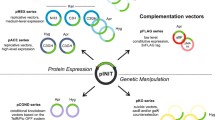
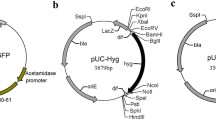
Abstract
Genetic manipulation of mycobacteria has historically been difficult. This is in large part due to the impenetrable nature of the cell wall, resulting in difficulty both in introducing DNA into the bacterium and subsequent isolation of intact plasmid DNA. In addition, the mycobacterial cell wall contains complex lipids and polysaccharides that can contaminate DNA preparations. The hydrophobic nature of the cell wall results in cells clumping in culture, hampering the isolation of clonal populations important for many molecular biological purposes. In spite of these obstacles, the advent of efficient mycobacterial transformation systems (1) resulted in an explosion of research into plasmid vectors and numerous genetic systems for Mycobacterium tuberculosis have now been described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snapper S. B., Lugosi L., Jekkel A., Melton R. E., Kieser T., Bloom B. R., and Jacobs W. R.,Jr. (1988) Lysogeny and transformation in mycobacteria: stable expression of foreign genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 6987–6991.
Labidi A., Dauguet C., Goh K. S., and David H. L. (1984) Plasmid profiles of Mycobacterium fortuitum complex isolates. Curr. Microbiol. 11, 235–240.
Snapper S. B., Melton R. E., Mustafa S., Kieser T., and Jacobs W. R.,Jr. (1990) Isolation and characterization of efficient plasmid transformation mutants of Mycobacterium smegmatis. Mol. Microbiol. 4, 1911–1919.
Ranes M. G., Rauzier J., Lagranderie M., Gheorghiu M., and Gicquel B. (1990) Functional analysis of pAL5000, a plasmid from Mycobacterium fortuitum: construction of a “mini” mycobacterium-Escherichia coli shuttle vector. J. Bacteriol. 172, 2793–2797.
Stover C. K., de la Cruz V. F., Fuerst T. R., Burlein J. E., Benson L. A., Bennett L. T., Bansal G. P., Young J. F., Lee M. H., Hatfull G. F., Snapper S. B., Barletta R. G., Jacobs W. R.,Jr., and Bloom B. R. (1991) New use of BCG for recombinant vaccines. Nature 351, 456–460.
Jacobs W. R.,Jr., Kalpana G. V., Cirillo J. D., Pascopella L., Snapper S. B., Udani R. A., Jones W., Barletta R. G., and Bloom B. R. (1991) Genetic systems for mycobacteria. Methods Enzymol. 204, 537–555.
Guilhot C., Gicquel B., and Martin C. (1992) Temperature-sensitive mutants of the Mycobacterium plasmid pAL5000. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 77, 181–186.
Beggs M. L., Crawford J. T., and Eisenach K. D. (1995) Isolation and sequencing of the replication region of Mycobacterium avium plasmid pLR7. J. Bacteriol. 177, 4836–4840.
Goto Y., Taniguchi H., Udou T., Mizuguchi Y., and Tokunaga T. (1991) Development of a new host vector system in mycobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 67, 277–282.
Gavigan J. A., Ainsa J. A., Perez E., Otal I., and Martin C. (1997) Isolation by genetic labeling of a new mycobacterial plasmid, pJAZ38, from Mycobacterium fortuitum. J. Bacteriol. 179, 4115–4122.
Bachrach G., Colston M. J., Bercovier H., Dror B., Anderson C., and Papavinasasundaram K. G. (2000) A new single-copy plasmid, pMF 1, from Mycobacterium fortuitum which is compatible with the pAL5000 replicon. Microbiology 146, 297–303.
Picardeau M., Le Dantec C., and Vincent V. (2000) Analysis of the internal replication region of a mycobacterial linear plasmid. Microbiology 146, 305–313.
David M., Lubinsky-Mink S., Ben-Zvi A., Ulitzur S., Kuhn J., and Suissa M. (1992) A stable Escherichia coli-Mycobacterium smegmatis plasmid shuttle vector containing the mycobacteriophage D29 origin. Plasmid 28, 267–271.
Bardarov S., Kriakov J., Carriere C., Yu S., Vaamonde C., McAdam R.A., Bloom B. R., Hatfull G. F., and Jacobs W. R.,Jr. (1997) Conditionally replicating mycobacteriophages: A system for transposon delivery to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 10,961–10,966.
Radford A. J. and Hodgson A. L. (1991) Construction and characterization of a Mycobacterium-Escherichia coli shuttle vector. Plasmid 25, 149–153.
Zainuddin Z. F., Kunze Z. M., and Dale J. W. (1989) Transformation of Mycobacterium smegmatis with Escherichia coli plasmids carrying a selectable resistance marker. Mol. Microbiol. 3, 29–34.
Gormley E. P. and Davies J. (1991) Transfer of plasmid RSF1010 by conjugation from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces lividans and Mycobacterium smegmatis. J. Bacteriol. 173, 6705–6708.
Hermans J., Martin C., Huijberts G. N., Goosen T., and de Bont J. A. (1991) Transformation of Mycobacterium aurum and Mycobacterium smegmatis with the broad host-range gram-negative cosmid vector pJRD215. Mol. Microbiol. 5, 1561–1566.
Jacobs W. R.,Jr., Tuckman M., and Bloom B. R. (1987) Introduction of foreign DNA into mycobacteria using a shuttle phasmid. Nature 327, 532–535.
Lee M. H., Pascopella L., Jacobs W. R.,Jr., and Hatfull G. F. (1991) Site-specific integration of mycobacteriophage L5, Integration-proficient vectors for Mycobacterium smegmatis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and bacille Calmette-Guerin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 3111–3115.
Anes E., Portugal I., and Moniz-Pereira J. (1992) Insertion into the Mycobacterium smegmatis genome of the aph gene through lysogenization with the temperate mycobacteriophage Ms6. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 74, 21–25.
Martin C., Mazodier P., Mediola M. V., Gicquel B., Smokvina T., Thompson C. J., and Davies J. (1991) Site-specific integration of the Streptomyces plasmid pSAM2 in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Mol. Microbiol. 5, 2499–2502.
England P. M., Wall S., and McFadden J. (1991) IS900-promoted stable integration of a foreign gene into mycobacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 5, 2047–2052.
Dellagostin O. A., Wall S., Norman E., O’Shaughnessy T., Dale J. W., and McFadden J. (1993) Construction and use of integrative vectors to express foreign genes in mycobacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 10, 983–993.
Paget E. and Davies J. (1996) Apramycin resistance as a selective marker for gene transfer in mycobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 178, 6357–6360.
Marklund B. I., Speert D. P., and Stokes R. W. (1995) Gene replacement through homologous recombination in Mycobacterium intracellulare. J. Bacteriol. 177, 6100–6105.
Ho Y. I., Chan C. Y., and Cheng A. F. (1997) In vitro activities of aminoglycoside-aminocyclitols against mycobacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 40, 27–32.
Pelicic V., Jackson M., Reyrat J. M., Jacobs W. R.,Jr., Gicquel B., and Guilhot C. (1997) Efficient allelic exchange and transposon mutagenesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 10,955–10,960.
Guilhot C., Otal I., Van Rompaey I., Martin C., and Gicquel B. (1994) Efficient transposition in mycobacteria: construction of Mycobacterium smegmatis inser-tional mutant libraries. J. Bacteriol. 176, 535–539.
Garbe T. R., Barathi J., Barnini S., Zhang Y., Abou Zeid C., Tang D., Mukherjee R., and Young D. B. (1994) Transformation of mycobacterial species using hygromycin resistance as selectable marker. Microbiology 140, 133–138.
Donnelly-Wu M. K., Jacobs W. R.,Jr., and Hatfull G. F. (1993) Superinfection immunity of mycobacteriophage L5, applications for genetic transformation of mycobacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 7, 407–417.
Baulard A., Escuyer V., Haddad N., Kremer L., Locht C., and Berche P. (1995) Mercury resistance as a selective marker for recombinant mycobacteria. Microbiology 141, 1045–1050.
Pelicic V., Reyrat J. M., and Gicquel B. (1996) Expression of the Bacillus subtilis sacB gene confers sucrose sensitivity on mycobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 178, 1197–1199.
Sander P., Meier A., and Beottger E. C. (1995) rpsL +: a dominant selectable marker for gene replacement in mycobacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 16, 991–1000.
Norman E., Dellagostin O. A., McFadden J., and Dale J. W. (1995) Gene replacement by homologous recombination in Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Mol. Microbiol. 16, 755–760.
Matsuo K., Yamaguchi R., Yamazaki A., Tasaka H., Terasaka K., Totsuka M., Kobayashi K., Yukitake H., and Yamada T. (1990) Establishment of a foreign antigen secretion system in mycobacteria. Infect. Immun. 58, 4049–4054.
Stover C. K., Bansal G. P., Hanson M. S., Burlein J. E., Palaszynski S. R., Young J. F., Koenig S., Young D. B., Sadziene A., and Barbour A. G. (1993) Protective immunity elicited by recombinant bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) expressing outer surface protein A (OspA) lipoprotein: a candidate Lyme disease vaccine. J. Exp. Med. 178, 197–209.
Haeseleer F. (1994) Structural instability of recombinant plasmids in mycobacteria. Res. Microbiol. 145, 683–687.
Triccas J.A., Parish T., Britton W. J., and Gicquel B. (1998) An inducible expression system permitting the efficient purification of a recombinant antigen from Mycobacterium smegmatis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 167, 151–156.
Murray P. J., Aldovini A., and Young R. A. (1996) Manipulation and potentiation of antimycobacterial immunity using recombinant bacille Calmette-Guerin strains that secrete cytokines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 934–939.
Heithoff D. M., Conner C. P., and Mahan M. J. (1997) Dissecting the biology of a pathogen during infection. Trends Microbiol. 5, 509–513.
Timm J., Lim E. M., and Gicquel B. (1994) Escherichia coli-mycobacteria shuttle vectors for operon and gene fusions to lacZ: The pJEM series. J. Bacteriol. 176, 6749–6753.
Dellagostin O. A., Esposito G., Eales L. J., Dale J. W., and McFadden J. (1995) Activity of mycobacterial promoters during intracellular and extracellular growth. Microbiology 141, 1785–1792.
Das Gupta S. K., Bashyam M. D., and Tyagi A. K. (1993) Cloning and assessment of mycobacterial promoters by using a plasmid shuttle vector. J. Bacteriol. 175, 5186–5192.
Parish T., Mahenthiralingam E., Draper P., Davis E. O., and Colston M. J. (1997) Regulation of the inducible acetamidase gene of Mycobacterium smegmatis. Microbiology 143, 2267–2276.
Curcic R., Dhandayuthapani S., and Deretic V. (1994) Gene expression in myco-bacteria: Transcriptional fusions based on xylE and analysis of the promoter region of the response regulator mtrA from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mol. Microbiol. 13, 1057–1064.
Lim E. M., Rauzier J., Timm J., Torrea G., Murray A., Gicquel B., and Portnoi D. (1995) Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA sequences encoding exported proteins by using phoA gene fusions. J. Bacteriol. 177, 59–65.
Downing K. J., McAdam R. A., and Mizrahi V. (1999) Staphylococcus aureus nuclease is a useful secretion reporter for mycobacteria. Gene 239, 293–299.
Andrew P. W. and Roberts I. S. (1993) Construction of a bioluminescent mycobacterium and its use for assay of antimycobacterial agents. J. Clin. Microbiol. 31, 2251–2254.
Jacobs W. R.,Jr., Barletta R. G., Udani R., Chan J., Kalkut G., Sosne G., Kieser T., Sarkis G. J., Hatfull G. F., and Bloom B. R. (1993) Rapid assessment of drug susceptibilities of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by means of lucif erase reporter phages. Science 260, 819–822.
Gordon S., Parish T., Roberts I. S., and Andrew P. W. (1994) The application of lucif erase as a reporter of environmental regulation of gene expression in mycobacteria. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 19, 336–340.
Hickey M. J., Arain T. M., Shawar R. M., Humble D. J., Langhorne M. H., Morgenroth J. N., and Stover C. K. (1996) Luciferase in vivo expression technology: use of recombinant mycobacterial reporter strains to evaluate antimycobacterial activity in mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 40, 400–407.
Kremer L., Baulard A., Estaquier J., Poulain-Godefroy O., and Locht C. (1995) Green fluorescent protein as a new expression marker in mycobacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 17, 913–922.
Dhandayuthapani S., Via L. E., Thomas C. A., Horowitz P. M., Deretic D., and Deretic V. (1995) Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression and cell biology of mycobacterial interactions with macrophages. Mol. Microbiol. 17, 901–912.
Parker A. E., and Bermudez L. E. (1997) Expression of the green fluorescent protein (GFP) in Mycobacterium avium as a tool to study the interaction between mycobacteria and host cells. Microb. Path. 22, 193–198.
Barker L. P., Porcella S. F., Wyatt R. G., and Small P. L. (1999) The Mycobacterium marinum G1 3 promoter is a strong sigma 70-like promoter that is expressed in Escherichia coli and mycobacteria species. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 175, 79–85.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Casali, N., Ehrt, S. (2001). Plasmid Vectors. In: Parish, T., Stoker, N.G. (eds) Mycobacterium tuberculosis Protocols. Methods in Molecular Medicine, vol 54. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-147-7:001
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-147-7:001
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-0-89603-776-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-59259-147-3
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols