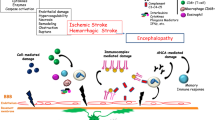
Abstract
Purpose of Review
Peripheral nervous system vasculitides (PNSV) are a heterogeneous group of disorders with a clinical subset that may differ in prognosis and therapy. We provide a comprehensive update on the clinical assessment, diagnosis, complications, treatment, and follow-up of PNSV.
Recent Findings
Progress in neuroimaging, molecular testing, and peripheral nerve biopsy has improved clinical assessment and decision-making of PNSV, also providing novel insights on how to prevent misdiagnosis and increase diagnostic certainty. Advances in imaging techniques, allowing to clearly display the vessel walls, have also enhanced the possibility to differentiate inflammatory from non-inflammatory vascular lesions, while recent histopathology data have identified the main morphological criteria for more accurate diagnosis and differential diagnoses. Overall, the identification of peculiar morphological findings tends to improve diagnostic accuracy by defining a clearer boundary between systemic and non-systemic neuropathies. Therefore, the definition of epineurium vessel wall damage, type of vascular lesion, characterization of lymphocyte populations, antibodies, and inflammatory factors, as well as the identification of direct nerve damage or degeneration, are the common goals for pathologists and clinicians, who will both benefit for data integration and findings translation. Nevertheless, to date, treatment is still largely empiric and, in some cases, unsatisfactory, thus often precluding precise prognostic prediction. In this context, new diagnostic techniques and multidisciplinary management will be essential in the proper diagnosis and prompt management of PNSV, as highlighted in the present review.
Summary
Thirty to fifty percent of all patients with vasculitis have signs of polyneuropathy. Neuropathies associated with systemic vasculitis are best managed according to the guidelines of the underlying disease because appropriate workup and initiation of treatment can reduce morbidity. Steroids, or in severe or progressive cases, cyclophosphamide pulse therapy is the standard therapy in non-systemic vasculitic neuropathies. Some patients need long-term immunosuppression. The use of novel technologies for high-throughput genotyping will permit to determine the genetic influence of related phenotypes in patients with PNSV.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Burns TM, Schaublin GA, Dyck PJ. Vasculitic neuropathies. Neurol Clin. 2007;25(1):89–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2006.11.002.
• Mansueto G, Lanza G, Fisicaro F, Alaouieh D, Hong E, Girolami S, et al. Central and peripheral nervous system complications of vasculitis syndromes from pathology to bedside: part 1-central nervous system. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2022;22(1):47–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-022-01172-z. A comprehensive update on the clinical assessment, diagnosis, complications, and treatment of primary central nervous system vasculitis.
• Beachy N, Satkowiak K, Gwathmey KG. Vasculitic neuropathies. Semin Neurol. 2019;39(5):608–19. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1688990. An organization of the vasculitic neuropathies and an overview of principles of diagnosis and treatment for the clinical neurologist.
• Gwathmey KG, Tracy JA, Dyck PJB. Peripheral nerve vasculitis: classification and disease associations. Neurol Clin. 2019;37(2):303–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2019.01.013. Useful review on the classification, clinical presentation, diagnostic approach, etiologies, and treatment of the vasculitic neuropathies.
•• Collins MP, Hadden RD. The nonsystemic vasculitic neuropathies. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13(5):302–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2017.42. An update on the classification of the Peripheral Nerve Society guideline group published in 2010, and the new diagnostic criteria for vasculitic neuropathy by the Brighton Collaboration in 2015. Clear description of nonsystemic vasculitic neuropathy subtypes. Useful pearls on diagnosis and treatment.
•• Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F, et al. 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.37715. The nomenclature and classification of vasculitis.
•• Collins MP, Dyck PJ, Gronseth GS, Guillevin L, Hadden RD, Heuss D, et al. Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on the classification, diagnosis, investigation, and immunosuppressive therapy of non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy: executive summary. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2010;15(3):176–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8027.2010.00281.x. The nomenclature and classification non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy (NSVN). diagnostic criteria for vasculitic neuropathy, classification criteria for NSVN, and therapeutic approaches to NSVN are defined.
• Hoffman GS, Calabrese LH. Vasculitis: determinants of disease patterns. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(8):454–62. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2014.89. An unteresting update on pathophysiology, this review explaims how certain antigens, including infectious agents, might become disease-relevant and how vascular diversity could influence disease phenotypes and the spectrum of vascular inflammatory diseases.
Mizisin AP, Weerasuriya A. Homeostatic regulation of the endoneurial microenvironment during development, aging and in response to trauma, disease and toxic insult. Acta Neuropathol. 2011;121(3):291–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0783-x.
Collins MP, Periquet MI, Mendell JR, Sahenk Z, Nagaraja HN, Kissel JT. Nonsystemic vasculitic neuropathy: insights from a clinical cohort. Neurology. 2003;61(5):623–30. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000082715.48844.3e.
Nicolle MW, Barron JR, Watson BV, Hammond RR, Miller TA. Wartenberg’s migrant sensory neuritis. Muscle Nerve. 2001;24(3):438–43. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4598(200103)24:3%3c438::aid-mus1020%3e3.0.co;2-y.
Wolf J, Schmitt V, Palm F, Grau AJ, Bergner R. Peripheral neuropathy as initial manifestation of primary systemic vasculitides. J Neurol. 2013;260(4):1061–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-012-6760-7.
•• Hadden RDM, Collins MP, Zivkovic SA, Hsieh ST, Bonetto C, Felicetti P, et al. Vasculitic peripheral neuropathy: case definition and guidelines for collection, analysis, and presentation of immunisation safety data. Vaccine. 2017;35(11):1567–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.11.047. The Brighton Collaboration refines diagnostic approach by combining clinical and pathological evidence to describe three levels of case definition of vasculitic neuropathy.
Martinez V, Cohen P, Pagnoux C, Vinzio S, Mahr A, Mouthon L, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulins for relapses of systemic vasculitides associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies: results of a multicenter, prospective, open-label study of twenty-two patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(1):308–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.23147.
Nathani D, Spies J, Barnett MH, Pollard J, Wang MX, Sommer C, et al. Nerve biopsy: current indications and decision tools. Muscle Nerve. 2021;64(2):125–39. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.27201.
Vital C, Vital A, Canron MH, Jaffre A, Viallard JF, Ragnaud JM, et al. Combined nerve and muscle biopsy in the diagnosis of vasculitic neuropathy. A 16-year retrospective study of 202 cases. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2006;11(1):20–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1085-9489.2006.00060.x.
Collins MP, Dyck PJ (2014) Vasculitides. In: Vallant J, Weis J, (Eds). Peripheral nerve disorders: pathology and genetics vol International Society of Neuropathology Series: Wiley Blackwel. p. 175–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118618424.ch24
• Kao JC, Liao B, Markovic SN, Klein CJ, Naddaf E, Staff NP, et al. Neurological complications associated with anti-programmed death 1 (PD-1) antibodies. JAMA Neurol. 2017;74(10):1216–22. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.1912. Vasculic neuropathy associated with the use of anti-programmed death 1 (PD-1) antibodies in the treatment of solid-organ tumors.
• Ramineni KK, Chandra SR, Mahadevan A, Kulkarni GB, Ramanujam CN. Clinical, electrophysiological and laboratory parameters, and outcome in patients with biopsy proven systemic and nonsystemic vasculitic neuropathy. Neurol India. 2019;67(Supplement):S62–70. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.250709. The clinical features, electrophysiology, laboratory results, and nerve biopsy ino non-systemic and systemic vasculitic neuropathies from patients esamined in a developing country.
Takahashi M, Koike H, Ikeda S, Kawagashira Y, Iijima M, Hashizume A, et al. Distinct pathogenesis in nonsystemic vasculitic neuropathy and microscopic polyangiitis. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2017;4(6):e407. https://doi.org/10.1212/NXI.0000000000000407.
Schneider C, Wunderlich G, Bleistein J, Fink GR, Deckert M, Brunn A, et al. Lymphocyte antigens targetable by monoclonal antibodies in non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2017;88(9):756–60. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2017-315878.
Takeuchi H, Kawasaki T, Shigematsu K, Kawamura K, Oka N. Neutrophil extracellular traps in neuropathy with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated microscopic polyangiitis. Clin Rheumatol. 2017;36(4):913–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3546-4.
•• Castiglione JI, Marrodan M, Alessandro L, Taratuto AL, Brand P, Nogues M, et al. Vasculitic peripheral neuropathy, differences between systemic and non-systemic etiologies: a case series and biopsy report. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2021;8(1):155–61. https://doi.org/10.3233/JND-200576. A well-documented case series. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate as an usedul tool to help distinguish between systemic vasculitic neuropathy and non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy. Early nerve biopsy in untreated patients increases diagnostic accuracy.
Dhinakaran S, Mahadevan A, Unchagi A, Kulkarni GB, Nagappa M, Chickabasaviah YT, et al. Is Perls Prussian blue stain for hemosiderin a useful adjunct in the diagnosis of vasculitic neuropathies? Neurol India. 2021;69(1):140–6. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.310064.
Hui M, Meena AK, Rajasekhar L, Sireesha Y, Afshan J, Mridula R, et al. Vasculitic neuropathy: a retrospective analysis of nerve biopsies and clinical features from a single tertiary care center. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2019;22(2):180–6. https://doi.org/10.4103/aian.AIAN_47_18.
Luigetti M, Di Paolantonio A, Bisogni G, Romano A, Conte A, Barbato F, et al. Sural nerve biopsy in peripheral neuropathies: 30-year experience from a single center. Neurol Sci. 2020;41(2):341–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-04082-0.
Pant I, Jha K, Singh R, Kushwaha S, Chaturvedi S. Peripheral neuropathy and the role of nerve biopsy: a revisit. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2018;61(3):339–44. https://doi.org/10.4103/IJPM.IJPM_402_17.
Suanprasert N, Taylor BV, Klein CJ, Roforth MM, Karam C, Keegan BM, et al. Polyneuropathies and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019;30:284–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msard.2019.02.026.
Sireesha Y, Kanikannan MA, Pyal A, Sandeep G, Uppin MS, Kandadai RM, et al. Patterns of peripheral neuropathy in Sjogren’s syndrome in a tertiary care hospital from South India. Neurol India. 2019;67(Supplement):S94–9. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.250714.
• Rodrigues R, Branco M, Silva R, Ruano L, Fontao L, Lopes M, et al. Peripheral neuropathy in systemic vasculitis and other autoimmune diseases - a report of five cases emphasizing the importance of etiologic characterization. eNeurologicalSci. 2020;21:100272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensci.2020.100272. An useful case study in vasculitic neuropathies.
Kawamura N, Dyck PJ, Schmeichel AM, Engelstad JK, Low PA. Inflammatory mediators in diabetic and non-diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2008;115(2):231–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0326-2.
•• Pinto MV, Ng PS, Howe BM, Laughlin RS, Thapa P, Dyck PJ, et al. Lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy: neurologic outcomes and survival in a population-based study. Neurology. 2021;96(16):e2098–108. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000011799. (.)
Stork AC, van der Meulen MF, van der Pol WL, Vrancken AF, Franssen H, Notermans NC. Wartenberg’s migrant sensory neuritis: a prospective follow-up study. J Neurol. 2010;257(8):1344–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5530-7.
Nakamura T, Kawarabayashi T, Seino Y, Hirohata M, Wakabayashi K, Shoji M. Perineuritis successfully treated with early aggressive immunotherapy. Intern Med. 2019;58(19):2875–8. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.2638-19.
Imboden JB. Involvement of the peripheral nervous system in polyarteritis nodosa and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies-associated vasculitis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2017;43(4):633–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2017.06.011.
Bischof A, Manigold T, Barro C, Heijnen I, Berger CT, Derfuss T, et al. Serum neurofilament light chain: a biomarker of neuronal injury in vasculitic neuropathy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(7):1093–4. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212045.
Sakai K, Komai K, Yanase D, Yamada M. Plasma VEGF as a marker for the diagnosis and treatment of vasculitic neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76(2):296. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2004.047571.
Graf J, Imboden J. Vasculitis and peripheral neuropathy. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2019;31(1):40–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0000000000000559.
Sandbrink F, Klion AD, Floeter MK. “Pseudo-conduction block” in a patient with vasculitic neuropathy. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 2001;41(4):195–202.
McCluskey L, Feinberg D, Cantor C, Bird S. “Pseudo-conduction block” in vasculitic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 1999;22(10):1361–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-4598(199910)22:10%3c1361::aid-mus4%3e3.0.co;2-1.
Zivkovic SA, Ascherman D, Lacomis D. Vasculitic neuropathy–electrodiagnostic findings and association with malignancies. Acta Neurol Scand. 2007;115(6):432–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.2006.00781.x.
Vrancken AF, Said G. Vasculitic neuropathy. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;115:463–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-52902-2.00026-6.
Illes Z, Blaabjerg M. Cerebrospinal fluid findings in Guillain-Barre syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathies. Handb Clin Neurol. 2017;146:125–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804279-3.00009-5.
Schneider C, Sprenger A, Weiss K, Slebocki K, Maintz D, Fink GR, et al. MRI detects peripheral nerve and adjacent muscle pathology in non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy (NSVN). J Neurol. 2019;266(4):975–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09224-0.
Grimm A, Decard BF, Bischof A, Axer H. Ultrasound of the peripheral nerves in systemic vasculitic neuropathies. J Neurol Sci. 2014;347(1–2):44–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2014.09.017.
Grimm A, Heiling B, Schumacher U, Witte OW, Axer H. Ultrasound differentiation of axonal and demyelinating neuropathies. Muscle Nerve. 2014;50(6):976–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.24238.
Uceyler N, Schafer KA, Mackenrodt D, Sommer C, Mullges W. High-resolution ultrasonography of the superficial peroneal motor and sural sensory nerves may be a non-invasive approach to the diagnosis of vasculitic neuropathy. Front Neurol. 2016;7:48. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2016.00048.
Collins MP. The vasculitic neuropathies: an update. Curr Opin Neurol. 2012;25(5):573–85. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e3283580432.
Yates M, Watts RA, Bajema IM, Cid MC, Crestani B, Hauser T, et al. EULAR/ERA-EDTA recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(9):1583–94. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209133.
Mukhtyar C, Guillevin L, Cid MC, Dasgupta B, de Groot K, Gross W, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of primary small and medium vessel vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(3):310–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2008.088096.
Ntatsaki E, Carruthers D, Chakravarty K, D’Cruz D, Harper L, Jayne D, et al. BSR and BHPR guideline for the management of adults with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53(12):2306–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ket445.
Litchfield I, Greenfield S, Harper L. Addressing the transition to a chronic condition: exploring independent adoption of self-management by patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2021;5(3):rkab075. https://doi.org/10.1093/rap/rkab075.
Ginsberg L. Vasculitis and the peripheral nervous system. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(Suppl 3):iii55–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keaa075.
Uceyler N, Geng A, Reiners K, Toyka KV, Sommer C. Non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy: single-center follow-up of 60 patients. J Neurol. 2015;262(9):2092–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-015-7813-5.
•• Younger DS. Treatment of vasculitis of the nervous system. Neurol Clin. 2019;37(2):399–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2019.01.014. Useful general guidelines for treating peripheral nerve vasculitides: diagnosis accuracy, induction therapy, and maintenance immunosuppression.
Said G, Lacroix C. Primary and secondary vasculitic neuropathy. J Neurol. 2005;252(6):633–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0833-9.
Gold R, Fontana A, Zierz S. Therapy of neurological disorders in systemic vasculitis. Semin Neurol. 2003;23(2):207–14. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2003-41133.
Langford CA. 15. Vasculitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111(2 Suppl):S602-112. https://doi.org/10.1067/mai.2003.80.
Stone JH, Merkel PA, Spiera R, Seo P, Langford CA, Hoffman GS, et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(3):221–32. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0909905.
Jayne DR, Chapel H, Adu D, Misbah S, O’Donoghue D, Scott D, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin for ANCA-associated systemic vasculitis with persistent disease activity. QJM. 2000;93(7):433–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/93.7.433.
Levy Y, Uziel Y, Zandman G, Rotman P, Amital H, Sherer Y, et al. Response of vasculitic peripheral neuropathy to intravenous immunoglobulin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1051:779–86. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1361.121.
Tsurikisawa N, Taniguchi M, Saito H, Himeno H, Ishibashi A, Suzuki S, et al. Treatment of Churg-Strauss syndrome with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004;92(1):80–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61714-0.
Pietrogrande M, De Vita S, Zignego AL, Pioltelli P, Sansonno D, Sollima S, et al. Recommendations for the management of mixed cryoglobulinemia syndrome in hepatitis C virus-infected patients. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10(8):444–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2011.01.008.
Cacoub P, Terrier B, Saadoun D. Hepatitis C virus-induced vasculitis: therapeutic options. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(1):24–30. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203883.
Gritsenko D, Hughes G. Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (harvoni): improving options for hepatitis C virus infection. P T. 2015;40(4):256–76.
Murai H, Inaba S, Kira J, Yamamoto A, Ohno M, Goto I. Hepatitis C virus associated cryoglobulinemic neuropathy successfully treated with plasma exchange. Artif Organs. 1995;19(4):334–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1594.1995.tb02337.x.
Scarpato S, Tirri E, Naclerio C, Moscato P, Salvati G. Plasmapheresis in cryoglobulinemic neuropathy: a clinical study. Dig Liver Dis. 2007;39(Suppl 1):S136–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1590-8658(07)80027-2.
Braun A, Neumann T, Oelzner P, Hein G, Grone HJ, Ziemer M, et al. Cryoglobulinaemia type III with severe neuropathy and immune complex glomerulonephritis: remission after plasmapheresis and rituximab. Rheumatol Int. 2008;28(5):503–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-007-0462-y.
Ramos-Casals M, Stone JH, Cid MC, Bosch X. The cryoglobulinaemias. Lancet. 2012;379(9813):348–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60242-0.
Montero N, Fava A, Rodriguez E, Barrios C, Cruzado JM, Pascual J, et al. Treatment for hepatitis C virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinaemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;5:CD011403. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011403.pub2.
Dammacco F, Tucci FA, Lauletta G, Gatti P, De Re V, Conteduca V, et al. Pegylated interferon-alpha, ribavirin, and rituximab combined therapy of hepatitis C virus-related mixed cryoglobulinemia: a long-term study. Blood. 2010;116(3):343–53. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-10-245878.
Soares CN. Refractory mononeuritis multiplex due to hepatitis C infection and cryoglobulinemia: efficient response to rituximab. Neurologist. 2016;21(3):47–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/NRL.0000000000000075.
Guillevin L. Infections in vasculitis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2013;27(1):19–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2013.01.004.
Patel N, Khan T, Espinoza LR. HIV infection and clinical spectrum of associated vasculitides. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2011;13(6):506–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-011-0214-6.
Collins MP, Kissel JT (2005) Neuropathies with systemic vasculitis. In: Dyck PJ, P.K. T (Eds). Peripheral neuropathy. 4th ed.: Elsevier Inc. p. 2335–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-7216-9491-7.X5001-7
Fargeot G, Perillaud-Dubois C, Deback C, Noel N, Adam C, Cauquil C, et al. Parvovirus B19-related peripheral nerve necrotizing vasculitis following SARS-CoV-2 infection. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2022;178(1–2):158–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurol.2021.07.013.
Guillevin L, Pagnoux C, Seror R, Mahr A, Mouthon L, Toumelin PL. The Five-Factor Score revisited: assessment of prognoses of systemic necrotizing vasculitides based on the French Vasculitis Study Group (FVSG) cohort. Medicine (Baltimore). 2011;90(1):19–27. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0b013e318205a4c6.
Rutgers A, Heeringa P, Damoiseaux JG, Tervaert JW. ANCA and anti-GBM antibodies in diagnosis and follow-up of vasculitic disease. Eur J Intern Med. 2003;14(5):287–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0953-6205(03)00097-9.
Lurati-Ruiz F, Spertini F. Predictive value of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in small-vessel vasculitis. J Rheumatol. 2005;32(11):2167–72.
A‐Rahman AKM, Spencer D (2003) Totally implantable vascular access devices for cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (3):CD004111. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004111
Ginsberg L. Chapter 42 Specific painful neuropathies. Handb Clin Neurol. 2006;81:635–52.
Attal N, Cruccu G, Haanpaa M, Hansson P, Jensen TS, Nurmikko T, et al. EFNS guidelines on pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13(11):1153–69. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01511.x.
Murnion BP. Neuropathic pain: current definition and review of drug treatment. Aust Prescr. 2018;41(3):60–3. https://doi.org/10.18773/austprescr.2018.022.
Saarto T, Wiffen PJ (2005) Antidepressants for neuropathic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (3):CD005454. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005454
Finnerup NB, Sindrup SH, Jensen TS. The evidence for pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Pain. 2010;150(3):573–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2010.06.019.
Sindrup SH, Otto M, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS. Antidepressants in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;96(6):399–409. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto_96696601.x.
Rowbotham MC, Goli V, Kunz NR, Lei D. Venlafaxine extended release in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Pain. 2004;110(3):697–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2004.05.010.
Bril V, England J, Franklin GM, Backonja M, Cohen J, Del Toro D, et al. Evidence-based guideline: treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2011;76(20):1758–65. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182166ebe.
Said G, Lacroix-Ciaudo C, Fujimura H, Blas C, Faux N. The peripheral neuropathy of necrotizing arteritis: a clinicopathological study. Ann Neurol. 1988;23(5):461–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410230506.
Dyck PJ, Benstead TJ, Conn DL, Stevens JC, Windebank AJ, Low PA. Nonsystemic vasculitic neuropathy. Brain. 1987;110(Pt 4):843–53. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/110.4.843.
Torvik A, Berntzen AE. Necrotizing vasculitis without visceral involvement. Postmortem examination of three cases with affection of skeletal muscles and peripheral nerves. Acta Med Scand. 1968;184(1–2):69–77.
Pagnoux C, Seror R, Henegar C, Mahr A, Cohen P, Le Guern V, et al. Clinical features and outcomes in 348 patients with polyarteritis nodosa: a systematic retrospective study of patients diagnosed between 1963 and 2005 and entered into the French Vasculitis Study Group Database. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(2):616–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27240.
Atkinson MA, Maclaren NK. The pathogenesis of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1994;331(21):1428–36. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199411243312107.
Grimaldi LM, Martino G, Braghi S, Quattrini A, Furlan R, Bosi E, et al. Heterogeneity of autoantibodies in stiff-man syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1993;34(1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410340111.
Younger DS, Rosoklija G, Hays AP, Trojaborg W, Latov N. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of sural nerve biopsies. Muscle Nerve. 1996;19(6):722–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4598(199606)19:6%3c722::AID-MUS6%3e3.0.CO;2-C.
Younger DS. Diabetic neuropathy: a clinical and neuropathological study of 107 patients. Neurol Res Int. 2010;2010:140379. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/140379.
Dyck PJ, Windebank AJ. Diabetic and nondiabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathies: new insights into pathophysiology and treatment. Muscle Nerve. 2002;25(4):477–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.10080.
Dyck PJ, Norell JE. Non-diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy: natural history, outcome and comparison with the diabetic variety. Brain. 2001;124(Pt 6):1197–207. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/124.6.1197.
Younger DS. Diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy: a postmortem studied patient and review of the literature. J Neurol. 2011;258(7):1364–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-5938-8.
Blaes F. Diagnosis and therapeutic options for peripheral vasculitic neuropathy. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2015;7(2):45–55. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759720X14566617.
Carmona FD, Mackie SL, Martin JE, Taylor JC, Vaglio A, Eyre S, et al. A large-scale genetic analysis reveals a strong contribution of the HLA class II region to giant cell arteritis susceptibility. Am J Hum Genet. 2015;96(4):565–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.02.009.
Saruhan-Direskeneli G, Hughes T, Aksu K, Keser G, Coit P, Aydin SZ, et al. Identification of multiple genetic susceptibility loci in Takayasu arteritis. Am J Hum Genet. 2013;93(2):298–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.05.026.
Jostins L, Ripke S, Weersma RK, Duerr RH, McGovern DP, Hui KY, et al. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2012;491(7422):119–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11582.
Fischer A, Ellinghaus D, Nutsua M, Hofmann S, Montgomery CG, Iannuzzi MC, et al. Identification of immune-relevant factors conferring sarcoidosis genetic risk. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;192(6):727–36. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201503-0418OC.
Gao S, Ma W, Lin X, Huang S, Yu M. Identification of key genes and underlying mechanisms in acute Kawasaki disease based on bioinformatics analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e930547. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.930547.
Carmona FD, Coit P, Saruhan-Direskeneli G, Hernandez-Rodriguez J, Cid MC, Solans R, et al. Analysis of the common genetic component of large-vessel vasculitides through a meta-Immunochip strategy. Sci Rep. 2017;7:43953. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43953.
Ortiz-Fernandez L, Carmona FD, Lopez-Mejias R, Gonzalez-Escribano MF, Lyons PA, Morgan AW, et al. Cross-phenotype analysis of Immunochip data identifies KDM4C as a relevant locus for the development of systemic vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(4):589–95. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212372.
Stone JH, Klearman M, Collinson N. Trial of tocilizumab in giant-cell arteritis. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(15):1494–5. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1711031.
Samson M, Espigol-Frigole G, Terrades-Garcia N, Prieto-Gonzalez S, Corbera-Bellalta M, Alba-Rovira R, et al. Biological treatments in giant cell arteritis & Takayasu arteritis. Eur J Intern Med. 2018;50:12–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2017.11.003.
Yachoui R, Kreidy M, Siorek M, Sehgal R. Successful treatment with ustekinumab for corticosteroid- and immunosuppressant-resistant Takayasu’s arteritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2018;47(3):246–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/03009742.2017.1278788.
Onouchi Y, Suzuki Y, Suzuki H, Terai M, Yasukawa K, Hamada H, et al. ITPKC and CASP3 polymorphisms and risks for IVIG unresponsiveness and coronary artery lesion formation in Kawasaki disease. Pharmacogenomics J. 2013;13(1):52–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2011.45.
Alphonse MP, Duong TT, Shumitzu C, Hoang TL, McCrindle BW, Franco A, et al. Inositol-triphosphate 3-kinase c mediates inflammasome activation and treatment response in Kawasaki disease. J Immunol. 2016;197(9):3481–9. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1600388.
Madian AG, Wheeler HE, Jones RB, Dolan ME. Relating human genetic variation to variation in drug responses. Trends Genet. 2012;28(10):487–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2012.06.008.
Khera AV, Chaffin M, Aragam KG, Haas ME, Roselli C, Choi SH, et al. Genome-wide polygenic scores for common diseases identify individuals with risk equivalent to monogenic mutations. Nat Genet. 2018;50(9):1219–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0183-z.
Singh P, Singh M, Khinda R, Valecha S, Kumar N, Singh S, et al. Genetic scores of eNOS, ACE and VEGFA genes are predictive of endothelial dysfunction associated osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(3):1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030972.
Zhang Z, Liu S, Guo L, Wang L, Wu Q, Zheng W, et al. Clinical characteristics of peripheral neuropathy in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: a retrospective single-center study in China. J Immunol Res. 2020;2020:3530768. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3530768.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Gelsomina Mansueto, Giuseppe Lanza, Jessica Falleti, Pasquale Orabona, Danielle Alaouieh, Emily Hong, Sara Girolami, Marco Montella, Francesco Fisicaro, Anna Galdieri, Puneetpal Singh, and Mario Di Napoli each declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mansueto, G., Lanza, G., Falleti, J. et al. Central and Peripheral Nervous System Complications of Vasculitis Syndromes from Pathology to Bedside: Part 2—Peripheral Nervous System. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 23, 83–107 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-023-01249-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-023-01249-3