels of striatal DA and its metabolites and induced bradykinesia. In mice treated with DDC+MPTP, degenerative areas were found in striatum, substantia nigra and tuberculum olfactorium by assessment of the binding of [125I]RTI-121, a DA transporter ligand. Pretreatment with a MAO-B inhibitor selegiline prior to the administration of DDC and MPTP completely inhibited the decrease in the levels of DA and its metabolites, bradykinesia and degeneration of dopaminergic nerve terminals. In contrast, the protective action of clorgyline was not clearly observed in this model system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received December 9, 2002; accepted March 12, 2003 Published online June 10, 2003
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahata, K., Shimazu, S., Yoneda, F. et al. Effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors on the diethyldithiocarbamate-induced enhancement of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine toxicity in C57BL/6 mice. J Neural Transm 110, 859–869 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0003-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0003-0