- Academic Editor
-
-
-
†These authors contributed equally.
Endometriosis patients exhibit a cancer-like glycolytic phenotype. The pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2)/hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) axis plays important roles in glycolysis-related diseases, but its role in patients with endometrial polyps (EPs) combined with endometriosis has not been validated.
EP samples were collected from patients with and without endometriosis. PKM2, HIF-1α, and transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) levels were detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC), quantitative polymerase chain reaction, western blotting, and/or immunofluorescence. Primary endometrial stromal cells (ESCs) and non-endometriotic patient-derived ESCs (NESCs) were isolated from patients with EP with or without endometriosis. PKM2 loss-of-function assays in ESCs and gain-of-function assays in NESCs were performed to assess the function of PKM2. The effects of PKM2 and TGF-β1 on the promoter activity of HIF-1α were determined by dual-luciferase reporter assay.
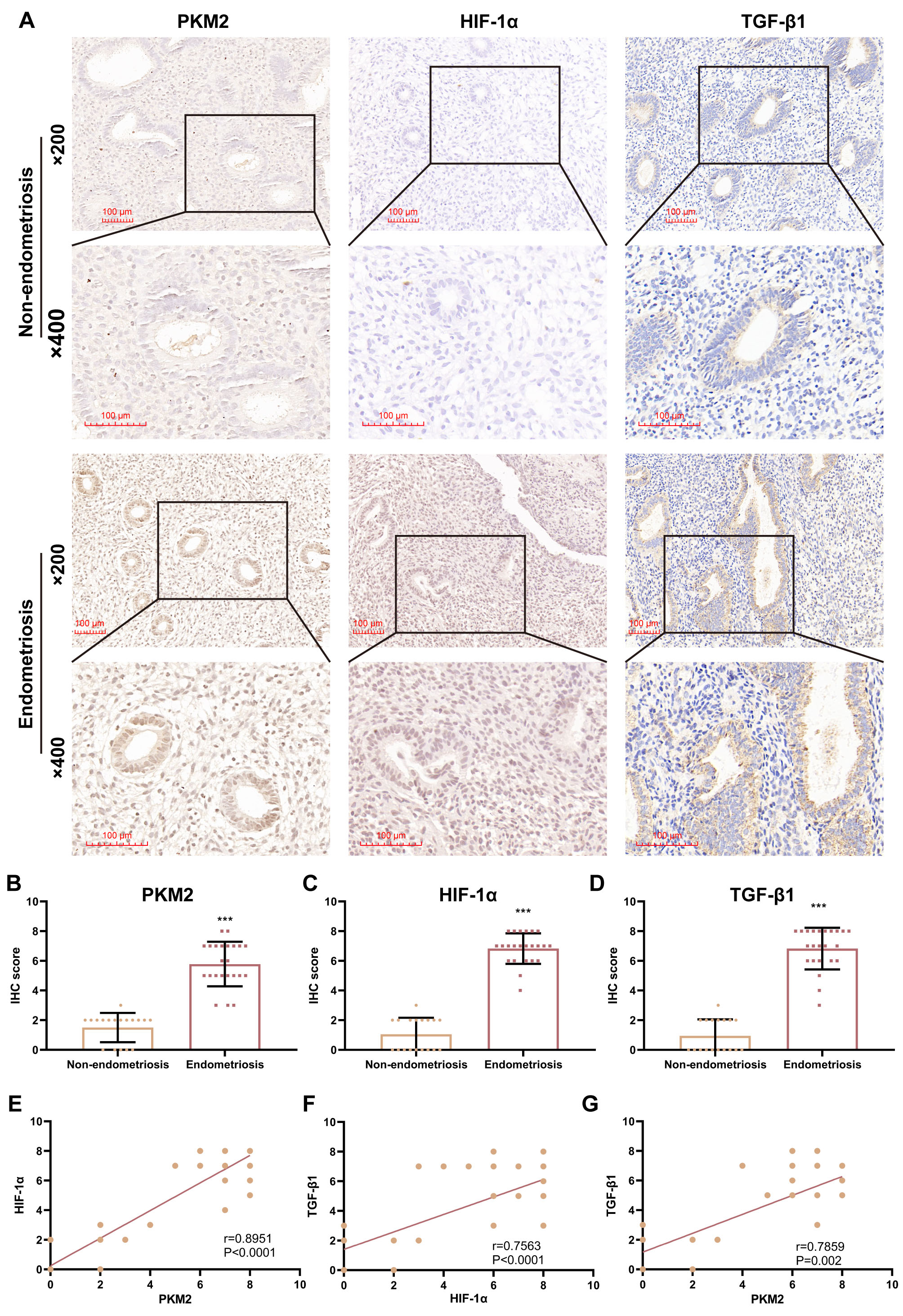
PKM2 was overexpressed in ESCs compared to NESCs. Furthermore, PKM2 knockdown repressed viability, decreased migration and invasion, and restrained glycolysis of ESCs, accompanied by reduced HIF-1α levels and weakened promoter activity of HIF-1α. In addition, PKM2 overexpression had the opposite effect on these indicators in NESCs. Of note, an anti-TGF-β1 Ab reversed the PKM2-overexpression-mediated effects on cell viability, migration, and invasion, but not glycolysis or HIF-1α promoter activity, in NESCs. Additionally, PKM2, HIF-1α, and TGF-β1 levels were higher in EP samples with endometriosis than in EP samples without endometriosis, and there were positive correlations between PKM2, HIF-1α, and TGF-β1 IHC scores in all EP samples.
PKM2/HIF-1α-axis-dependent glycolysis participates in the pathogenesis of EP combined with endometriosis by mediating TGF-β1 signaling.