Abstract
Quantum computers have long been anticipated to excel in simulating quantum many-body physics. In this work, we demonstrate the power of variational quantum circuits for resource-efficient simulations of dynamical and equilibrium physics in non-Hermitian systems. Using a variational quantum compilation scheme for fermionic systems, we reduce gate count, save qubits, and eliminate the need for postselection, a major challenge in simulating non-Hermitian dynamics via standard Trotterization. On the Quantinuum H1 trapped-ion processor, we experimentally observed a supersonic mode on an n = 18 fermionic chain after a non-Hermitian, nearest-neighbor interacting quench, which would otherwise be forbidden in a Hermitian system. Additionally, we investigate sequential quantum circuits generated by tensor networks for ground-state preparation using a variance minimization scheme, accurately capturing correlation functions and energies across an exceptional point on a dissipative spin chain up to length n = 20 using only 3 qubits. On the other hand, we provide an analytical example demonstrating that simulating single-qubit non-Hermitian dynamics for \(\Theta (\log (n))\) time from certain initial states is exponentially hard on a quantum computer. Our work raises many intriguing questions about the intrinsic properties of non-Hermitian systems that permit efficient quantum simulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
In quantum mechanics, Hamiltonian Hermiticity is typically considered a fundamental postulate. However, this requirement can be relaxed in open systems, such as quantum hardware experiencing noise, atoms undergoing spontaneous decay, or other scenarios involving measurement and postselection—the process of monitoring a quantum system and analyzing its behavior following the quantum trajectory of specific measurement outcomes (see Fig. 1a). This selective process enables an effective description of the system’s dynamics using pure states evolving under a non-Hermitian Hamiltonian, providing new strategies for efficient numerical simulation and an alternative physical perspective for studying open quantum systems1.
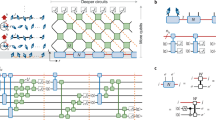
a A minimal example of a non-Hermitian system: Consider a two-level atom with eigenstates \(\{\left\vert 0\right\rangle,\left\vert 1\right\rangle \}\). When in the excited state \(\left\vert 1\right\rangle\), the atom spontaneously decays to a dark state \(\left\vert d\right\rangle\) at a rate γ. A cat observer closely monitors the population in the dark state, and by postselecting on the absence of decay, the atom can be effectively thought of as undergoing non-Hermitian time evolution1. b The use of VQAs in simulating the non-Hermitian quantum quench of Eq. (5) resolves the postselection issue: The half-filled free-fermion ground state is first prepared with a circuit generated by a Gaussian matrix product state, as detailed in Algorithm 4. Additional layers of variational unitary circuits are then attached to compress the non-Hermitian time evolution. c Numerical observation of a supersonic mode in non-Hermitian quench dynamics. The different modes can be distinguished from the intensity ‘valleys’ of the correlation function. The white solid line denotes the Lieb-Robinson bound and the dashed lines represent the first two supersonic modes. d For the same physical parameter as in c at n = 18, we emulate the compressed quench dynamics using 100,000 shots and report the connected density-density correlator averaged over bulk sites to enhance signal level. (e) Experimental data of the same circuit in d collected using Quantinuum’s H1 quantum computer at t = 1 and t = 2 for 5000 shots each. We compare the averaged connected density-density correlator to a classical TEBD simulation. The error bars represent two standard deviations and the shaded blue region indicates the conventional lightcone at r = 2vt where t = 2.
The study of non-Hermitian physics traces back to the complex field theory approach by Yang and Lee, who used it to explore new phases of matter2. Since then, it has been established that Hamiltonian non-Hermicity leads to unconventional phase transitions and unique phenomena3,4,5,6, such as exceptional points7, the non-Hermitian skin effect8, supersonic modes9,10, topological phases11, and unique entanglement behaviors12,13. Although these discoveries have generated new possibilities and excitement in the era of quantum information, non-Hermiticity poses an engineering challenge for conventional electrical, mechanical, photonic and cold atom platforms, and experimental demonstrations have been largely confined to few-particle problems14,15,16.
The recent progress of programmable quantum computers is expected to offer new opportunities to solve computational tasks17, enable cryptography18, sample hard distributions19, and, crucially, to simulate many-body physics20. However, the presence of physical noise creates a significant obstacle in the faithful execution of such tasks. More essentially, the postselection nature of non-Hermitian dynamical simulations brings the challenge to another level: In a “direct” simulation by Trotterization, the success rate of postselection would vanish exponentially in time, creating a huge sampling overhead. To date, digital quantum simulations of non-Hermitian physics have also been limited in scale compared to those of Hermitian quantum systems21,22.
On the other hand, variational quantum algorithms (VQAs)23, such as the quantum approximate optimization algorithm (QAOA)24 and the variational quantum eigensolver (VQE)25 promise to offer advantages in the simulation of quantum systems with near-term quantum hardware26. Combined with machine learning27 and tensor-network techniques28, VQAs have already yielded successful applications in reducing the resource cost in quantum time evolution29,30 and quantum state preparation31. It is then natural to ask whether one could utilize these methods in the quantum simulation of non-Hermitian systems. Intuitively, VQAs explore the large degree of freedom in the Hilbert space and could mitigate the postselection issue, and even reduce the circuit gate count.
In this work, we demonstrate the power of variational quantum algorithms through the analytical, numerical, and experimental study of various non-Hermitian systems. First, combining variational quantum compilation (VQC) and Gaussian matrix product state (GMPS) method, we simulate the non-Hermitan quench dynamics in a strongly correlated fermionic system10 without post-selection, drastically reducing the quantum resources required compared to a Trotterization scheme. Most significantly, this includes a ~1019 sampling overhead due to post-selection, as we estimate. On Quantinuum’s H1 trapped-ion quantum processor, we observe a non-Hermitian supersonic mode where correlation functions propagate faster than the conventional light cone. Second, by integrating the data compression capabilities of quantum matrix product states (qMPS)28,32 with a variance minimization algorithm, we devise an eigenstate-finding algorithm for non-Hermitian systems suitable for near-term quantum computers. Testing our algorithm on Quantinuum’s H1 trapped-ion quantum computer, we accurately capture the energy and correlation functions of a n = 20 non-Hermitian spin chain around an exceptional point (EP), where the real-valued ground energy merges with the first excited state to form a Hermitian conjugate pair. This result leverages the qMPS compression capabilities, wherein a classical MPS with bond dimension χ can be stored on a quantum computer using memory scaling as \(q \sim \log \chi\)28,31, extending the quantum memory advantages of qMPS to the study of non-Hermitian systems.
Results
Observation of a supersonic mode
One of the most striking dynamical properties of non-Hermitian physics is the violation of the Lieb-Robinson (LR) bound33, a cornerstone of quantum dynamics that imposes strict limits on the propagation of information in many-body systems. Although LR upper bounds the information spreading velocity in a locally interacting Hermitian quantum system, the dynamics under strictly geometrically two local non-Hermitian Hamiltonians can allow supersonic information propagation modes9, without introducing any (quasi) long-range interactions34,35. This can be probed by studying the two-point correlation functions of the quenched dynamics, starting from the ground state of some Hermitian Hamiltonian \(\left\vert {\psi }_{0}\right\rangle\) and time-evolved with a different non-Hermitian Hamiltonian H:
where \(N(t)\equiv \langle \psi (t)\vert \psi (t)\rangle\) is the normalization factor, and \({{\mathcal{O}}}(t)={e}^{iHt}{{\mathcal{O}}}{e}^{-iHt}\) is pseudo-Heisenberg evolution. In (4), the pseudo-Heisenberg evolved operators are restricted by the Lieb-Robinson bound, yet in general the term \({e}^{i{H}^{{\dagger} }t}{e}^{-iHt}\) can be long-range, enabling supersonic modes even in non-interacting models. In this work, we consider the following non-Hermitian, interacting fermionic chain with open boundary conditions, whose low energy spectrum corresponds to a \({{\mathcal{PT}}}\)-symmetric Luttinger liquid10,36:
Although H is local, it is possible to show that the system has modes corresponding to the velocity at x = 2kvt through a bosonized effective theory calculation10, where k is an integer, and
is the LR velocity. This is in strong contrast with the Hermitian case or systems in a full Linbladian evolution9, where only the first (k = 1) mode is permitted. We study the quench dynamics of the system starting with the free-fermion ground state at Jz = 0 and time evolving the state with a non-zero Jz Hamiltonian. We observe the supersonic modes through measuring a connected density-density correlator \({C}_{nn}^{0,r}(t)=[\langle {n}_{0}{n}_{r}\rangle (t)-\langle {n}_{0}\rangle (t)\langle {n}_{r}\rangle (t)]\), which reveals both the presence of supersonic light cones and their decay, as theoretically predicted and numerically shown in Fig. 1c.
Non-Hermitian time evolution can result from conditional Lindblad-type dynamics, where continuous environmental monitoring is applied to prevent quantum jumps. However, in a direct simulation with, e.g., Trotterizaiton37 and block encoding38, the likelihood of post-selection diminishes over time, and thus observing non-Hermitian dynamics becomes increasingly challenging. In fact, the post-selection rate would decay exponentially in t even if one could simulate open system dynamics exactly with an analog simulator. Nevertheless, the suppressed supersonic modes in the correlation function shown in Fig. 1a suggest that the post-quench state still exerts some form of locality at least for \(t \sim \log (n)\), providing an opportunity to be compressed by a low complexity state. For a finite given accuracy, it suffices to truncate the correlation function at a finite mode number and set the cut-off supersonic mode as the effective light cone, which would still be efficiently simulable.
In this work, we circumvent this challenge by utilizing two tensor-network-inspired techniques: GMPS39 for preparing the initial state and VQC29 for approximating the non-Hermitian time evolution. As we explain in the supplement, GMPS provides an efficient approximation to the Gaussian mean-field state by exploiting the near-area-law entanglement nature of the ground state, and VQC dramatically compresses time-evolved states that have high entanglement but low complexity. Sketched in Fig. 1b, we start with a compressed representation of the initial free fermion state and variationally compute a circuit representation at each Trotterized time step, as detailed in Algorithm 1. In practice, we found that it suffices to use a shallow, unitary variational circuit to capture the action of the non-Hermitian dynamics, without the necessity to introduce ancillary qubits.
Algorithm 1
– Compressed quantum quench with VQC
1: Find the GMPS representation that prepares the free-fermion ground state. This could be done either deterministically or variationally39,40. Denote this state as \(\left\vert {\psi }_{0}\right\rangle\).
2: for t = Δt, 2Δt, . . . , T do
3: Calculate the normalized target state after a Trotterized time evolution, \(\vert {\psi }_{t}\rangle \propto {e}^{-iHt}\vert {\psi }_{{t}_{0}}\rangle\)
4: Initialize the parametrized quantum circuit.\(\, \left\vert \tilde{\psi }\right\rangle\) at θ0; then use a gradient descent method to minimize infidelity \(1-{{\mathcal{F}}}=1-{\left\vert \left\langle {\psi }_{t}| \tilde{\psi }({{\boldsymbol{\theta }}})\right\rangle \right\vert }^{2}\) wrt. θ
5: Record optimized parameter θ*(t), θ0 ← θ*
6: if \(1-{{\mathcal{F}}}\, > \, \epsilon\) then
7: Add a layer of PQC to the time evolution layers which we initialize at the identity
8: Return to 4
9: end if
10: end for
For the parameterized quantum circuit (PQC), we use a parameterized gate known as the ‘fSim’ gate41, which preserves the U(1) symmetry, as detailed in Supplementary Note 1. This choice offers three key benefits: it reduces the number of variational parameters from 15 to 5 per gate, decreases the number of CNOT gates from 3 to 2 per gate, and enables error mitigation with essentially no additional cost. A similar circuit architecture has been proposed in40 and is denoted as the GMPS+X ansatz. Notice that, generally, the imaginary time evolution does not necessarily conserve charge—only when the initial state is in a single charge sector—which is the situation we consider here. Fixing the target infidelity \(1-{{\mathcal{F}}}=0.02\) and comparing our VQC to a naive Trotterization implementation, we find a reduction of CNOT gate count by a factor of 9 and the elimination of auxiliary qubits, reducing their number from 9 to 0. Most significantly, the compressed evolution method does not require postselection, unlike block encoding. As estimated in the Supplementary Note 1, this avoids a sampling overhead of 1019.
Another experimental challenge is that supersonic modes have relatively low amplitudes. Increasing the magnitude of Jz can increase the intensity of the supersonic modes, but there is a threshold ~ −1.33, above which the Lutingger Liquid prediction would fail10 and thus we set our Jz = − 1.3. Still, observing the signal level is demanding: In the classical simulation result with time-evolving block decimation (TEBD) Fig. 1 at n = 61, the correlation strength of the first supersonic model already drops below ~0.01.
To resolve this, instead of reporting the correlation function \({C}_{nn}^{i,i+r}(t)\) for a specific initial position in the chain, we report the correlation function averaged over all bulk sites \(\overline{{C}_{nn}^{i,i+r}(t)}\) because the supersonic mode should be a universal property within the system. Asymptotically, this post-processing technique effectively increased the amount of data by a factor of ~ (n − r), roughly an order of magnitude in this case. We illustrate our experimental details in Supplementary Note 1.
Comparing the TEBD and emulation results between panels a) and b) of Fig. 1, we find the supersonic mode is preserved in \(\overline{{C}_{nn}^{i,i+r}(t)}\). Limited by the number of shots as trapped-ion simulators tend to have a slower clock rate in exchange for higher fidelity, we choose t = 1 and t = 2 for experimental implementation on Quantinuum’s H1 machine. As demonstrated in Fig. 1c), the vast majority (>95%) of data points align with the classical prediction within two standard deviations with merely 5000 shots. This would not have been possible without the usage of variational circuits and proper data processing. To compare, a recent dynamical digital simulation on a merely n = 6 non-interacting fermionic chain took 160,000 shots22 to implement for each Trotter step.
Two clear trends emerge from the data: the supersonic mode gains amplitude over time, while the LR mode loses amplitude. Additionally, by observing the shift in the LR peak between the two time slices (from r = 2 to r = 3.5), we estimate the LR velocity to be \({v}_{\exp }=1.5\), which closely matches the theoretical prediction of v = 1.4.
It is worth noticing that for the time evolution generated by a generic non-Hermitian Hamiltonian, completely circumventing postselection with poly(n) gates is nearly impossible even with the use of variational compilation unless complexity classes collapses: BQP = PostBQP = PP42. But what if we make strong assumptions about the Hamiltonians, such as they are physically local? Surprisingly, for certain initial states, we find an example where the time evolution of a Hamiltonian consisting only of single qubit terms could be too powerful to simulate, even for a very short period:
Theorem 2.1
(Single qubit non-Hermitian dynamics for logarithmic time can be hard to simulate with a quantum circuit) There exist \(\left\vert {\psi }_{0}\right\rangle\) and a non-Hermitian Hamiltonian H consisting with single-qubit terms only, such that the circuit C returns
for merely \(t=\Theta (\log (n))\) requires eΩ(n) two-qubit gates to implement.
One example is to take \(\left\vert {\psi }_{0}\right\rangle\) to be a Haar random state and \(H=-i{\sum}_{i}{Z}_{i}\): running the time evolution for \(t=\Theta (\log (n))\) allows one to distinguish the Haar random state to a maximally mixed state, which should be exponentially hard even for quantum circuits43. We provide a detailed analytical proof of this no-go theorem in the Methods section. As a corollary, we also show that the theorem can be thought of as an oracle separation between complexity classes BQP and PostBQP, as well as between BQP and PostQNC0 (to be defined in the Methods).
Crossing the exceptional point
We now focus on studying eigenstates of non-Hermitian Hamiltonians through variational circuits. We first recall that the matrix spectral theorem does not hold for non-Hermitian Hamiltonians (H ≠ H†), which implies the eigenvalues of H are not necessarily real, and the left eigenvectors are not the Hermitian conjugates of the right eigenvectors:
The eigenstates within each left and right set are no longer orthogonal to each other. Instead, we have the biorthogonal relationship that exists between left and right eigenstates:
In designing a variational algorithm targeting eigenstates of non-Hermitian Hamiltonians, these observations imply that the traditional objective function in a ground-state search, namely \({{\mathcal{L}}}=\langle \psi ({{\boldsymbol{\theta }}})| H| \psi ({{\boldsymbol{\theta }}})\rangle\) is no longer suitable. Fortunately, a ‘variance minimization’ method has been recently proposed44. Instead of directly minimizing the energy function, it optimizes the following variance quantity, which is semi-positive definite:
Here E is a complex variable we optimize over. When \({{{\mathcal{L}}}}^{{\prime} }=0\) we are guaranteed that \(\left\vert \psi ({{\boldsymbol{\theta }}})\right\rangle\) is a right eigenstate of H and E is an eigenvalue (for the rest of the paper, we focus on the property of right eigenstates, and the left eigenstates can be found by substituting H ← H†). Using this method, the authors devised a numerical optimizer and were able to numerically compute the left and right eigenstates, verifying the biorthogonal relations, as well as evaluating many observables44.
Although the variance minimization scheme presented in Ref. 44 includes all the fundamental components of a variational quantum algorithm, the simulated system sizes were limited to only 7 qubits due to two main obstacles: First, they used a direct, full-state preparation method that is demanding on both classical and quantum memory. Capturing long-range correlations would then require a large circuit volume, making it impractical for larger systems. Second, the termination condition for variance minimization only ensures that some eigenstate is found, but not necessarily the one of interest. Given that the number of eigenvalues increases exponentially with system size, a random guess for E is likely to result in an undesired eigenstate.
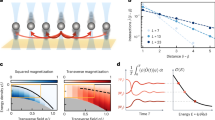
To solve the first obstacle, we make use of quantum circuit tensor network state (qTNS) techniques28, to sequentially simulate many-body quantum states, as shown in Fig. 2. Rather than a direct one-to-one encoding between a spin and a qubit, sequential simulation introduces q ancilla qubits, or bond qubits, with local circuit depth τ to faithfully capture the near-area law entanglement structure of a physical state, generating a sequence of quantum operations that allows one to sample properties of the many-body state along a spatial direction without storing the full state in quantum memory; we defer a more detailed explanation to Supplementary Note 1.
a While any many-body wavefunction can be cast as an MPS, it permits especially efficient ground state representations for 1d systems. In the right canonical form, each tensor in the MPS is an isometry28,71. To implement on a quantum computer, each isometry is embedded as a 2χ × 2χ unitary through a QR decomposition. The MPS is then cast into a sequential quantum circuit with Algorithm 3. b Each UA can be synthesized from SU(4) gates with certain local geometries. Here we demonstrate a ladder geometry and a brickwall geometry. The depth of the local circuit is denoted τ. The sequential quantum circuit can then be used as a variational ansatz. Due to having limited access to quantum resources, we first classically variationally optimize each SU(4) gate based on the cost function, e.g. Eq. (10), and then compile each SU(4) gate into native gates of the Quantinuum H1 processor before executing. The energy of the spin system is calculated from sampling correlation functions in the real experiment. See also Supplementary Note 1 for more experimental details.
For the second obstacle, we designed a ‘warm start’ method, as widely used in many other variational algorithms29. Namely, we first turn off the non-Hermitian field and solve for the Hamiltonian’s ground state with a VQE algorithm and gradually turn on the imaginary field, feeding the previous optimization result as an initialization. Concretely, we consider the 1d-transversal field Ising model with an imaginary longitudinal field45:
where J and κ are real numbers. To find the ground state at a certain \({\kappa }_{{{\rm{targ}}}}\), we execute the procedure in Algorithm 2:
Algorithm 2
– VQE algorithm for dissipative Ising model with variance minimizaiton
1: Set the target Hamiltonian to be H = HIsing(J, κ = 0)
2: Initialize \(\left\vert \psi ({{\boldsymbol{\theta }}})\right\rangle\) where the circuit with a variational circuit generated by quantum matrix product state (qMPS)31
3: Find the Hamiltonian’s ground state by minimizing \({{\mathcal{L}}}=\langle \psi ({{\boldsymbol{\theta }}})| H| \psi ({{\boldsymbol{\theta }}})\rangle\) and record the optimized circuit parameter θ* and energy E*;
4: for\(\kappa=\Delta \kappa,2\Delta \kappa,\ldots {\kappa }_{{{\rm{targ}}}}\)do
5: Initialize the circuit at θ0 ← θ* and E0 ← E*
6: Minimize the target function \(\left\langle \psi ({{\boldsymbol{\theta }}})\right\vert (H-E)({H}^{{\dagger} }-{E}^{*})\left\vert \psi ({{\boldsymbol{\theta }}})\right\rangle\) over θ and E.
7: Record optimized parameter θ*(κ) and energy E*(κ)
8: end for
The dissipative Ising model exerts \({{\mathcal{PT}}}\)-symmetry, but it goes through spontaneous symmetry breaking at κc, the so-called exceptional point: at κ < κc, the ground state energy remains real despite the non-Hermicity; at κ > κc, the ground state energy merges with the first excited state to form a complex conjugate pair in their energy values. The exceptional point is very sensitive to J and the parity of the length of the chain.
In the antiferromagnetic phase and open boundary condition, there will be a real to complex transition only when the system size is odd; when n is even, such transition does not happen due to the ground state and first excited state being in different charge sectors45. In Fig. 3, we compare simulation results for our numerical results to density-matrix renormalization group generalized to non-Hermitian systems (NH-DMRG) with iTensor46 at χ = 100. Setting Δκ = 0.05 and using a ladder sequential circuit with q = 2 and τ = 2, the variance minimization algorithm accurately captures the EP physics for different J and κ at system sizes n = 19 and n = 20. At each J, the optimizer returns a relative energy error below 0.01% until κ gets close to the EP, where the error rises to as high as ~ 0.3% and drops again, suggesting an increase in difficulty in representing the states near EP.
(a) The real and (b) imaginary parts of variational right ground state preparation results of a n = 19 non-Hermitian Ising chain are compared with that from a χ = 100 NH-DMRG. The exceptional point can be read from the imaginary part of E. We experimentally execute the J = − 1, κ ∈ {0.2, 0.5} circuits for 2,000 measurement shots and report the energy outcomes, which are both within 2% error of the DMRG values. (c) The absolute value of relative energy difference. Notice that the peak on each curve corresponds to the EP read from b. (d) and (e) repeat the study of (a) and (b), except now the system size is set to 20 so that the system is EP-free. f Comparing ZZ correlation functions measured in Quantinuum’s H1 processor (2,000 shots) to DMRG results. All results are prepared with a q = 2, τ = 2 ladder architecture as defined in Fig. 2, and error bars represent one statistical standard deviation. More experimental details on the implementation can be found in the Supplementary Note 1.
Additional numerical results for a non-Hermitian XXZ chain with size n = 64 can be found in the Supplementary Note 1. In Hermitian physics, it is known that quantum computers offer a “data compression” advantage in representing physical states31,32,40, as a quantum computer can store a MPS with bond dimension χ with merely \(\sim \log \chi\) bond qubits. Our result extends this quantum advantage to non-Hermitian quantum material simulations.
Discussion
We have combined two quantum state compression techniques, GMPS and VQC, to experimentally study the quenched dynamics of an extended strongly-correlated non-Hermitian system. Using a trapped-ion implementation on the Quantinuum H1 quantum processor, we have observed a supersonic mode in the connected density-density correlation function of a fermionic chain following a non-Hermitian quantum quench—a phenomenon conventionally forbidden by the Lieb-Robinson bound in Hermitian systems. The system sizes, time scales, and low sample complexity achieved in our experiments are enabled by the convergence of the advantages offered by universal quantum computers and the variational formulation of the dynamics employed in our experiments, allowing us to bypass costly postselection-based implementations with an affordable approach based on unitary dynamics. Similarly, we exploited the efficient compression offered by qMPS to experimentally prepare eigenstates of a non-hermitian spin chain where we experimentally measured correlation functions and energies across an exceptional point on a dissipative spin chain up to length n = 20 using only 3 qubits. These results show that universal quantum computers have great potential and offer an advantage as compared to traditional non-universal experimental platforms in the study of non-Hermitian quantum matters.
Our work also raises a number of intriguing questions regarding the opportunities and challenges of using digital quantum computers for simulating non-Hermitian systems. In particular, in Theorem II.1 we established the hardness of the simulation of quench dynamics of certain initial states under single qubit non-Hermitian dynamics. A key open question arising from our experiments and theoretical findings is to determine the properties of the initial state and the non-Hermitian Hamiltonian that enable efficient unitary simulation. Here, a natural direction is to explore the use of VQC to alleviate the postselection requirements which are often encountered in systems such as those exhibiting measurement-induced phase transitions47. Similarly, these and other related questions can be reframed in the context of quantum algorithms for solving dissipative differential equations. Specifically, under what conditions can quantum computers provide a significant advantage in solving these equations? This problem has been studied from an algorithmic perspective48 and can potentially offer new insights into the question of simulability of non-hermitian systems more broadly.
A natural extension of our work is to explore dynamics and eigenstate properties beyond one-dimensional systems where interesting non-Hermitian phenomena emerge49. One possibility is, that instead of doing a sudden quench, one could use our protocol to simulate non-adiabatic passage across an EP and investigate the proposed unconventional Kibble-Zurek mechanism50,51. Another interesting direction would be exploring the asymptotic quantum memory costs to approximate the ground states in different non-Hermitian phases of matter. In Hermitian systems, one could relate the hardness of compression to entanglement entropy laws52. It is worth pursuing what metric one should use in the non-Hermitian case, as there does not exist a good entanglement measure due to the lack of an orthonormal basis6. As we push the boundaries of quantum computation, the techniques and insights gained from our study not only illuminate new pathways for exploring non-Hermitian physics but also pave the way for future advancements in quantum simulation aided by the convergence of innovative techniques such as compression and variational compilation with cutting-edge quantum hardware.
Methods
This section details the numerical and analytical methods used throughout the work. We give a motivating example of non-Hermitian physics, followed by the discussion of sequential circuits generated by Matrix Product States (MPS) and Gaussian Matrix Product States (GMPS), explaining how they enable efficient quantum representations of near-area-law quantum states. Additionally, we provide an analytical proof of Theorem I.1.
Non-Hermitian physics: a motivating example
We argued in the main text that a physical way to motivate non-Hermitian physics is from open quantum system dynamics. Usually, the Linbladian equation is used to describe the Markovian evolution of a system interacting with a thermal bath53:
Here, the system density matrix ρ evolves under H, the system Hamiltonian, and {Li} is a set of jump operators corresponding to the dissipations due to the bath. In the second line, we have redefined \({H}_{{{\rm{eff}}}}=H-\frac{i}{2}{\sum}_{i}{\gamma }_{i}{L}^{{\dagger} }L\).
The last term in Eq. (13), \({\sum}_{i}{\gamma }_{i}{L}_{i}\rho {L}_{i}^{{\dagger} }\), describes quantum jump processes that can be associated with a measurable physical quantity, such as a spontaneous emission of a photon. The stochastic time evolution can be classified into different quantum trajectories depending on the number of quantum jumps. Now, if we postselect on the absence of quantum jumps, we end up with a Schrodinger-like time evolution with a non-Hermitian Hamiltonian:
Review of sequential circuits
In a quantum system consisting of n qubits, the sequential quantum circuits are defined as follows:
Definition 4.1
(τ-sequential quantum circuit) Given a local universal gate set \({{\mathcal{G}}}\subseteq U(4)\), a quantum circuit consisting of local gates in the set is called a τ-sequential quantum circuit if each qubit is at most acted upon by τ gates in the circuit.
Various interesting examples emerge at τ ≪ n. For example, when τ is a constant, from the definition, we can bound its computational power:
-
1.
Strictly contains all constant depth circuits;
-
2.
Is strictly contained in the set of linear depth circuits.
The first inclusion holds because any constant-depth circuit is a sequential circuit and sequential circuits can prepare long-range correlates that cannot be accessed from constant-depth circuits such as the GHZ state. The second bound can be deduced from a) these sequential circuits are at most depth O(n), as their circuit volume is O(n) by definition and b) they cannot generate volume law entanglement states, which are permitted in linear depth circuits.
As such, sequential circuits are of particular interest in the NISQ era: Compared with a constant depth circuit, it has more representation power as its light cone can cover the whole system; compared to a ‘dense’ constant depth circuit, it permits a compressed representation yet accurately captures certain classes of states, such as thermal states of locally interacting spin chains54, electronic mean-field ground states40, chiral topological orders55, maps between gapped phases56, projected entangled-pair states57, etc.; they can be combined with adaptive circuits to improve their representation power58,59,60, and experimental proposals on cQED devices have been proposed61,62.
Matrix product states
The discussion of sequential circuits originated from a celebrated quantum state compression method: MPS. Any pure quantum state \(\left\vert \Psi \right\rangle\) can be expressed as a matrix-product state by sequentially performing Schmidt decompositions between local sites, turning wave-function amplitudes into a 1D tensor train (in physical states considered in this work, we focus on open boundary 1D chains with sites x ∈ {1, 2, …n}, although the method can be generalized to infinite systems and larger on-site dimensions):
In this context, sx ∈ {0, 1} labels the basis states for site x, and \({A}^{{s}_{x}}\) are χ × χ matrices. The vectors ℓ are χ-dimensional and determine the left boundary conditions. The memory and computational cost of Matrix Product State (MPS) computations scale with the bond dimension, χ, which is lower bounded by the bipartite entanglement entropy across a cut through the bond.
Although representing a generic quantum state, such as the Haar random state still requires the bond dimension χ = eO(n), many quantum states of physical interests such as 1D short-range correlated, area-law entangled states40,52,63, or thermal mixed states54,64, it is possible to truncate the entanglement spectrum to χ = O(1) independent of system size, allowing for efficient classical simulations of 1D gapped ground states.
Higher-dimensional systems can also be represented as MPS by treating them as a 1D stack of (d − 1)-dimensional cross-sections. Yet even for area-law entangled states the required bond dimension grows exponentially with the cross-sectional area, making classical simulation impractical. In such cases including classically intractable cases such as 2D and 3D ground-states with symmetry-breaking40 or (non-chiral) topological order65, and finite-time quantum dynamics from any qMPS31,66, applying tensor network methods on a quantum computer could offer a significant advantage.
Sequential quantum circuits generated by MPS (qMPS)
Properties of any MPS in right-canonical form (RCF)32 can be measured by sampling on a quantum computer and implementing its transfer-matrix as a quantum channel67 acting on 1 “physical” qubit and \(q={\log }_{2}\chi\) bond qubits (see Fig. 2 for a graphical representation). Each tensor A is then embedded as a block of larger unitary operator UA acting on a fixed initial state \(\left\vert 0\right\rangle\) of the physical qubits. After the application of UA, the physical qubits can be measured in any desired basis while entanglement information is consistently stored on the bond qubits. The process is then repeated for each site in sequence from left to right. In this way, one can measure any product operator of the form \({\prod }_{x=1}^{n}{{{\mathcal{O}}}}_{x}\), which forms a complete basis for general observables. Crucially, once measured, the physical qubit for site x can be reset to \(\left\vert 0\right\rangle\) and reused as the physical qubits for site x + 1, enabling a small quantum processor to achieve quantum simulation tasks with sizes far larger than the number of qubits available31.
To summarize, the qMPS procedure for sampling an observable of the form \(\left\langle \psi \right\vert \mathop{\prod }_{x=1}^{n}{O}_{x}\left\vert \psi \right\rangle\) is:
Algorithm 3
– Generating sequential quantum circuits from MPS
1: Prepare the bond qubits in a state corresponding to the left boundary vector ℓ. This can be done with up to \(\log \chi\) ancilla qubits
2: for x = 1…n do
3: Perform a synthesized quantum circuit UA at site x, entangling the physical and bond qubits.
4: Measure the physical qubit in the eigenbasis of Ox and weight the measurement outcome by the corresponding eigenvalue of that observable.
5: Reset the physical qubit for site x in a fixed reference state, \(\left\vert 0\right\rangle\).
6: end for
7: Discard the bond qubits.
Moreover, the entanglement spectrum of the bond-qubits in between sites x and x + 1 coincides with the bipartite entanglement spectrum of the physical MPS at that entanglement cut, further enabling measurement of non-local entanglement observables, as recently demonstrated experimentally31. The left boundary vector ℓ is prepared by a unitary circuit acting on the bond space. For an open chain, there is no need to specify the right boundary condition as no entanglement is to be stored beyond x = n, and thus the bond qubits are disentangled with the physical qubit and can be traced out. When all UA matrices are set to be the same, the lack of right boundary conditions in the formalism describes a semi-infinite wire31.
By exploiting the efficient compression68 of physically interesting states, such as low-energy states of local Hamiltonians, qTNS methods enable simulation of many-body systems relevant to condensed-matter physics and materials science with much smaller quantum memory than would be required to directly encode the many-body wave-function.
Gaussian MPS
While MPS is a generic approach to quantum state compression, a subclass of MPS, the Gaussian MPS (GMPS), explores the near-area law entanglement of free fermion systems, enabling even more efficient representations. The Hamiltonian of a Gaussian (i.e. non-interacting) fermion system with n sites has the form
This system can be fully characterized by its n × n two-point Green’s function \({G}_{ij}=\langle {c}_{i}^{{\dagger} }{c}_{j}\rangle\) with highly degenerate eigenvalues of either 0 (unoccupied) or 1 (occupied sites). Crucially, Gij remains invariant under any unitary transformation as long as one does not mix occupied and unoccupied states.
The compression scheme presented by Fishman and White39 exploits this unitary invariance by progressively disentangling local degrees of freedom in blocks of B adjacent sites. Moreover, the ground states of Gaussian fermionic systems have near-area-law entanglement. Therefore, choosing block size B large enough, most of the block eigenvalues must be exponentially close to 0 or 1. This enables a sequence of operations that compresses the correlation matrix:
Algorithm 4
– GMPS compression
1: for x = 1…n do
2: Start with Gxx, examine the next B × B sub-matrix of G to the bottom right.
3: Identify the eigenvector with an eigenvalue closest to 0 or 1.
4: Apply a series of 2 × 2 single-particle unitary rotations \({\prod }_{\alpha=1}^{B-1}{u}_{x,\alpha }^{{\dagger} }\) on G to move this eigenvector to the first site of the block. Denote the resultant correlation matrix as \({G}^{{\prime} }\).
5: Set \(G\leftarrow {G}^{{\prime} }\)
6: end for
In each iteration, the compression algorithm separates a site from the rest of the system. At the end of execution, Green’s function is approximately diagonalized. Reversing the process allows one to transform a product state into the desired Gaussian fermionic state.
GMPS as a sequential quantum circuit
To simulate fermions on a quantum computer, these single-particle operations uα in the fermionic language, can be converted into a circuit for the many-particle Hilbert space of size 2n by replacing each 2 × 2 unitary \({u}_{x,\alpha }^{{\dagger} }\) with a two-qubit gate:
As pictured in Fig. 1(b), the resulting ladder circuit U = ∏x,α Ux,α can be interpreted as a B-sequential quantum circuit generated by MPS (Fig. 2) with bond dimension χ = 2B whose causal cone slightly differentiates from generic non-Gaussian (q)MPS of the same bond dimension. In the 1D Hamiltonian considered in Eq. 5 and Jz = 0, we numerically find that it suffices to choose block size B = 3 to prepare the ground state to energy infidelity <1% on a n = 18 chain.
Directly preparing an arbitrary Gaussian state with a ladder circuit on n qubits requires O(n2) two-qubit gates (as shown in69). To compare, a compressed GMPS ground state can be prepared with O(nB) two-qubit gates acting on O(B) qubits when implemented sequentially. The efficiency of this compression depends on the block size B needed for accurate state approximation.
Numerical evidence and entanglement-based arguments suggest that for ground states of local Hamiltonians in 1D systems of length L with a target error threshold \(\epsilon=1-\frac{1}{L}{\sum}_{i,j}| {G}_{ij}^{(\,{\mbox{GMPS}})}-{G}_{ij}|\), the required block size B scales as \(\log {\epsilon }^{-1}\) for gapped states or \(\log L\log {\epsilon }^{-1}\) for gapless metallic states. In Niu et al.40, these results are extended to d-dimensional systems, where B generally scales with the bipartite entanglement entropy S(L):
This result holds even for topologically non-trivial Chern band insulators that have an obstruction to forming a fully localized Wannier-basis. Compared to standard adiabatic state-preparation protocols, this method dramatically reduces the number of qubits required (Ld−1B vs. Ld) to implement the GMPS on a quantum computer40; the compressed state can be then used as an initial state for quantum quench or adiabatic state preparations.
Analytical proof of Thm. I.1 and implication in complexity theory
In this section, we provide analytical proof of Theorem I.1, which says there exists a non-Hermitian H consisting of single qubit terms only and an initial state \(\left\vert {\psi }_{0}\right\rangle\) where the dynamics for \(\Theta (\log (n))\) time can be exponentially hard to approximate with a quantum circuit. One explicit example is to take \(\left\vert {\psi }_{0}\right\rangle\) to be a Haar random state \(\left\vert {\psi }_{{{\rm{Haar}}}}\right\rangle\) and \({H}_{z}=-i{\sum}_{i}{Z}_{i}\). Our hardness of approximation result comes from two facts:
-
1.
Applying the dynamics generated by Hz for evolution time \(t=\Theta (\log (n))\) and measure in the computational basis allows one to distinguish a Haar random state from a maximally mixed state \({\rho }_{m}={\mathbb{I}}/d\), where d = 2n.
-
2.
With overwhelmingly high probability, distinguishing a state sampled from Haar random ensemble from ρm is exponentially hard.
The task can be formalized into a decision problem:
Problem 4.2
(Distinguishes a Haar random state from a maximally mixed state) An oracle \({{\mathcal{O}}}\) prepares copies of a fixed quantum state on a n-qubit quantum register that is promised to be either a maximally mixed state or a pure state sampled Haar randomly. Decide which is the case with as few queries as possible.
We first prove that time evolution with a single qubit dissipation channel can efficiently solve Problem IV.2.
Lemma 4.3
(Single qubit dissipation distinguishes a Haar random state from a maximally mixed state) With O(k) queries and probably 1 − e−O(k), a quantum state sampled Haar randomly can be distinguished from a maximally mixed state by time evolving the state for \(t=\Theta (\log (n))\) with Hz.
Proof
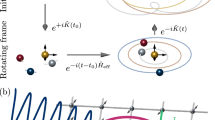
We consider the output distributions of a Haar random state before and after time evolution, measured on the computational basis
ps is known to fluctuate around its mean value i.e. the distribution of ps = 1/d, but with a variance exponentially small in n. This can be seen from the numerical experiments on the left panel of Fig. 4. As a result, it is exponentially hard to distinguish a Haar random state and a maximally mixed state with a naive computational basis measurement.
In both cases, the output weight of the Haar states fluctuates around the output value of the maximally mixed state. However, the variance on the left plot is exponentially small in n, and the variance after the non-Hermitian time evolution becomes a constant, allowing efficient distinguishment between the Haar random state and the maximally mixed state. This cannot be accomplished with any local quantum channels such as the amplitude damping channel72.
The effect of the time evolution generated by Hz is that it exponentially re-distributes weights of all output strings according to their Hamming weight ws, or the number of 0’s in s. This can already be told from a single qubit case:
We begin by finding t, such that after applying the evolution generated by Hz to the maximally mixed state, the output weight on the s = 1n can be a constant c. By setting:
and solving for t, we get
What would the output distribution look like for a Haar random state after applying the same time evolution? The normalized weight is just
In the second from last step, we use the fact that each entry of a Haar state vector consists of two standard normal variables and the weights on each string should follow the Porter-Thomas distribution: \({{\rm{PT}}}({p}_{s})={2}^{n}{e}^{-{2}^{n}{p}_{s}}\), and a sum over poly(n) terms would converge to its mean value. We may also ignore the \({p}_{{0}^{n}}{e}^{-2n}\) in the denominator as it is exponentially small in n.
Under the assumption of Eq. (20), we have
W.l.o.g., setting c = 1/2 gives η = 1; therefore the Eq. (28) returns
This means the variance of this distribution is now a constant independent of n. For example, the probability of \(P[{q}_{{1}^{n}}\ge 0.6]\) is
As evident from Fig. 4, with constant probability, a measurement in the computational basis now allows efficient distinguishing between the Haar random state and the maximally mixed state after the time evolution. Notice that, if we choose t = poly(n), the two states are once again hard to be distinguished because they both purify to a product state. This probability can be boosted to 1 − e−k by randomly applying a layer of X gates before the time evolution (namely, randomly selecting a string s to amplify and probe its amplitude) and repeating O(k) times. □
In the unitary setting, the minimum number of gates required to implement a measurement M that can distinguish a given quantum state \(\left\vert \psi \right\rangle\) from the maximally mixed state ρm to a certain resolution δ is defined as the strong state complexity. Formally, let \(\beta (r,\left\vert \psi \right\rangle )\) be the maximum bias with which \(\left\vert \psi \right\rangle\) can be distinguished from the maximally mixed state using a circuit with at most r gates from the gate set \({{\mathcal{G}}}\subseteq U(4)\):
Then the strong state complexity is defined as:
Definition 4.4
(Strong state complexity) For a given \(r\in {\mathbb{N}}\) and η ∈ (0, 1), a pure state \(\left\vert \psi \right\rangle\) has strong η-state complexity at most r if and only if \(\beta (r,\left\vert \psi \right\rangle )\ge 1-1/d-\delta\). We denote this \({{{\mathcal{C}}}}_{\delta }(\left\vert \psi \right\rangle )\le r\).
The 1/d in the definition comes from that any pure state can be trivially distinguished from a maximally mixed state with trace distance 1/d. For Haar random pure states, it has been shown that the vast majority of them have exponentially high strong state complexity:
Proposition 4.5
(Strong state complexity of Haar random states) The probability that \(\left\vert {\psi }_{{{\rm{Haar}}}}\right\rangle\) has strong circuit complexity less than r is
The proof given by43 essentially comes from a counting argument that any fixed measurement can only distinguish a small number of states, and thus to distinguish the vast majority of Haar random states, the complexity of measurement must grow exponential in n. Even for 1 − δ2 = 1/poly(n), this probability of distinguish remains exponentially small in n when r = poly(n). This means
Lemma 4.6
(Hardness of distinguishing a Haar random state with a BQP machine) With overwhelming probability, a BQP machine making polynomial queries to \({{\mathcal{O}}}\) cannot solve Problem IV.2.
Combining Lemma IV.3 and Lemma IV.6 completes the proof of Thm. I.1. Further, as we explain in Supplementary Note 1, each single-qubit dissipation channel can be implemented with a two-qubit gate and post-selection on the single ancillary qubit. It turns out that the result we have proved can be summarized in a computational complexity language: With overwhelming probability, Problem IV.2 can be solved by a quantum circuit at merely constant depth when postselection is allowed (denoted as PostQNC0), but also with overwhelming probability, it cannot be solved by a polynomial-size quantum circuit. Namely,
Corollary 4.7
(Oracle separation) There exists a quantum oracle \({{\mathcal{O}}}\) (as defined in Problem IV.2) such that \({{{\rm{PostQNC}}}}_{0}^{{{\mathcal{O}}}} \nsubseteq {{{\rm{BQP}}}}^{{{\mathcal{O}}}}\); relative to the same oracle, \({{{\rm{BQP}}}}^{{{\mathcal{O}}}}\subset {{{\rm{PostBQP}}}}^{{{\mathcal{O}}}}\).
Data availability
The generated in this study have been deposited in70.
Code availability
The simulation code used in this work can be found at70.
References
Dalibard, J., Castin, Y. & Mølmer, K. Wave-function approach to dissipative processes in quantum optics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 580 (1992).
Yang, C.-N. & Lee, T.-D. Statistical theory of equations of state and phase transitions. i. theory of condensation. Phys. Rev. 87, 404 (1952).
Fisher, M. E. Yang-lee edge singularity and ϕ 3 field theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 40, 1610 (1978).
Hatano, N. & Nelson, D. R. Localization transitions in non-hermitian quantum mechanics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 570 (1996).
Hatano, N. & Nelson, D. R. Vortex pinning and non-hermitian quantum mechanics. Phys. Rev. B 56, 8651 (1997).
Ashida, Y., Gong, Z. & Ueda, M. Non-hermitian physics. Adv. Phys. 69, 249 (2020).
Bender, C. M. & Wu, T. T. Anharmonic oscillator. Phys. Rev. 184, 1231 (1969).
Yao, S. & Wang, Z. Edge states and topological invariants of non-hermitian systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 086803 (2018).
Ashida, Y. & Ueda, M. Full-counting many-particle dynamics: Nonlocal and chiral propagation of correlations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 185301 (2018).
Dóra, B. & Moca, C. P. Quantum quench in p t-symmetric luttinger liquid. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 136802 (2020).
Rudner, M. S. & Levitov, L. S. Topological transition in a non-hermitian quantum walk. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 065703 (2009).
Gopalakrishnan, S. & Gullans, M. J. Entanglement and purification transitions in non-hermitian quantum mechanics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 170503 (2021).
Kawabata, K., Numasawa, T. & Ryu, S. Entanglement phase transition induced by the non-hermitian skin effect. Phys. Rev. X 13, 021007 (2023).
Guo, A. et al. Observation of p t-symmetry breaking in complex optical potentials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 093902 (2009).
Rüter, C. E. et al. Observation of parity–time symmetry in optics. Nat. Phys. 6, 192 (2010).
Feng, L. et al. Nonreciprocal light propagation in a silicon photonic circuit. Science 333, 729 (2011).
Shor, P. W. Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring, in Proceedings 35th annual symposium on foundations of computer science (Ieee, 1994) pp. 124–134.
Pirandola, S. et al. Advances in quantum cryptography. Adv. Opt. photonics 12, 1012 (2020).
Aaronson, S. and Arkhipov, A. The computational complexity of linear optics, in Proceedings of the forty-third annual ACM symposium on Theory of computing (2011) pp. 333–342.
Feynman, R. P. Simulating physics with computers, in Feynman and Computation, edited by Hey, A. J. G. (CRC Press, 2018) pp. 133–153.
Wen, J. et al. Experimental demonstration of a digital quantum simulation of a general pt-symmetric system. Phys. Rev. A 99, 062122 (2019).
Shen, R., Chen, T., Yang, B. & Lee, C. H. Observation of the non-hermitian skin effect and fermi skin on a digital quantum computer. Nat. Commun. 16, 1340 (2025).
Cerezo, M. et al. Variational quantum algorithms. Nat. Rev. Phys. 3, 625 (2021).
Farhi, E., Goldstone, J. & Gutmann, S. A quantum approximate optimization algorithm. arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.4028 (2014).
Peruzzo, A. et al. A variational eigenvalue solver on a photonic quantum processor. Nat. Commun. 5, 4213 (2014).
Preskill, J. Quantum computing and the entanglement frontier. arXiv preprint arXiv:1203.5813 (2012).
Carrasquilla, J. & Melko, R. G. Machine learning phases of matter. Nat. Phys. 13, 431 (2017).
Schön, C., Solano, E., Verstraete, F., Cirac, J. I. & Wolf, M. M. Sequential generation of entangled multiqubit states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 110503 (2005).
Lin, S.-H., Dilip, R., Green, A. G., Smith, A. & Pollmann, F. Real-and imaginary-time evolution with compressed quantum circuits. PRX Quantum 2, 010342 (2021).
Zhang, Y., Wiersema, R., Carrasquilla, J., Cincio, L. & Kim, Y. B. Scalable quantum dynamics compilation via quantum machine learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.16346 (2024a).
Foss-Feig, M. et al. Holographic quantum algorithms for simulating correlated spin systems. Phys. Rev. Res. 3, 033002 (2021).
Perez-Garcia, D., Verstraete, F., Wolf, M. M. & Cirac, J. I. Matrix product state representations. Quantum Info. Comput. 7, 401–430 (2007).
Lieb, E. H. & Robinson, D. W. The finite group velocity of quantum spin systems. Commun. Math. Phys. 28, 251 (1972).
Eisert, J., Van Den Worm, M., Manmana, S. R. & Kastner, M. Breakdown of quasilocality in long-range quantum lattice models. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 260401 (2013).
Richerme, P. et al. Non-local propagation of correlations in quantum systems with long-range interactions. Nature 511, 198 (2014).
Moca, C. P. & Dóra, B. Universal conductance of a pt-symmetric luttinger liquid after a quantum quench. Phys. Rev. B 104, 125124 (2021).
Trotter, H. F. On the product of semi-groups of operators. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 10, 545 (1959).
Gilyén, A., Su, Y., Low, G. H., and Wiebe, N. Quantum singular value transformation and beyond: exponential improvements for quantum matrix arithmetics, in Proceedings of the 51st Annual ACM SIGACT Symposium on Theory of Computing (2019) pp. 193–204.
Fishman, M. T. & White, S. R. Compression of correlation matrices and an efficient method for forming matrix product states of fermionic gaussian states. Phys. Rev. B 92, 075132 (2015).
Niu, D. et al. Holographic simulation of correlated electrons on a trapped-ion quantum processor. PRX Quantum 3, 030317 (2022).
Arute, F. et al. Quantum supremacy using a programmable superconducting processor. Nature 574, 505 (2019).
Aaronson, S. Quantum computing, postselection, and probabilistic polynomial-time. Proc. R. Soc. A: Math., Phys. Eng. Sci. 461, 3473 (2005).
Brandão, F. G., Chemissany, W., Hunter-Jones, N., Kueng, R. & Preskill, J. Models of quantum complexity growth. PRX Quantum 2, 030316 (2021).
Xie, X.-D., Xue, Z.-Y. & Zhang, D.-B. Variational quantum eigensolvers for the non-hermitian systems by variance minimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.19807 (2023).
Von Gehlen, G. Critical and off-critical conformal analysis of the ising quantum chain in an imaginary field. J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 24, 5371 (1991).
Fishman, M., White, S. R. & Stoudenmire, E. M. The itensor software library for tensor network calculations, scipost phys. Codebases 4, 1 (2022).
Li, Y., Chen, X. & Fisher, M. P. Quantum zeno effect and the many-body entanglement transition. Phys. Rev. B 98, 205136 (2018).
Liu, J.-P. et al. Efficient quantum algorithm for dissipative nonlinear differential equations. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 118, e2026805118 (2021).
Yoshida, T., Kudo, K. & Hatsugai, Y. Non-hermitian fractional quantum hall states. Sci. Rep. 9, 16895 (2019).
Yin, S., Huang, G.-Y., Lo, C.-Y. & Chen, P. Kibble-zurek scaling in the yang-lee edge singularity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 065701 (2017).
Dóra, B., Heyl, M. & Moessner, R. The kibble-zurek mechanism at exceptional points. Nat. Commun. 10, 2254 (2019).
Hastings, M. B. An area law for one-dimensional quantum systems. J. Stat. Mech.: Theory Exp. 2007, P08024 (2007).
Manzano, D. A short introduction to the lindblad master equation. Aip Advances10 (2020).
Zhang, Y., Jahanbani, S., Niu, D., Haghshenas, R. & Potter, A. C. Qubit-efficient simulation of thermal states with quantum tensor networks. Phys. Rev. B 106, 165126 (2022).
Chen, X., Hermele, M. & Stephen, D. T. Sequential adiabatic generation of chiral topological states. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.03433 (2024a).
Chen, X. et al. Sequential quantum circuits as maps between gapped phases. Phys. Rev. B 109, 075116 (2024).
Wei, Z.-Y., Malz, D. & Cirac, J. I. Sequential generation of projected entangled-pair states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 010607 (2022).
Lu, T.-C., Lessa, L. A., Kim, I. H. & Hsieh, T. H. Measurement as a shortcut to long-range entangled quantum matter. PRX Quantum 3, 040337 (2022).
Foss-Feig, M. et al. Experimental demonstration of the advantage of adaptive quantum circuits. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.03029 (2023).
Malz, D., Styliaris, G., Wei, Z.-Y. & Cirac, J. I. Preparation of matrix product states with log-depth quantum circuits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 040404 (2024).
Osborne, T. J., Eisert, J. & Verstraete, F. Holographic quantum states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 260401 (2010).
Zhang, Y., Jahanbani, S., Riswadkar, A., Shankar, S. & Potter, A. C. Sequential quantum simulation of spin chains with a single circuit qed device. Phys. Rev. A 109, 022606 (2024).
Foss-Feig, M. et al. Entanglement from tensor networks on a trapped-ion qccd quantum computer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 150504 (2022).
Hauschild, J. et al. Finding purifications with minimal entanglement. Phys. Rev. B 98, 235163 (2018).
Soejima, T. et al. Isometric tensor network representation of string-net liquids. Phys. Rev. B 101, 085117 (2020).
Chertkov, E. et al. Holographic dynamics simulations with a trapped ion quantum computer, in Quantum Information and Measurement (Optical Society of America, 2021) pp. W3A–3.
Gyongyosi, L. & Imre, S. Properties of the quantum channel. arXiv preprint arXiv:1208.1270 (2012).
Orús, R. Tensor networks for complex quantum systems. Nat. Rev. Phys. 1, 538 (2019).
Arute, F. et al. Hartree-fock on a superconducting qubit quantum computer. Science 369, 1084 (2020).
Zhang, Y., yuxuanzhang1995/non_hermitian: Variational circuits for non-hermitian dynamics (2025).
Schön, C., Hammerer, K., Wolf, M. M., Cirac, J. I. & Solano, E. Sequential generation of matrix-product states in cavity qed. Phys. Rev. A 75, 032311 (2007).
Fefferman, B., Ghosh, S., Gullans, M., Kuroiwa, K. & Sharma, K. Effect of non-unital noise on random circuit sampling. PRX Quantum 5, 030317 (2024).
Acknowledgements
We thank Sarang Gopalakrishnan, Tim Hsieh, Lin Lin, Dvira Segal, Nathan Wiebe, Roeland Wiersema, Cenke Xu, and Yijian Zou for their insightful discussions. We extend gratitude to Michael Foss-Feig and Peter Groszkowski for their invaluable assistance in accessing Quantinuum’s hardware resources and thank the reviewers for their valuable feedback. J.C. acknowledges support from the Shared Hierarchical Academic Research Computing Network (SHARCNET), Compute Canada, and the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR) AI chair program. Y.Z., J.C., and Y.B.K. were supported by the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada. Y.Z. and Y.B.K. acknowledge support from the Center for Quantum Materials at the University of Toronto. Y.Z. was further supported by a CQIQC fellowship at the University of Toronto, and in part by grant NSF PHY-2309135 to the Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics (KITP). This research used resources of the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility, which is a DOE Office of Science User Facility supported under Contract DE-AC05-00OR22725, and, in part, by the Province of Ontario, the Government of Canada through CIFAR, and companies sponsoring the Vector Institute www.vectorinstitute.ai/#partners.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.C., Y.B.K. and Y.Z. conceived the project and designed the theoretical framework. J.C. and Y.B.K. supervised the project and contributed crucial insights on interpreting the results. Y.Z. performed numerical simulations, executed the quantum circuits, and analyzed the results. Y.Z. wrote the manuscript with input from all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
: Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Carrasquilla, J. & Kim, Y.B. Observation of a non-Hermitian supersonic mode on a trapped-ion quantum computer. Nat Commun 16, 3286 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-57930-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-57930-3