Abstract
Background:
Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (IHPS) has several known risk factors. The association between prematurity and IHPS and the timeline of presentation are poorly defined. Our aim was to evaluate the associations between IHPS and prematurity.
Methods:
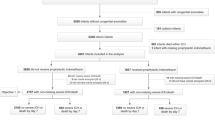
We performed a retrospective cohort study of 1,074,236 children born between June 2001 and April 2012 in the US Military Health System. IHPS cases and gestational ages (GA) were identified using billing codes. Additional risk factors for IHPS were controlled for in a multivariable logistic regression model.
Results:
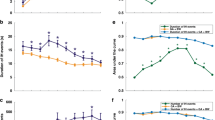
The incidence of IHPS was 2.99 per 1,000 in preterm infants and 2.25 per 1,000 in full term (relative risk (RR) = 1.33, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.16–1.54). The adjusted odds ratio for prematurity was 1.26 (95% CI 1.08–1.46). The median (interquartile range (IQR)) chronological age at presentation was 40 d (30–56) in preterm infants vs. 33 d (26–45) in full term (P < 0.001). Median postmenstrual age at presentation was 42 wk in preterm infants (40–42) vs. 45 wk (44–46) in full term (P < 0.001).
Conclusion:
Prematurity is associated with IHPS. Premature infants develop IHPS at a later chronological age, but earlier postmenstrual age, than term infants. Providers should have an increased concern for IHPS development in premature infants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Login or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ein SH, Masiakos PT, Ein A. The ins and outs of pyloromyotomy: what we have learned in 35 years. Pediatr Surg Int 2014;30:467–80.
Taylor ND, Cass DT, Holland AJ. Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: has anything changed? J Paediatr Child Health 2013;49:33–7.
Papadakis K, Chen EA, Luks FI, Lessin MS, Wesselhoeft CW Jr, DeLuca FG. The changing presentation of pyloric stenosis. Am J Emerg Med 1999;17:67–9.
Poon TS, Zhang AL, Cartmill T, Cass DT. Changing patterns of diagnosis and treatment of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: a clinical audit of 303 patients. J Pediatr Surg 1996;31:1611–5.
Lund M, Pasternak B, Davidsen RB, et al. Use of macrolides in mother and child and risk of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: nationwide cohort study. BMJ 2014;348:g1908.
Krogh C, Biggar RJ, Fischer TK, Lindholm M, Wohlfahrt J, Melbye M. Bottle-feeding and the Risk of Pyloric Stenosis. Pediatrics 2012;130:e943–9.
Krogh C, Gørtz S, Wohlfahrt J, Biggar RJ, Melbye M, Fischer TK. Pre- and perinatal risk factors for pyloric stenosis and their influence on the male predominance. Am J Epidemiol 2012;176:24–31.
Huang IF, Tiao MM, Chiou CC, Shih HH, Hu HH, Ruiz JP. Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis before 3 weeks of age in infants and preterm babies. Pediatr Int 2011;53:18–23.
Panteli C. New insights into the pathogenesis of infantile pyloric stenosis. Pediatr Surg Int 2009;25:1043–52.
Hamilton BE, Hoyert DL, Martin JA, Strobino DM, Guyer B. Annual summary of vital statistics: 2010-2011. Pediatrics 2013;131:548–58.
Adelstein P, Fedrick J. Pyloric stenosis in the Oxford Record Linkage Study area. J Med Genet 1976;13:439–48.
Katumba-Lunyenya J, Misra I, Chawda N, Erumbala G. Can you be too premature to develop pyloric stenosis? BMJ Case Rep 2012;2012:.
Rasmussen L, Green A, Hansen LP. The epidemiology of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in a Danish population, 1950-84. Int J Epidemiol 1989;18:413–7.
Gotley LM, Blanch A, Kimble R, Frawley K, Acworth JP. Pyloric stenosis: a retrospective study of an Australian population. Emerg Med Australas 2009;21:407–13.
Schechter R, Torfs CP, Bateson TF. The epidemiology of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 1997;11:407–27.
Svenningsson A, Svensson T, Akre O, Nordenskjöld A. Maternal and pregnancy characteristics and risk of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. J Pediatr Surg 2014;49:1226–31.
Krogh C, Fischer TK, Skotte L, et al. Familial aggregation and heritability of pyloric stenosis. JAMA 2010;303:2393–9.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants following pertussis prophylaxis with erythromycin--Knoxville, Tennessee, 1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 1999;48:1117–20.
Honein MA, Paulozzi LJ, Himelright IM, et al. Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis after pertussis prophylaxis with erythromcyin: a case review and cohort study. Lancet 1999;354:2101–5.
Eberly MD, Eide MB, Thompson JL, Nylund CM. Azithromycin in early infancy and pyloric stenosis. Pediatrics 2015;135:483–8.
Jadcherla SR, Klee G, Berseth CL. Regulation of migrating motor complexes by motilin and pancreatic polypeptide in human infants. Pediatr Res 1997;42:365–9.
Henderson JL, Brown JJ, Taylor WC. Clinical observations on pyloric stenosis in premature infants. Arch Dis Child 1952;27:173–8.
Hsu P, Klimek J, Nanan R. Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: does size really matter? J Paediatr Child Health 2014;50:827–8.
Perme T, Mali S, Vidmar I, et al. Prolonged prostaglandin E1 therapy in a neonate with pulmonary atresia and ventricular septal defect and the development of antral foveolar hyperplasia and hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Ups J Med Sci 2013;118:138–42.
Lacher M, Schneider K, Dalla Pozza R, Schweinitz DV. Gastric outlet obstruction after long-term prostaglandin administration mimicking hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Eur J Pediatr Surg 2007;17:362–4.
Shinohara K, Shimizu T, Igarashi J, Yamashiro Y, Miyano T. Correlation of prostaglandin E2 production and gastric acid secretion in infants with hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. J Pediatr Surg 1998;33:1483–5.
Holston A, Stokes T, Olsen C, et al. Novel noninvasive anthropometric measure in preterm and full-term infants: normative values for waist circumference:length ratio at birth. Pediatr Res 2013;74:299–306.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stark, C., Rogers, P., Eberly, M. et al. Association of prematurity with the development of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Pediatr Res 78, 218–222 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2015.92
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2015.92
This article is cited by
-
Randomized trial of azithromycin to eradicate Ureaplasma respiratory colonization in preterm infants: 2-year outcomes
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Laparoscopic pyloromyotomy for hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: a survey of 407 children
Pediatric Surgery International (2018)
-
Application of color Doppler ultrasound combined with Doppler imaging artifacts in the diagnosis and estimate of congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
Scientific Reports (2017)