Abstract
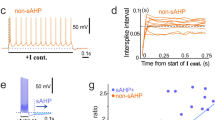
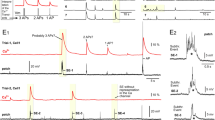
We have postulated that an excitatory postsynaptic potential (e.p.s.p.) may open voltage-sensitive K+ (‘M’) channels1, in an appropriate depolarizing range, and that this could alter the e.p.s.p. waveform. Consequently, the fast e.p.s.p. in neurones of sympathetic ganglia, elicited by a nicotinic action of acetylcholine (ACh)2, could be followed by a hyperpolarization, produced by the opening of M channels during the depolarizing e.p.s.p. and their subsequent slow closure (time constant∼150 ms)1. This introduces the concept that transmitter-induced p.s.ps may trigger voltage-sensitive conductances other than those initiating action potentials, and that in the present case this could produce a true post-e.p.s.p. hyperpolarization. (Some hyperpolarizations other than inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (i.p.s.ps) have been reported to follow e.p.s.ps3,4.) We show here that this is so.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, D. A. & Adams, P. R. Nature 283, 673–676 (1980).
Blackman, J. G., Ginsborg, B. L. & Ray, C. J. Physiol., Lond. 167, 355–373 (1963).
Tosaka, T., Chichibu, S. & Libet, B. J. Neurophysiol. 31, 396–409 (1968).
Coombs, J. S., Eccles, J. C. & Fatt, P. J. Physiol., Lond. 130, 374–395 (1955).
Libet, B., Chichibu, S. & Tosaka, T. J. Neurophysiol. 31, 383–395 (1968).
Nishi, S. & Koketsu, K. J. cell. comp. Physiol. 55, 15–30 (1960).
Koketsu, K. & Yamada, M. Br. J. Pharmac. 77, 75–82 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tosaka, T., Tasaka, J., Miyazaki, T. et al. Hyperpolarization following activation of K+ channels by excitatory postsynaptic potentials. Nature 305, 148–150 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/305148a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/305148a0