Abstract
Purpose
To illustrate whether De Ritis (aspartate transaminase-AST/alanine transaminase-ALT) ratio is useful in risk stratification of localized prostate cancer and propose an easy predictive model for biochemical recurrence-free survival (BCRFS).
Methods
In total, 438 patients who underwent radical prostatectomy were included in this study. Blood samples including AST and ALT were collected 1–7 days before surgery. An elevated AST and ALT value was defined as over 40 or 56 IU/L.
Results
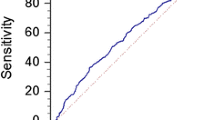
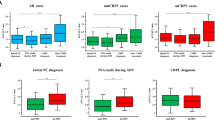
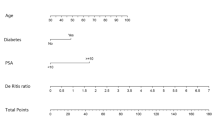
The median AST and ALT value was 18.5 (16–22) and 14 (11–18) IU/L. In total, 15 patients (3.4%) and 9 patients (2.1%) exhibited elevated AST value and ALT value. The median De Ritis ratio was 1.33 (1.11–1.60), and ROC curve indicated the best cutoff of 1.325 in predicting the occurrence of biochemical recurrence. Higher De Ritis ratio was found to be related to older age (p < 0.001), higher tumor stages (p < 0.001) and Gleason Score (p < 0.001), presence of seminal invasion (p < 0.001), positive surgical margin (p < 0.001) and lymph node metastasis (p = 0.003). Multivariate logistic regression confirmed that De Ritis ratio was an independent predictor for final Gleason Score (p < 0.001), and multivariate Cox regression demonstrated De Ritis ratio as an independent risk factor for BCRFS. A simple predictive model which incorporated De Ritis ratio, pathological tumor stage and final Gleason Score could help risk stratification for BCRFS.
Conclusion
Higher De Ritis ratio could be predictive for worse pathological outcomes and higher BCR in localized prostate cancer patients. A predictive model which incorporates De Ritis ratio, Gleason Score and pathological tumor stage could help risk stratification for BCRFS.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66(1):7–30
Heidenreich A, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, Mason M, Matveev V, Mottet N, Schmid HP, van der Kwast T, Wiegel T, Zattoni F, European Association of U (2011) EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and treatment of clinically localised disease. Eur Urol 59(1):61–71
Vagnoni V, Bianchi L, Borghesi M, Pultrone CV, Dababneh H, Chessa F, La Manna G, Rizzi S, Porreca A, Brunocilla E, Martorana G, Schiavina R (2016) Adverse features and competing risk mortality in patients with high-risk prostate cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer 15:e239–e248
Aoun F, Albisinni S, Henriet B, Tombal B, Van Velthoven R, Roumeguere T (2017) Predictive factors associated with biochemical recurrence following radical prostatectomy for pathological T2 prostate cancer with negative surgical margins. Scand J Urol 51(1):20–26
Gu X, Gao X, Li X, Qi X, Ma M, Qin S, Yu H, Sun S, Zhou D, Wang W (2016) Prognostic significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in prostate cancer: evidence from 16,266 patients. Sci Rep 6:22089
Lee H, Jeong SJ, Hong SK, Byun SS, Lee SE, Oh JJ (2016) High preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts biochemical recurrence in patients with localized prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. World J Urol 34(6):821–827
Botros M, Sikaris KA (2013) The De Ritis ratio: the test of time. Clin Biochem Rev 34(3):117–130
Banez LL, Loftis RM, Freedland SJ, Presti JC Jr, Aronson WJ, Amling CL, Kane CJ, Terris MK (2010) The influence of hepatic function on prostate cancer outcomes after radical prostatectomy. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 13(2):173–177
De Ritis F, Coltorti M, Giusti G (1957) An enzymic test for the diagnosis of viral hepatitis; the transaminase serum activities. Clin Chim Acta 2(1):70–74
Takenaka Y, Takemoto N, Yasui T, Yamamoto Y, Uno A, Miyabe H, Ashida N, Shimizu K, Nakahara S, Hanamoto A, Fukusumi T, Michiba T, Cho H, Yamamoto M, Inohara H (2016) Transaminase activity predicts survival in patients with head and neck cancer. PLoS ONE 11(10):e0164057
Zoppini G, Cacciatori V, Negri C, Stoico V, Lippi G, Targher G, Bonora E (2016) The aspartate aminotransferase-to-alanine aminotransferase ratio predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. Medicine 95(43):e4821
Lee H, Lee SE, Byun SS, Kim HH, Kwak C, Hong SK (2017) De Ritis ratio (aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase ratio) as a significant prognostic factor after surgical treatment in patients with clear-cell localized renal cell carcinoma: a propensity score-matched study. BJU Int 119(2):261–267
Bezan A, Mrsic E, Krieger D, Stojakovic T, Pummer K, Zigeuner R, Hutterer GC, Pichler M (2015) The preoperative AST/ALT (De Ritis) ratio represents a poor prognostic factor in a cohort of patients with nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 194(1):30–35
Nishikawa M, Miyake H, Fujisawa M (2016) De Ritis (aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase) ratio as a significant predictor of recurrence-free survival in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma following nephroureterectomy. Urol Oncol 34(9):417e9–417e15
Lee H, Choi YH, Sung HH, Han DH, Jeon HG, Chang Jeong B, Seo SI, Jeon SS, Lee HM, Choi HY (2016) De Ritis ratio (AST/ALT) as a significant prognostic factor in patients with upper tract urothelial cancer treated with surgery. Clin Genitourin Cancer S1558–7673(16):30257–30259. doi:10.1016/j.clgc.2016.08.023
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A (2010) AJCC cancer staging manual, 7th edn. Springer, New York
Cronin AM, Godoy G, Vickers AJ (2010) Definition of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy does not substantially impact prognostic factor estimates. J Urol 183(3):984–989
Pratt DS, Kaplan MM (2000) Evaluation of abnormal liver-enzyme results in asymptomatic patients. N Engl J Med 342(17):1266–1271
Tan X, Xiao K, Liu W, Chang S, Zhang T, Tang H (2013) Prognostic factors of distal cholangiocarcinoma after curative surgery: a series of 84 cases. Hepatogastroenterology 60(128):1892–1895
Chen SL, Li JP, Li LF, Zeng T, He X (2016) Elevated preoperative serum alanine aminotransferase/aspartate aminotransferase (ALT/AST) ratio is associated with better prognosis in patients undergoing curative treatment for gastric adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 17(6):911
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB (2009) Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 324(5930):1029–1033
Hsu PP, Sabatini DM (2008) Cancer cell metabolism: Warburg and beyond. Cell 134(5):703–707
Sookoian S, Pirola CJ (2015) Liver enzymes, metabolomics and genome-wide association studies: from systems biology to the personalized medicine. World J Gastroenterol 21(3):711–725
Conde VR, Oliveira PF, Nunes AR, Rocha CS, Ramalhosa E, Pereira JA, Alves MG, Silva BM (2015) The progression from a lower to a higher invasive stage of bladder cancer is associated with severe alterations in glucose and pyruvate metabolism. Exp Cell Res 335(1):91–98
Thornburg JM, Nelson KK, Clem BF, Lane AN, Arumugam S, Simmons A, Eaton JW, Telang S, Chesney J (2008) Targeting aspartate aminotransferase in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 10(5):R84
Glinghammar B, Rafter I, Lindstrom AK, Hedberg JJ, Andersson HB, Lindblom P, Berg AL, Cotgreave I (2009) Detection of the mitochondrial and catalytically active alanine aminotransferase in human tissues and plasma. Int J Mol Med 23(5):621–631
Jiang X, Chang H, Zhou Y (2015) Expression, purification and preliminary crystallographic studies of human glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase 1 (GOT1). Protein Expr Purif 113:102–106
Sripradha R, Sridhar MG, Agrawal A (2010) Can protein carbonyl/glutathione ratio be used as a potential biomarker to assess oxidative stress in alcoholic hepatitis? Indian J Med Sci 64(10):476–483
Lv W, Shang H, Pei X, Chen Y, Xie H, He D, Wang X, Li L (2017) A simple prognostic model involving prostate-specific antigen, alkaline phosphatase and albumin for predicting the time required to progress to castration-resistant prostate cancer in patients who received androgen deprivation therapy. Int Urol Nephrol 49(1):61–67
Metwalli AR, Rosner IL, Cullen J, Chen Y, Brand T, Brassell SA, Lesperance J, Porter C, Sterbis J, McLeod DG (2014) Elevated alkaline phosphatase velocity strongly predicts overall survival and the risk of bone metastases in castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Urol Oncol 32(6):761–768
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Fang, K., Zhang, J. et al. The significance of De Ritis (aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase) ratio in predicting pathological outcomes and prognosis in localized prostate cancer patients. Int Urol Nephrol 49, 1391–1398 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1618-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1618-7