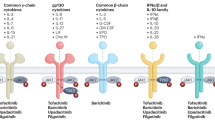
Abstract
The published results of the post-marketing ORAL Surveillance study, which compared the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor tofacitinib with anti-TNF therapy in older patients with rheumatoid arthritis who have cardiovascular risk factors, have led to changes in the recommendations for the use of JAK inhibitors. Although new safety signals have emerged for tofacitinib, namely malignancy and cardiovascular disease, it should be noted that these signals are relative to those seen with TNF blockers. The new data further raise our intrigue that venous thromboembolism might be a true risk related to JAK inhibition. Reassuringly, the totality of the findings from this newly published study and the other data collected to date suggest that JAK inhibitors can be used safely at approved doses by many patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ytterberg, S. R. et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 316–326 (2022).
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves Boxed Warning about increased risk of blood clots and death with higher dose of arthritis and ulcerative colitis medicine tofacitinib (Xeljanz, Xeljanz XR). https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-approves-boxed-warning-about-increased-risk-blood-clots-and-death-higher-dose-arthritis-and (2021).
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research: NDA 203,214 Tofacitinib for Rheumatoid Arthritis, Addendum to Primary Clinical Review. Edited by Department of Health and Human Services, 26 September 2012 edn. Silver Spring, MD. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2012/203214Orig1s000Approv.pdf (2012).
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT02092467 (2021).
Genovese, M. C. et al. Safety profile of baricitinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis over a median of 3 years of treatment: an updated integrated safety analysis. Lancet Rheumatol. 2, e347–e357 (2020).
Winthrop, K. L. et al. Integrated safety analysis update for filgotinib in patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis receiving treatment over a median of 2.2 years [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 73, 1698 (2021).
Strand, V. et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of serious infections with tofacitinib and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug treatment in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. Arthritis Res. Ther. 17, 362 (2015).
Parra-Izquierdo, I. et al. Janus kinase inhibitors ruxolitinib and baricitinib impair glycoprotein-VI mediated platelet function. Platelets https://doi.org/10.1080/09537104.2021.1934665 (2021).
Kremer, J. M. et al. Postapproval comparative safety study of tofacitinib and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 5-year results from a United States-based rheumatoid arthritis registry. ACR Open Rheumatol. 3, 173–184 (2021).
Cohen, S. B. et al. Long-term safety of tofacitinib up to 9.5 years: a comprehensive integrated analysis of the rheumatoid arthritis clinical development programme. RMD Open 6, e001395 (2020).
Winthrop, K. L. et al. Integrated safety analysis of filgotinib in patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis receiving treatment over a median of 1.6 years. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 81, 184–192 (2022).
Desai, R. J., Pawar, A., Khosrow-Khavar, F., Weinblatt, M. E. & Kim, S. C. Risk of venous thromboembolism associated with tofacitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based cohort study. Rheumatology 61, 121–130 (2021).
Marconi, V. C. et al. Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 9, 1407–1418 (2021).
Giles, J. T. et al. Cardiovascular safety of tocilizumab versus etanercept in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 72, 31–40 (2020).
Singh, S. et al. Comparative risk of cardiovascular events with biologic and synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 72, 561–576 (2020).
Khosrow-Khavar, F., Kim, S. C., Lee, H., Lee, S. B. & Desai, R. J. Tofacitinib and risk of cardiovascular outcomes: results from the Safety of TofAcitinib in Routine care patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (STAR-RA) study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221915 (2022).
Cohen, S. B. et al. Safety profile of upadacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis: integrated analysis from the SELECT phase III clinical programme. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 80, 304–311 (2020).
Sands, B. E. et al. Tofacitinib for the treatment of ulcerative colitis: analysis of nonmelanoma skin cancer rates from the Ulcerative Colitis Clinical Program. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2, 234–245 (2022).
Nocturne, G., Pascaud, J., Ly, B., Tahmasebi, F. & Mariette, X. JAK inhibitors alter NK cell functions and may impair immunosurveillance against lymphomagenesis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 17, 552–553 (2020).
Bhala, N. et al. Vascular and upper gastrointestinal effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: meta-analyses of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet 382, 769–779 (2013).
Wallis, R. S., Broder, M. S., Wong, J. Y., Hanson, M. E. & Beenhouwer, D. O. Granulomatous infectious diseases associated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Clin. Infect. Dis. 38, 1261–1265 (2004).
European Medicines Agency. Meeting highlights from the Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) 7–10 June 2021 https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/meeting-highlights-pharmacovigilance-risk-assessment-committee-prac-7-10-june-2021 (2021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to all aspects of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
K.L.W. declares that he has acted as a consultant for AbbVie, Union AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Chimique Belge (UCB), Eli Lilly & Company, Galapagos, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche and Sanofi, and has received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb and Pfizer. S.B.C. declares that he has acted as a consultant for and received research funding from AbbVie, Amgen, Gilead, Lilly and Pfizer.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Rheumatology thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winthrop, K.L., Cohen, S.B. Oral surveillance and JAK inhibitor safety: the theory of relativity. Nat Rev Rheumatol 18, 301–304 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-022-00767-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-022-00767-7
This article is cited by
-
Exploratory study on the efficacy of topical pan-JAK inhibitor in ocular and skin GVHD in a sclerodermatous GVHD mouse model
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Single cell immunoprofile of synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis with TNF/JAK inhibitor treatment
Nature Communications (2025)
-
A single-cell RNA-seq dataset of synovial fluid from rheumatoid arthritis treated with TNF-α/JAK inhibitor
Scientific Data (2025)
-
Efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors in patients aged > 60 years with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a 52-week multicenter, real-life study—IL AD (Italian Landscape Atopic Dermatitis)
Archives of Dermatological Research (2025)
-
Epigenetic targets of Janus kinase inhibitors are linked to genetic risks of rheumatoid arthritis
Inflammation and Regeneration (2024)