Abstract
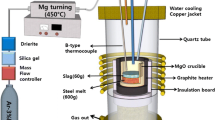
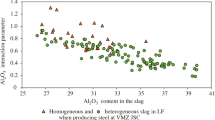
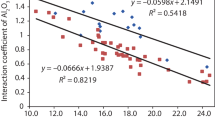
Industrial experiments were carried out to study the cyclic use of ladle furnace refining slag on desulfurization. Sampling of refining slag and steel were undertaken simultaneously at roughly equal intervals of time. The desulfurization capacity remained almost unchanged in the recycling slag compared with the primary slag. The amount of lime added was gradually increased each time when the slag was reused. As a result, the basicity increased, and therefore the sulfide capacity (Cs) increased. Cs reached a maximum when the lime added was 816 kg. The effect of sulfur enrichment on desulfurization reaction in ladle furnace slag-recycled process could be partially offset mainly by two aspects: the amount of slag increased with increases in the number of times recycled slag reused and in the quantity of lime added, which could directly reduce the mass fraction of sulfur in the recycled slag; on the other hand, during the process of transport, casting, and pouring recycled slag into next ladle, a part of CaS in the recycled slag has opportunity to be oxidized by air. Based on such favorable conditions for desulfurization, a final desulfurization ratio of up to 82.6 % was obtained, and the end-point sulfur content can be reduced to about 40 ppm.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Zhao L, Lin L, Wu Q (2016) Experimental study on sulfur removal from ladle furnace refining slag in hot state by blowing air. Int J Miner Metall Mater 23:33–39
Rađenović A, Malina J, Sofilić T (2013) Characterization of ladle furnace slag from carbon steel production as a potential adsorbent. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2013:1–6
Navarro C, Díaz M, Villa-García MA (2010) Physico-chemical characterization of steel slag. Study of its behavior under simulated environmental conditions. Environ Sci Technol 44:5383–5388
Barella S, Gruttadauria A, Magni F, Mapelli C, Mombelli D (2012) Survey about safe and reliable use of EAF slag. ISIJ Int 52:2295–2302
Iacobescu RI, Pontikes Y, Koumpouri D, Angelopoulos GN (2013) Synthesis, characterization and properties of calcium ferroaluminate belite cements produced with electric arc furnace steel slag as raw material. Cement Concr Compos 44:1–8
Bernardo G, Marroccoli M, Nobili M, Telesca A, Valenti GL (2007) The use of oil well-derived drilling waste and electric arc furnace slag as alternative raw materials in clinker production. Resour Conserv Recycl 52:95–102
Zhang H, Wang H, Zhu X, Qiu YJ, Li K, Chen R, Liao Q (2013) A review of waste heat recovery technologies towards molten slag in steel industry. Appl Energy 112:956–966
Serjun VZ, Mirtič B, Mladenovič A (2013) Evaluation of ladle slag as a potential material for building and civil engineering. Mater Tehnol 47:543–550
Dippenaar R (2005) Industrial uses of slag (the use and re-use of iron and steelmaking slags). Ironmaking Steelmaking 32:35–46
Geiseler J (1996) Use of steelworks slag in Europe. Waste Manag 16:59–63
Vilaplana ASG, Ferreira VJ, López-Sabirón AM, Aranda-Usón A, Cristina LG, Cecilia BC, Germán F (2015) Utilization of ladle furnace slag from a steelwork for laboratory scale production of Portland cement. Constr Build Mater 94:837–843
Tanaka T, Ogiso Y, Ueda M, Lee J (2010) Trial on the application of capillary phenomenon of solid CaO to desulfurization of liquid Fe. ISIJ Int 50:1071–1077
Matsubae-Yokoyama K, Kubo H, Nagasaka T (2010) Recycling effects of residual slag after magnetic separation for phosphorus recovery from hot metal dephosphorization slag. ISIJ Int 50:65–70
Altun IA, Yılmaz I (2002) Study on steel furnace slags with high MgO as additive in Portland cement. Cem Concr Res 32:1247–1249
Setién J, Hernández D, González JJ (2009) Characterization of ladle furnace basic slag for use as a construction material. Constr Build Mater 23:1788–1794
Nzotta MM, Sichen D, Seetharaman S (1998) Sulphide capacities in some multi component slag systems. ISIJ Int 38:1170–1179
Young RW, Duffy JA, Hassall GJ, Xu Z (1992) Use of optical basicity concept for determining phosphorus and sulphur slag-metal partitions. Ironmaking Steelmaking 19:201–219
Sommerville ID (1986) The composition and temperature dependence of the sulfide capacity of metallurgical slags. Metall Trans B 17:331–337
Andersson MAT, Jönsson PG, Nzotta MM (1999) Application of the sulphide capacity concept on high-basicity ladle slags used in bearing-steel production. ISIJ Int 39:1140–1149
Ban-Ya S, Hobo M, Kaji T, Itoh T, Hino M (2004) Sulphide capacity and sulphur solubility in CaO-Al2O3 and CaO-Al2O3-CaF2 slags. ISIJ Int 44:1810–1816
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51574190 and 51574020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was B. Mishra.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Yang, S., Li, J. et al. Cyclic Use of Ladle Furnace Refining Slag for Desulfurization. J. Sustain. Metall. 3, 274–279 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-016-0078-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-016-0078-0